Abstract
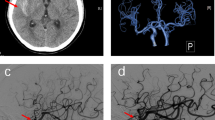
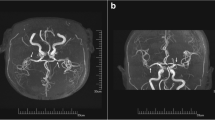
The aim of this study was to present a case of disruption of the blood-brain barrier during the coronary and lower extremity angiographies with radiological and clinical findings. This condition was secondary to intraarterial use of a nonionic, monomeric contrast medium. A total of 450 cc contrast media was used. Computed tomography examination showed contrast enhancement of the right occipital and frontoparietal cortical regions, which returned to normal one day after. The patient also fully recovered from the neurological symptoms within 24 h. We discussed the possible mechanism for blood-brain barrier disruption in this case.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Wispelaere JF, Trigaux JP, van Beers B, Gilliard C (1992) Cortical and CSF hyperdensity after iodinated contrast medium overdose: CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:998–1003
Okazaki H, Tanaka K, Shishido T et al. (1989) Disruption of the blood-brain-barrier caused by nonionic contrast medium used for abdominal angiography: CT demonstration. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13:893–895
Numaguchi Y, Fleming MS, Hasuo K, Puyao FA, Nice NC Jr (1984) Blood-brain-barrier disruption due to cerebral arteriography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8:936–939
Studdard WE, Davis DO, Young SW (1981) Cortical blindness after cerebral angiography. J Neurosurg 54:240–244
Lantos G (1989) Cortical blindness due to osmotic disruption of the blood-brain-barrier by angiographic contrast material: CT and MRI studies. Neurology 39:567–571
Eckel TS, Breiter SN, Monsein LH (1988) Subarachnoid contrast enhancement after spinal angiography mimicking diffuse subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJR 170:503–505
Sage MR, Wilson AJ (1994) The blood-brain-barrier: an important concept in neuroimaging. AJNR 15:601–622
Almen T (1994) The etiology of contrast medium reactions. Invest Radiol 29:37–45
Fattori R, Piva R, Schicchi F et al. (1994) Iomeprol and iopamidol in cardiac angiography: a randomised, double blind, parallel-group comparison. Eur J Radiol 18:61–66
Rosati G (1994) Clinical pharmacology of iomeprol. Eur J Radiol 18:51–60
Simonetti G, Guazzaroni M, Carpanese L et al. (1994) A double-blind comparative study of the safety and efficacy of iomeprol in renal intraarterial digital substraction angiography. Eur J Radiol 18:73–76
Ugolotti U, Larini P, Marcato C et al. (1994) Peripheral arteriography with a new nonionic agent: comparison of iomeprol with iopamidol. Eur J Radiol 18:77–82
Tadano K, Yuzuriha T, Motojii N, Hasegawa S, Kawai N, Shigematsu A (1992) Pharmacokinetic studies of 125 I-iomeprol after a single intravenous administration in male rats. Prog Med 12:38–49
Tadano K, Yuzuriha T, Motojii N, Hasegawa S, Kawai N, Shigematsu A (1992) Pharmacokinetic studies of 125 I-iomeprol after a single intravenous administration in beagle dogs. Prog Med 12:65–77
Lorusso V, Taroni P, Alvino S, Spinazzi A (2001) Pharmacokinetics and safety of iomeprol in healthy volunteers and in patients with renal impairment or end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis. Invest Radiol 36:309–316
Giang DW, Kido DK (1989) Transient global amnesia associated with cerebral angiography performed with use of iopamidol. Radiology 172:195–196
Wales LR, Nov AA (1981) Transient global amnesia: complication of cerebral angiography. AJNR 2:275–277
Junck L, Marshall WH (1983) Neurotoxicity of radiological contrast agents. Ann Neurol 13:469–484
Minuk J, Melancon D, Tampieri D, Ethier R (1990) Transient global amnesia associated with cerebral angiography performed with use of iopamidol. Radiology 174:285–286
Essig M, Kummer R von, Egelhof T, Winter R, Sartor K (1996) Vascular MR contrast enhancement in cerebrovascular disease. AJNR 17:887–894
Imakita S, Nishimura T, Naito H et al. (1987) Magnetic resonance imaging of human cerebral infarction: enhancement with Gd-DTPA. Neuroradiology 29:422–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yıldız, A., Yencilek, E., Apaydın, F.D. et al. Transient partial amnesia complicating cardiac and peripheral arteriography with nonionic contrast medium. Eur Radiol 13 (Suppl 6), L113–L115 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1975-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-1975-8