Abstract
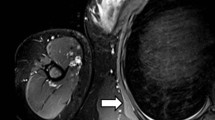
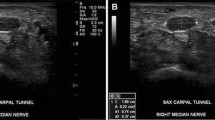
The diagnosis of nerve entrapment and compressive neuropathy has been traditionally based on the clinical and electrodiagnostic examinations. As a result of improvements in the magnetic resonance (MR) imaging modality, it plays not only a fundamental role in the detection of space-occupying lesions but also a compensatory role in clinically and electrodiagnostically inconclusive cases. Although ultrasound has undergone further development in the past decades and shows high resolution capabilities, it has inherent limitations due to its operator dependency. We review the general concepts that should be known to evaluate the entrapment and compressive neuropathy in MR imaging. We also review the course of normal peripheral nerves, as well as various clinical demonstrations and pathological features of compressed and entrapped nerves in the lower extremities on MR imaging, according to the nerves involved. The common sites of nerve entrapment of the lower extremity are as follows: sciatic nerve around the piriformis muscle; tibial nerve at the popliteal fossa and tarsal tunnel, common peroneal nerve around the fibular neck, and digital nerve near the metatarsal head. Although MR imaging can depict the peripheral nerves in the extremities effectively, radiologists should be familiar with nerve pathways, common sites of nerve compression, and common space-occupying lesions resulting in nerve compression in MR imaging.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spratt JD, Stanley, AJ, Grainger AJ, Hide IG, Campbell RS (2002) The role of diagnostic radiology in compressive and entrapment neuropathies. Eur Radiol 12:2352–2364
Hochman MG, Zilberfarb JL (2004) Nerves in a pinch: imaging of nerve compression syndromes. Radiol Clin North Am 42:221–245
Bacigalupo L, Bianchi S, Valle M, Martinoli C (2003) Ultrasonography of peripheral nerves. Radiologe 43:841–849
Beekman R, Visser LH (2004) High-resolution sonography of the peripheral nervous system—a review of the literature. Eur J Neurol 11:305–314
Chiou HJ, Chou YH, Chiou SY, Liu JB, Chang CY (2003) Peripheral nerve lesions: role of high-resolution US. Radiographics 23:e15
Grant GA, Britz GW, Goodkin R, Jarvik JG, Maravilla K, Kliot M (2002) The utility of magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating peripheral nerve disorders. Muscle Nerve 25:314–331
Howe FA, Filler AG, Bell BA, Griffiths JR (1992) Magnetic resonance neurography. Magn Reson Med 28:328–338
Kuntz Ct, Blake L, Britz G, Filler A, Hayes CE, Goodkin R, Tsuruda J, Maravilla KM (1996) Magnetic resonance neurography of peripheral nerve lesions in the lower extremity. Neurosurgery 39:750–756; discussion 756–757
Lee CH, Kim TK, Yoon ES, Dhong ES (2005) Correlation of high-resolution ultrasonographic findings with the clinical symptoms and electrodiagnostic data in carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Plast Surg 54:20–23
Martinoli C, Bianchi S, Gandolfo N, Valle M, Simonetti S, Derchi LE (2000) US of nerve entrapments in osteofibrous tunnels of the upper and lower limbs. Radiographics 20:S199–S217
Stuart RM, Koh ES, Breidahl WH (2004) Sonography of peripheral nerve pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:123–129
Grechenig W, Mayr J, Peicha G, Boldin C (2003) Subluxation of the ulnar nerve in the elbow region—ultrasonographic evaluation. Acta Radiol 44:662–664
Martinoli C, Bianchi S, Giovagnorio F, Pugliese F (2001) Ultrasound of the elbow. Skeletal Radiol 30:605–614
Jacobson JA, Jebson PJ, Jeffers AW, Fessell DP, Hayes CW (2001) Ulnar nerve dislocation and snapping triceps syndrome: diagnosis with dynamic sonography—report of three cases. Radiology 220:601–605
Cudlip SA, Howe FA, Griffiths JR, Bell BA (2002) Magnetic resonance neurography of peripheral nerve following experimental crush injury, and correlation with functional deficit. J Neurosurg 96:755–759
Filler AG, Kliot M, Howe FA, Hayes CE, Saunders DE, Goodkin R, Bell BA, Winn HR, Griffiths JR, Tsuruda JS (1996) Application of magnetic resonance neurography in the evaluation of patients with peripheral nerve pathology. J Neurosurg 85:299–309
Maravilla KR, Bowen BC (1998) Imaging of the peripheral nervous system: evaluation of peripheral neuropathy and plexopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1011–1023
Grant GA, Goodkin R, Kliot M (1999) Evaluation and surgical management of peripheral nerve problems. Neurosurgery 44:825–839; discussion 839–840
