Abstract
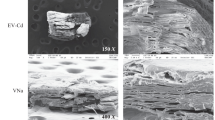
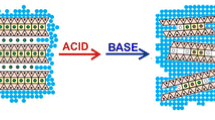
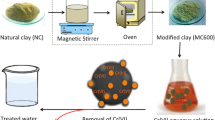
The performance of chemically modified vermiculite clay (VCM) and unmodified vermiculite clay (VCL) was evaluated for the removal of 4-aminoantipyrine from aqueous solution. The chemical modification of VCL was achieved using cellulose nanocrystals and nitrilotriacetic acid via facile dispersion and intercalation. After the modification, the BET surface area of VCL increased from 4 to 96 m2 g−1 in VCM. The removal of 4-aminoantipyrine was pH dependent which followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. Langmuir isotherm model provided the best fit for the sorption data while a percentage removal of 4-aminoantipyrine unto VCM of up to 98.410% was attained. Quantum chemical computational analysis was also used to describe the sorption process in molecular terms. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital and highest occupied molecular orbital are distributed over the molecule of 4-aminoantipyrine, and interaction between the surfaces of VCL/VCM and 4-aminoantipyrine may have occurred via donor–acceptor interactions. A regeneration capacity of 76% was obtained for VCM while that of VCL was 60%. The study has revealed that the property of vermiculite clay can be improved via facile dispersion and intercalation with the potential of removing pharmaceutical pollutants from water system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Putra EK, Pranowo R, Sunarso J, Indraswati N, Ismadji S (2009) Performance of activated carbon and bentonite for adsorption of amoxicillin from wastewater: mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics. Water Res 43:2419–2430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.02.039
Kawahara Y (1993) Immobilization of glucose oxidase in wild silk fiber (Antheraea pernyi) treated with an alkaline solution. J Seric Sci Jpan 62:272–275
Wang F, Zhang Y-Q (2015) Chapter eight—bioconjugation of silk fibroin nanoparticles with enzyme and peptide and their characterization. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 98:263–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apcsb.2014.11.005
Deshmukh P, Soni PK, Kankoriya A, Halve AK, Dixit R (2015) 4-Aminoantipyrine: a significant tool for the synthesis of biologically active schiff bases and metal complexes. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 34:162–170
Alam MS, Lee DU (2016) Physicochemical analyses of a bioactive 4-aminoantipyrine analogue—synthesis, crystal structure, solid state interactions, antibacterial, conformational and docking studies. EXCLI J 15:614–629. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2016-477
Hamdaoui O, Naffrechoux E (2007) Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon Part I. Two-parameter models and equations allowing determination of thermodynamic parameters. J Hazard Mater 147:381–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.021
Ismadji S, Soetaredjo FE, Ayucitra A (2015) Clay materials for environmental remediation. Springer, Berlin
Lagaly G (1982) Layer charge heterogeneity in vermiculites. Clays Clay Miner 30:215–222
Guggenheim S, Adams JM, Bain DC, Bergaya F, Bigatti MF, Drits VA, Formoso MLL, Galán E, Kogue T, Stanjek H (2006) Summary of recommendations of nomenclature committees relevant to clay mineralogy: report of the association internationale pour L’Étude des Argiles (AIPEA) nomenclature committee for 2006. Clays Clay Miner 54:761–772; Clay Miner 41:863–877
Valášková M, Martynková GS (2012) Vermiculite: structural properties and examples of the use. In: Valaskova Marta (ed) Clay minerals in nature: their characterization, modification and application. InTech, Rijeka, pp 210–238. https://doi.org/10.5772/51237
Weiss Z, Valvoda V, Chmielová M (1994) Dehydration and rehydration of natural mgvermiculite. Geol Carpath 45:33–39
de la Calle C, Suquet H, Pons CH (1988) Stacking order in 14.30 Å Mg-vermiculite. Clays Clay Miner 36:481–490
Medeiros MA, Sansiviero MTC, Araujo MH, Lago RM (2009) Modification of vermiculite by polymerization and carbonization of glycerol to produce highly efficient materials for oil removal. Appl Clay Sci 45:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.06.008
Moura FCC, Lago RM (2009) Catalytic growth of carbon nanotubes and nanofibers on vermiculite to produce floatable hydrophobic ‘nanosponges’ for oil spill remediation. Appl Catal B Environ 90:436–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.04.003
Zhang H, Yu J, Kuang D (2012) Effect of expanded vermiculite on aging properties of bitumen. Constr Build Mater 26:244–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.06.017
