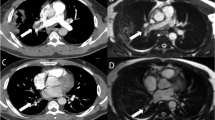
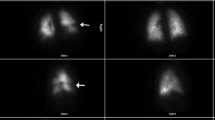
Abstract
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a very common and potentially life-threatening disease. In comparison with CT, the clinical relevance of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of PE is low. Nevertheless, as there are some potential advantages of MRI over CT (e.g. radiation free method, better safety profile of MR contrast media, capability of functional imaging). In certain patient, groups MRI might therefore be considered as a valuable alternative in the assessment of suspected PE. This article reviews the relevant MRI techniques for the evaluation of PE and gives an overview of the current literature for contrast-enhanced MR angiography of PE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silverstein MD, Heit JA, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ 3rd (1998) Trends in the incidence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a 25-year population-based study. Arch Intern Med 158:585–593
Goldhaber SZ (2004) Pulmonary embolism. Lancet 363:1295–1305
Tan KT, van Beek EJ (2002) Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary embolism: An overview. Imaging Decis 6:3–10
Investigators TP (1990) Value of the ventilation/perfusion scan in acute pulmonary embolism. Results of the prospective investigation of pulmonary embolism diagnosis (PIOPED). The PIOPED investigators. JAMA 263:2753–2759
Schoepf UJ, Costello P (2004) CT angiography for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: state of the art. Radiology 230:329–337
Thomsen HS (2006) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: A serious late adverse reaction to gadodiamide. Eur Radiol 16:2619–2621
Tombach B, Heindel W (2002) Value of 1.0-M gadolinium chelates: review of preclinical and clinical data on gadobutrol. Eur Radiol 12:1550–1556
Wells PS, Ginsberg JS, Anderson DR et al (1998) Use of a clinical model for safe management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med 129:997–1005
Mayo JR, Aldrich J, Müller NL (2003) Radiation exposure at chest CT: A statement of the fleischner society. Radiology 228:15–21
Parker MS, Hui FK, Camacho MA, Chung JK, Broga DW, Sethi NN (2005) Female breast radiation exposure during CT pulmonary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:1228–1233
Scarsbrook AF, Evans AL, Owen AR, Gleeson FV (2006) Diagnosis of suspected venous thromboembolic disease in pregnancy. Clin Radiol 61:1–12
Yousefzadeh DK, Ward MB, Reft C (2006) Internal barium shielding to minimize fetal irradiation in spiral chest CT: a phantom simulation experiment. Radiology 239:751–758
Groves AM, Yates SJ, Win T et al (2006) CT pulmonary angiography versus ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy in pregnancy: implications from a UK survey of doctors' knowledge of radiation exposure. Radiology 240:765–770
Webb JA, Thomsen HS, Morcos SK (2005) The use of iodinated and gadolinium contrast media during pregnancy and lactation. Eur Radiol 15:1234–1240
Kwong RY, Schussheim AE, Rekhraj S et al (2003) Detecting acute coronary syndrome in the emergency department with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 107:531–537
Schellinger PD, Jansen O, Fiebach JB et al (2000) Feasibility and practicality of MR imaging of stroke in the management of hyperacute cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1184–1189
Goyen M, Shamsi K, Schoenberg SO (2006) Vasovist-enhanced MR angiography. Eur Radiol 16(Suppl 2):B9–B14
Abolmaali ND, Hietschold V, Appold S, Ebert W, Vogl TJ (2002) Gadomer-17-enhanced 3D navigator-echo MR angiography of the pulmonary arteries in pigs. Eur Radiol 12:692–697
Fink C, Ley S, Puderbach M, Plathow C, Bock M, Kauczor HU (2004) 3D pulmonary perfusion MRI and MR angiography of pulmonary embolism in pigs after a single injection of a blood pool MR contrast agent. Eur Radiol 14:1291–1296
van Beek EJ, Wild JM, Fink C, Moody AR, Kauczor HU, Oudkerk M (2003) MRI for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:627–640
Nael K, Michaely HJ, Kramer U et al (2006) Pulmonary circulation: contrast-enhanced 3.0-T MR angiography—initial results. Radiology 240:858–868
Korosec FR, Frayne R, Grist TM, Mistretta CA (1996) Time-resolved contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography. Magn Reson Med 36:345–351
Schoenberg SO, Bock M, Floemer F et al (1999) High-resolution pulmonary arterio-and venography using multiple-bolus multiphase 3D-Gd-mRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:339–346
Goyen M, Laub G, Ladd ME et al (2001) Dynamic 3D MR angiography of the pulmonary arteries in under four seconds. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:372–377
Meaney JF, Weg JG, Chenevert TL, Stafford-Johnson D, Hamilton BH, Prince MR (1997) Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with magnetic resonance angiography. N Engl J Med 336:1422–1427
Gupta A, Frazer CK, Ferguson JM et al (1999) Acute pulmonary embolism: diagnosis with MR angiography. Radiology 210:353–359
