Abstract
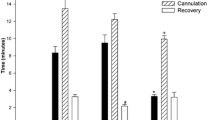
Eleven lactating female Weddell seals were immobilised using inhaled isoflurane and oxygen, having initially been sedated using an intramuscular injection of midazolam. The seals were selected from colonies in Long Fjord, East Antarctica. Isoflurane was delivered using a precision, out-of-circle vaporiser in a portable, heated, semi-closed circle system anaesthetic machine. Induction time (time from injection of midazolam to detected maximal effect of midazolam) ranged from 12 min to 29 min. The maximal effect of midazolam was assessed as being either moderate sedation (n=9) or heavy sedation (n=2), and the maximal effect of inhaled isoflurane and oxygen was assessed as being light anaesthesia (n=11). The level of chemical restraint achieved using this combination allowed attachment of heart rate monitoring units and collection of biological samples. Recovery time ranged from 1 min to 11 min. The anaesthetic regime proved a practical, safe and reliable method for the immobilisation of lactating Weddell seals under conditions of low environmental temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornemann H, Plõtz J (1993) A field method for immobilising Weddell seals. Wildl Soc Bull 21:437–441
Castellini MA, Kooyman GL (1990) Length, girth and mass relationship in Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii). Mar Mammal Sci 6:75–77
Gales NJ (1989) Chemical restraint and anaesthesia of pinnipeds: a review. Mar Mammal Sci 5:228–256
Gales NJ, Burton HR (1988) Use of emetics and anaesthesia for dietary assessment of Weddell seals. Aust Wildl Res 15:423–433
Gales NJ, Mattlin R (1998) Fast, safe, field-portable gas anaesthesia for otariids. Mar Mammal Sci 14:355–360
Gales N, Barnes J, Chittick B, Gray M, Robinson S, Burns J and Costa D (2005) Effective, field-based inhalation anaesthesia for ice seals (in review)
Hall LW, Clarke KW (1991) Principles of sedation, analgesia and premedication. In: Clarke KW, Hall LW (eds) Veterinary Anaesthesia 9th edn. Ballière Tindall, London, pp 51–79
Hammond D, Elsner R (1977) Anaesthesia in phocid seals. J Zoo An Med 8: 7–13
Haulena M, Heath RB (2001) Marine mammal anaesthesia, chap 29. In: Gulland F(eds) CRC Handbook of marine mammal medicine. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 655–688
Higgins DP, Rogers TL, Irvine AD and Hall-Aspland SA (2002) Use of midazolam/pethidine and tiletamine/zolazepam combinations for the chemical restraint of leopard seals (Hydrurga leptonyx). Mar Mammal Sci 18:483–499
Karesh WB, Cook RA, Stetter M, Uhart MM, Hoogesteijn A, Lewis MN, Campagna C, Mailuf P, Torres A, House C, Thomas L, Braselton WE, Dierenfeld ES, McNamara TS, Duignan P, Raverty S and Linn M (1997) South American pinnipeds: immobilisation, telemetry and health evaluations. Ann Mtg Am Assoc Zoo Vet, Houston, pp 291–295
Kusagaya H, Sato K (2001) A safe and practical inhalation anaesthesia for Weddell seals. Polar Biol 24:549–552
Lynch MJ, Tahmindjis MA, Gardner H (1999) Immobilisation of pinniped species. Aust Vet J 77:181–185
Phelan JR, Green K (1992) Chemical restraint of Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) with a combination of tiletamine and zolazepam. J Wildl Dis 28:230–235
Plumb DC (1999a) Isoflurane. In: Plumb DC (ed) Veterinary drug handbook, 3rd edn. Iowa University Press, Ames, pp 403–404
Plumb DC (1999b) Midazolam hydrochloride In: Plumb DC (ed) Veterinary drug handbook 3rd edn. Iowa University Press, Ames, pp 498–500
Slip DJ, Woods R (1996) Intramuscular and intravenous immobilisation of juvenile southern elephant seals. J Wildl Manag 60:802–807
Stirling I (1966) A technique for handling live seals. J Mammal 47:543–544
Tahmindjis MA, Higgins DP, Lynch ML, Barnes JA and Southwell CJ (2003) Use of a pethidine and midazolam combination for the reversible sedation of crabeater seals (Lobodon carcinophagus). Mar Mammal Sci 19:581–589
Thornton SJ and Hochachka PW (2004) Oxygen and the diving seal. Undersea Hyperbaric Med 31:81–95
Woods R, McLean S, Nichol S, Burton H (1994) A comparison of some cyclohexamine based drug combinations for chemical restraint of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina). Mar Mammal Sci 10:412–429
Woods R, McLean S, Nichol S, Slip DJ, Burton H (1996) Use of the respiratory stimulant doxapram in southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina). Vet Rec 138:514–517
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Marjolein van Polanen Petel for her excellent work as a field assistant and the other ANARE expeditioners at Davis Station over the 2002/03 summer. Fieldwork in Antarctica was supported by the Australian Antarctic Division, Sea World Research and Rescue Foundation and the University of Tasmania. Roche Products Pty Ltd generously donated the flumazenil used in the study. The study was conducted with the permission from Antarctic Animal Ethics Committee, Australian Antarctic Division and Animal Ethics Committee of the University of Tasmania. We thank the referees appointed by the editor for valuable advice on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bodley, K., Petel, T.v.P. & Gales, N. Immobilisation of free-living Weddell seals Leptonychotes weddellii using midazolam and isoflurane. Polar Biol 28, 631–636 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-005-0725-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-005-0725-6