de Mesquita JP, Reis LS, Purceno AD, Donnici CL, Lago RM, Pereira FV (2013) Carbon-clay composite obtained from the decomposition of cellulose nanocrystals on the surface of expanded vermiculite. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88:1130–1135. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.3952
Wang J, Gao M, Ding F, Shen T (2018) Organo-vermiculites modified by heating and gemini pyridinium surfactants: preparation, characterization and sulfamethoxazole adsorption. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 546:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.03.014
Wu C-N, Saito T, Fujisawa S, Fukuzumi H, Isogai A (2012) Ultrastrong and high gas-barrier nanocellulose/clay-layered composites. Biomacromol 13:1927–1932. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm300465d
de Mesquita JP, Donnici CL, Pereira FV (2010) Biobased nanocomposites from layer-by-layer assembly of cellulose nanowhiskers with chitosan. Biomacromol 11:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm9011985
El Mouzdahir Y, Elmchaouri A, Mahbouba R, Gilb A, Korili SA (2009) Synthesis of nano-layered vermiculite of low density by thermal treatment. Powder Technol 189:2–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2008.06.013
Sutcu M (2015) Influence of expanded vermiculite on physical properties and thermal conductivity of clay bricks. Ceram Inter 41:2819–2827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.10.102
Duman O, Tunç S, Polat TG (2015) Determination of adsorptive properties of expanded vermiculite for the removal of C. I. Basic Red 9 from aqueous solution: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Appl Clay Sci 109–110:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.003
Duman O, Tunç S (2008) Electrokinetic properties of vermiculite and expanded vermiculite: effects of pH, clay concentration and mono- and multivalent electrolytes. Sep Sci Technol 43:3755–3776. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390802219109
Adewuyi A, Pereira FV (2017) Chemical modification of cellulose isolated from underutilized Hibiscus sabdariffa via surface grafting: a potential bio-based resource for industrial application. Kemija u industriji 66:327–338. https://doi.org/10.15255/KUI.2016.024
Muiambo HF, Focke WW, Atanasova M, Westhuizen IV, Tiedt LR (2010) Thermal properties of sodium-exchanged palabora vermiculite. Appl Clay Sci 50:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.06.023
Macheca AD, Focke WW, Muiambo HF, Kaci M (2016) Stiffening mechanisms in vermiculite–amorphous polyamide bio-nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 74:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2015.11.013
Stawinski W, Freitas O, Chmielarz L, Wegrzyn A, Komedera K, Błachowski A, Figueiredo S (2016) The influence of acid treatments over vermiculite based material as adsorbent for cationic textile dyestuffs. Chemosphere 153:115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.004
Muir IJ, Nesbitt HW (1991) Effects of aqueous cations on the dissolution of labradorite feldspar. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:3181–3189. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(91)90482-K
Huang W-L, Longo JM (1992) The effect of organics on feldspar dissolution and the development of secondary porosity. Chem Geol 98:271–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(92)90189-C
Fein JB (1994) Porosity enhancement during clastic diagenesis as a result of aqueous metal-carboxylate complexation: experimental studies. Chem Geol 115:263–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)00003-Q
Santos SSG, Silva HRM, de Souza AG, Alves APM, da Silva Filho EC, Fonseca MG (2015) Acid-leached mixed vermiculites obtained by treatment with nitric acid. Appl Clay Sci 104:286–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.12.008
Sharma RK (2012) A study in thermal properties of graft copolymers of cellulose and methacrylates. Adv Appl Sci Res 3:3961–3969
Balima F, Nguyen A-N, Reinert L, Floch SL, Pischedda V, Duclaux L, San-Miguel A (2015) Effect of the temperature on the structural and textural properties of a compressed K-vermiculite. Chem Eng Sci 134:555–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2015.05.061
Salopek B, Krasic D, Filipovic S (1992) Measurement and application of zeta-potential. Rudarsko-geolosko-naftni zbornik 4:147–151. https://hrcak.srce.hr/24757
Hanaor DAH, Michelazzi M, Leonelli C, Sorrell CC (2012) The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J Eur Ceram Soc 32:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.08.015
Lazaridis NK, Karapantsios TD, Georgantas D (2003) Kinetic analysis for the removal of a reactive dye from aqueous solution onto hydrotalcite by adsorption. Water Res 37:3023–3033. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00121-0