Oudkerk M, van Beek EJ, Wielopolski P et al (2002) Comparison of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography and conventional pulmonary angiography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a prospective study. Lancet 359:1643–1647
Blum A, Bellou A, Guillemin F, Douek P, Laprevote-Heully MC, Wahl D (2005) Performance of magnetic resonance angiography in suspected acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost 93:503–511
Pleszewski B, Chartrand-Lefebvre C, Qanadli SD et al (2006) Gadolinium-enhanced pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography in the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism: a prospective study on 48 patients. Clin Imaging 30:166–172
Kluge A, Luboldt W, Bachmann G (2006) Acute pulmonary embolism to the subsegmental level: diagnostic accuracy of three MRI techniques compared with 16-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:W7–W14
Ohno Y, Higashino T, Takenaka D et al (2004) MR angiography with sensitivity encoding (SENSE) for suspected pulmonary embolism: comparison with MDCT and ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:91–98
Fink C, Risse F, Semmler W, Schoenberg SO, Kauczor HU, Reiser MF (2006) MRT der Lungenperfusion. Radiologe 46:290–299
Levin DL, Chen Q, Zhang M, Edelman RR, Hatabu H (2001) Evaluation of regional pulmonary perfusion using ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 46:166–171
Fink C, Bock M, Puderbach M, Schmahl A, Delorme S (2003) Partially parallel three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of lung perfusion—initial results. Invest Radiol 38:482–488
Nikolaou K, Schoenberg SO, Attenberger U et al (2005) Pulmonary arterial hypertension: diagnosis with fast perfusion MR imaging and high-spatial-resolution MR angiography—preliminary experience. Radiology 236:694–703
Nikolaou K, Schoenberg SO, Brix G et al (2004) Quantification of pulmonary blood flow and volume in healthy volunteers by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using a parallel imaging technique. Invest Radiol 39:537–545
Amundsen T, Torheim G, Kvistad KA et al (2002) Perfusion abnormalities in pulmonary embolism studied with perfusion MRI and ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy: an intra-modality and inter-modality agreement study. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:386–394
Fink C, Puderbach M, Bock M et al (2004) Regional lung perfusion: assessment with partially parallel three-dimensional MR imaging. Radiology 231:175–184
Kluge A, Gerriets T, Stolz E et al (2006) Pulmonary perfusion in acute pulmonary embolism: agreement of MRI and SPECT for lobar, segmental and subsegmental perfusion defects. Acta Radiol 47:933–940
Ley S, Fink C, Zaporozhan J et al (2005) Value of high spatial and high temporal resolution magnetic resonance angiography for differentiation between idiopathic and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: initial results. Eur Radiol 15:2256–2263
Kluge A, Gerriets T, Lange U, Bachman G (2005) MRI for short-term follow-up of acute pulmonary embolism. Assessment of thrombus appearance and pulmonary perfusion: a feasibility study. Eur Radiol 15:1969–1977
Remy-Jardin M, Louvegny S, Remy J et al (1997) Acute central thromboembolic disease: posttherapeutic follow-up with spiral CT angiography. Radiology 203:173–180
Sampson FC, Goodacre SW, Thomas SM, van Beek EJ (2007) The accuracy of MRI in diagnosis of suspected deep vein thrombosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 17:175–181
Obernosterer A, Aschauer M, Portugaller H, Koppel H, Lipp RW (2005) Three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography used as a "one-stop shop'' imaging procedure for venous thromboembolism: a pilot study. Angiology 56:423–430
Kluge A, Mueller C, Strunk J, Lange U, Bachmann G (2006) Experience in 207 combined MRI examinations for acute pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1686–1696
Edelman RR, Hatabu H, Tadamura E, Li W, Prasad PV (1996) Noninvasive assessment of regional ventilation in the human lung using oxygen-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Med 2:1236–1239
Nakagawa T, Sakuma H, Murashima S, Ishida N, Matsumura K, Takeda K (2001) Pulmonary ventilation-perfusion MR imaging in clinical patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:419–424
Kreitner KF, Ley S, Kauczor HU et al (2004) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: pre-and postoperative assessment with breath-hold MR imaging techniques. Radiology 232:535–543
Roeleveld RJ, Marcus JT, Faes TJ et al (2005) Interventricular septal configuration at mr imaging and pulmonary arterial pressure in pulmonary hypertension. Radiology 234:710–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fink, C., Ley, S., Schoenberg, S.O. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Radiol 17, 2546–2553 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0664-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0664-4