Abstract
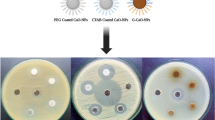
Oligoaniline (OANI) was prepared using chemical oxidative method using ascorbic acid as a dopant and ammonium persulfate as an oxidant. As-synthesized OANI was subjected for the preparation of various drug composites. All the synthesized compounds were characterized by FTIR, 1HNMR, TGA, GPC, etc. The thermal stability of the compounds was determined by TGA. The molecular weight was determined by GPC. Antibacterial studies of the synthesized compounds were investigated against four Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus MTCC 96, Streptococcus pyogenes MTCC 442, B. subtilis MTCC 441 and S. mutans MTCC 890) and four Gram-negative (Escherichia coli MTCC 443, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 1688, KL. pneumoniae MTCC 109 and S. typhi MTCC 98) bacteria based on their clinical and pharmacological importance. Some of the synthesized compounds showed excellent antibacterial activity as compared to individual bacterial activity of OANI and drugs to be used for preparation of composites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiang JC, MacDiarmid AG (1986) ‘Polyaniline’: protonic acid doping of the emeraldine form to the metallic regime. Synth Met 13(3):193–205
Li D, Huang J, Kaner RB (2009) Polyaniline nanofibers: a unique polymer nanostructure for versatile applications. Acc Chem Res 42(1):135–145
Baker CO, Shedd B, Tseng RJ, Martinez-Morales AA, Ozkan CS, Ozkan M, Yang Y, Kaner RB (2011) Size control of gold nanoparticles grown on polyaniline nanofibers for bistable memory devices. ACS Nano 5(5):3469–3474
Tseng RJ, Huang J, Ouyang J, Kaner RB, Yang Y (2005) Polyaniline nanofiber/gold nanoparticle nonvolatile memory. Nano Lett 5(6):1077–1080
Wang LX, Soczka-Guth T, Havinga E, Mullen K (1996) Poly(phenylenesulfidephenylenamine) (PPSA)—the “Compound” of polyphenylenesulfide with polyaniline. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 35(13):1495–1497
Libert J, Cornil J, dos Santos DA, Bredas JL (1997) From neutral oligoanilines to polyanilines: a theoretical investigation of the chain-length dependence of the electronic and optical properties. Phys Rev B 56(14):8638–8650
Wei Y, Yang C, Ding T (1996) A one-step method to synthesize N, N′-bis(4′-aminophenyl)-1,4-quinonenediimine and its derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett 37(6):731–734
Yu Y, Mao H, Chen L, Lu X, Zhang W, Wei Y (2004) Synthesis of a novel oligoaniline: ‘Dumbbell-shaped’ oligoaniline. Macromol Rapid Commun 25:664–668
Lu FL, Wudl F, Nowak M, Heeger AJ (1986) Phenyl-capped octaaniline (COA): an excellent model for polyaniline. J Am Chem Soc 108(26):8311–8313
Wei Z, Laitinen T, Smarsly B, Ikkala O, Faul CFJ (2005) Self-assembly and electrical conductivity transitions in conjugated oligoaniline-surfactant complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 44(5):751–756
Zhang WJ, Feng J, MacDiarmid AG, Epstein A (1997) Synthesis of oligomeric anilines synthetic metals. Synth Met 84(1–3):119–120
Kim H, Park JW (2010) Self-assembly of rod-coils consisting of tetraaniline and alkyl chains in different oxidation states. J Mater Chem 20(6):1186–1191
Guo B, Finne-Wistrand A, Albertsson AC (2011) Simple route to size-tunable degradable and electroactive nanoparticles from the self-assembly of conducting coil–rod–coil triblock copolymers. Chem Mater 23(17):4045–4055
Udeh CU, Fey N, Faul CFJ (2011) Functional block-like structures from electroactive tetra(aniline) oligomers. J Mater Chem 21:18137–18153
Guo B, Finne-Wistrand A, Albertsson AC (2011) Degradable and electroactive hydrogels with tunable electrical conductivity and swelling behavior. Chem Mater 23(5):1254–1262
Guo B, Finne-Wistran A, Albertsson AC (2011) Universal two-step approach to degradable and electroactive block copolymers and networks from combined ring-opening polymerization and post-functionalization via oxidative coupling reactions. Macromolecules 44(13):5227–5236
Yehgambaram P, Prasad RGSV, Jakka VS, Aparna RSL, Phani AR (2013) Antifungal activity of nanostructured polyaniline combined with fluconazole. J Pharma Res 6:26–31
Jotiram KP, Prasad RGSV, Jakka VS, Aparna RSL, Phani AR (2013) Antibacterial activity of nanostructured polyaniline combined with mupirocin. Nano Biomed Eng 4(3):144–149
Gizdavic-Nikolaidis MR, Bennett JR, Swift S, Easteal AJ, Ambrose M (2011) Broad spectrum antimicrobial activity of functionalized polyanilines. Acta Biomater 7(12):4204–4209
Gizdavic-Nikolaidis MR, Bennett JR, Zujovic Z, Swift S, Bowmaker G (2012) Characterization and antimicrobial efficacy of acetone extracted aniline oligomers. Synth Met 162:1114–1119
Shi N, Guo X, Jing H, Gong J, Sun C, Yang K (2006) Antibacterial effect of the conducting polyaniline. J Mater Sci Technol 22(3):289–290
Dhivya C, Vandarkuzhali SAA, Radha N (2016) Antimicrobial activities of nanostructured polyanilines doped with aromatic nitro compounds. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.12.005
Acknowledgements
The financial support provided by University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India, to one of the authors (Gunjan Kashyap) is gratefully acknowledged. Authors are also thankful to SICART Vallabh Vidyanagar and SAIF, Chandigarh, for analytical and spectral data. We are also thankful to Microcare Laboratory, Surat, for biological screening of synthesized compounds.
Funding
Funding was provided by CSIR/UGC-SRF (No.F.2(UGC/JRF/MLSU/2017/2755).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashyap, G., Meghwal, K., Ameta, C. et al. Synthesis of ascorbic acid-doped oligoaniline, its drug composites and study of their antibacterial behavior. Polym. Bull. 76, 2439–2451 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2502-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2502-z