Oladoja NA, Adelagun ROA, Ahmad AL, Unuabonah EI, Bello HA (2014) Preparation of magnetic, macro-reticulated cross-linked chitosan for tetracycline removal from aquatic systems. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 117:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.02.006
Schoonheydt RA, Johnston CT (2006) Surface and interface chemistry of clay minerals. In: Bergaya F, Theng BKG, Lagal G (eds) Handbook of clay science. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 24:1–39
Alhamed YA (2009) Adsorption kinetics and performance of packed bed adsorber for phenol removal using activated carbon from dates’ stones. J Hazard Mater 170:763–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.002
Shek TH, Ma A, Lee VKC, McKay G (2009) Kinetics of zinc ions removal from effluents using ion exchange resin. Chem Eng J 146:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.05.019
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon solution. J Sanit Eng Div Am Soc Civ Eng 89:31–59
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Proc Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Yu M, Gao M, Shen T, Wang J (2018) Organo-vermiculites modified by low-dosage Gemini surfactants with different spacers for adsorption toward p-nitrophenol. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 553:601–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.08.001
Khaldi K, Hadjel M, Benyoucef A (2018) Removal of quinmerac by diatomite and modified diatomite from aqueous solution. Surf Engin Appl Electrochem 54:194–202. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375518020084
Wu F-C, Tseng R-L, Juang R-S (2009) Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem Eng J 150:366–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.014
Hameed BH, Mahmoud DK, Ahmad AL (2008) Equilibrium modeling and kinetic studies on the adsorption of basic dye by a low-cost adsorbent: coconut (Cocos nucifera) bunch waste. J Hazard Mater 158:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.034
Mohan S, Karthikeyan J (1997) Removal of lignin and tannin color from aqueous solution by adsorption on to activated carbon solution by adsorption on to activated charcoal. Environ Pollut 97:183–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(97)00025-0
Tempkin MI, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys Chim USSR 12:327–356
Obot IB, Obi-Egbedi NO, Ebenso EE, Afolabi AS, Oguzie EE (2013) Experimental, quantum chemical calculations, and molecular dynamic simulations insight into the corrosion inhibition properties of 2-(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)oxazolo [5,4-f] [1, 10]phenanthroline on mild steel. Res Chem Intermed 39:1927–1948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-0726-3
Obi-Egbedi NO, Obot IB, El-Khaiary MI (2011) Quantum chemical investigation and statistical analysis of the relationship between corrosion inhibition efficiency and molecular structure of xanthene and its derivatives on mild steel in sulphuric acid. J Mol Struct 1002:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.07.003
Njoku DI, Ukaga I, Ikenna OB, Oguzie EE, Oguzie KL, Ibisi N (2016) Natural products for materials protection: corrosion protection of aluminium in hydrochloric acid by Kola nitida extract. J Mol Liq 219:417–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.03.049
Oguzie EE, Li Y, Wang SG, Wanga F (2011) Understanding corrosion inhibition mechanisms-experimental and theoretical approach. RSC Adv 1:866–873. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ra00148e
Oguzie EE, Adindu CB, Enenebeaku CK, Ogukwe CE, Chidiebere MA, Oguzie KL (2012) Natural products for materials protection: mechanism of corrosion inhibition of mild steel by acid extracts of Piper guineense. J Phys Chem C 116:13603–13615. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp300791s
Lesar A, Milosev I (2009) Density functional study of the corrosion inhibition properties of 1,2,4-triazole and its amino derivatives. Chem Phys Lett 483:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2009.10.082
Acknowledgements
Author will like to thank TWAS-CNPq for the provision of postdoctoral fellowship. Author is also grateful for the support received from Prof. Pereira Vargas Fabiano and the Department of Chemistry, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adewuyi, A., Oderinde, R.A. Chemically modified vermiculite clay: a means to remove emerging contaminant from polluted water system in developing nation. Polym. Bull. 76, 4967–4989 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2643-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2643-0