Abstract.
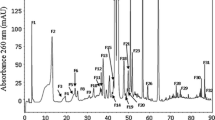
Red calli occur frequently in callus cultures of Prunus incisa Thunb. Calli that become red in color stop growing and turn brown while calli that remain green continue to grow. This study was carried out to compare the accumulation of antioxidant activity in red and green calli. The anthocyanin content, peroxidase isoforms and peroxidase activity were different in red and green calli. Red calli contained higher levels of anthocyanins, cell wall peroxidase activity and lower soluble peroxidase activity than green calli. A basic cell wall peroxidase (pI 10.0) was present only in red calli. Two acidic peroxidases (pI 6.0 and 6.8) had higher accumulation in green calli than in red calli. In the cell wall fraction of red calli, a peroxidase isoform with an apparent molecular mass of 30 kDa was found. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and internal amino acid sequence analysis indicate that this protein has a very high similarity with the cell wall peroxidase of Beta vulgaris L.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, .S., Sauve, .R. & Howard, .E. Identification of a cell wall peroxidase in red calli of Prunus incisa Thunb.. Plant Cell Rep 21, 380–384 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-002-0527-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-002-0527-z