Hormann M, Traxler H, Ba-Ssalamah A, Mlynarik V, Shodaj-Baghini M, Kubiena H, Trattnig S (2003) Correlative high-resolution MR-anatomic study of sciatic, ulnar, and proper palmar digital nerve. Magn Reson Imaging 21:879–885
Filler AG, Howe FA, Hayes CE, Kliot M, Winn HR, Bell BA, Griffiths JR, Tsuruda JS (1993) Magnetic resonance neurography. Lancet 341:659–661
Jarvik JG, Kliot M, Maravilla KR (2000) MR nerve imaging of the wrist and hand. Hand Clin 16:13–24; vii
Britz GW, Haynor DR, Kuntz C, Goodkin R, Gitter A, Kliot M (1995) Carpal tunnel syndrome: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging, clinical, electrodiagnostic, and intraoperative findings. Neurosurgery 37:1097–1103
Britz GW, Haynor DR, Kuntz C, Goodkin R, Gitter A, Maravilla K, Kliot M (1996) Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging, clinical, electrodiagnostic, and intraoperative findings. Neurosurgery 38:458–465; discussion 465
Gebarski SS, Telian SA, Niparko JK (1992) Enhancement along the normal facial nerve in the facial canal: MR imaging and anatomic correlation. Radiology 183:391–394
Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Wessig C, Solymosi L (2002) Sequential MR imaging of denervated muscle: experimental study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1427–1431
Bendszus M, Wessig C, Reiners K, Bartsch AJ, Solymosi L, Koltzenberg M (2003) MR imaging in the differential diagnosis of neurogenic foot drop. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1283–1289
Bredella MA, Tirman PF, Fritz RC, Wischer TK, Stork A, Genant HK (1999) Denervation syndromes of the shoulder girdle: MR imaging with electrophysiologic correlation. Skeletal Radiol 28:567–572
Inokuchi W, Ogawa K, Horiuchi Y (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging of suprascapular nerve palsy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 7:223–227
Linker CS, Helms CA, Fritz RC (1993) Quadrilateral space syndrome: findings at MR imaging. Radiology 188:675–676
Sallomi D, Janzen DL, Munk PL, Connell DG, Tirman PF (1998) Muscle denervation patterns in upper limb nerve injuries: MR imaging findings and anatomic basis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171:779–784
West GA, Haynor DR, Goodkin R, Tsuruda JS, Bronstein AD, Kraft G, Winter T, Kliot M (1994) Magnetic resonance imaging signal changes in denervated muscles after peripheral nerve injury. Neurosurgery 35:1077–1085; discussion 1085–1076
Jankiewicz JJ, Hennrikus WL, Houkom JA (1991) The appearance of the piriformis muscle syndrome in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. A case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res 262:205–209
Mastaglia FL (2000) Tibial nerve entrapment in the popliteal fossa. Muscle Nerve 23:1883–1886
Sansone V, Sosio C, da Gama Malcher M, de Ponti A (2002) Two cases of tibial nerve compression caused by uncommon popliteal cysts. Arthroscopy 18:E8
Delfaut EM, Demondion X, Bieganski A, Thiron MC, Mestdagh H, Cotten A (2003) Imaging of foot and ankle nerve entrapment syndromes: from well-demonstrated to unfamiliar sites. Radiographics 23:613–623
Dellon AL, Mackinnon SE (1984) Tibial nerve branching in the tarsal tunnel. Arch Neurol 41:645–646
Havel PE, Ebraheim NA, Clark SE, Jackson WT, DiDio L (1988) Tibial nerve branching in the tarsal tunnel. Foot Ankle 9:117–119
Oh SJ, Meyer RD (1999) Entrapment neuropathies of the tibial (posterior tibial) nerve. Neurol Clin 17:593–615; vii
Lau JT, Daniels TR (1999) Tarsal tunnel syndrome: a review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int 20:201–209
Zanetti M, Ledermann T, Zollinger H, Hodler J (1997) Efficacy of MR imaging in patients suspected of having Morton’s neuroma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:529–532
Weishaupt D, Treiber K, Kundert HP, Zollinger H, Vienne P, Hodler J, Willmann JK, Marincek B, Zanetti M (2003) Morton neuroma: MR imaging in prone, supine, and upright weight-bearing body positions. Radiology 226:849–856
Zanetti M, Strehle JK, Zollinger H, Hodler J (1997) Morton neuroma and fluid in the intermetatarsal bursae on MR images of 70 asymptomatic volunteers. Radiology 203:516–520
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Choi, JY., Huh, YM. et al. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in entrapment and compressive neuropathy—what, where, and how to see the peripheral nerves on the musculoskeletal magnetic resonance image: part 1. Overview and lower extremity. Eur Radiol 17, 139–149 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0179-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0179-4