Abstract
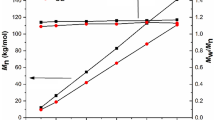
Co(II) and Mn(II) salts were assessed to be good catalysts for the bulk ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters. These polymerizations are reasonably controlled leading to the formation of polymer with good number average molecular weights (M n) and narrow molecular weight distributions. The polymerizations were studied in the presence and absence of benzyl alcohol and the polymerization tendency was found to increase in the presence of benzyl alcohol. The polymerization proceeds through the activated monomer mechanism, resulting in the formation of polymers containing the initiator as one of the end terminal groups. All the polymerizations show first-order kinetics with respect to monomer concentration. Ease of handling and low cost of Co(II) and Mn(II) salts make the catalytic process economically attractive.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The term “bioassimilable” is used here to describe a polymer that will eventually be eliminated or metabolized by natural pathways.
References
Mecking S (2004) Nature or petrochemistry?-biologically degradable materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:1078–1085. doi:10.1002/anie.200301655
Coates GW, Hillmyer MA (2009) A virtual issue of macromolecules: “polymers from renewable resources”. Macromolecules 42:7987–7989. doi:10.1021/ma902107w
Biela T, Kowalski A, Libiszowski J, Duda A, Penczek S (2006) Progress in polymerization of cyclic esters: mechanisms and synthetic applications. Macromol Symp 240:47–55. doi:10.1002/masy.200650807
Gross RA, Kalra B (2002) Biodegradable polymers for the environment. Science 297:803–807. doi:10.1126/science.297.5582.803
Okada M (2002) Chemical syntheses of biodegradable polymers. Prog Polym Sci 27:87–133. doi:10.1016/S0079-6700(01)00039-9
O’Keefe BJ, Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2001) Polymerization of lactide and related cyclic esters by discrete metal complexes. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans 2215–2224. doi:10.1039/B104197P
Dechy-Cabaret O, Martin-Vaca B, Bourissou D (2004) Controlled ring-opening polymerization of lactide and glycolide. Chem Rev 104:6147–6176. doi:10.1021/cr040002s
Platel RH, Hodgson LM, Williams CK (2008) Biocompatible initiators for lactide polymerization. Polym Rev 48:11–63. doi:10.1080/15583720701834166
Wu J, Yu T-L, Chen C-T, Lin C-C (2006) Recent developments in main group metal complexes catalyzed/initiated polymerization of lactides and related cyclic esters. Coord Chem Rev 250:602–626. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.07.010
Abdessamad A, Redshaw C (2010) Metal catalysts for ε-caprolactone polymerisation. Polym Chem 1:801–826. doi:10.1039/B9PY00334G
Linblad MS, Liu Y, Albertsson A-C, Ranucci E, Karlsson S (2002) Polymer from renewable resources in advances in polymer science. In: A-C Albertsson (ed) Springer, New York, 157:139–61
Penczek S (2000) Cationic ring-opening polymerization (CROP) major mechanistic phenomena. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 38:1919–1933. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(20000601)38:11<1919
Kubisa P, Penczek S (1999) Cationic activated monomer polymerization of heterocyclic monomers. Prog Polym Sci 24:1409–1437. doi:10.1016/S0079-6700(99)00028-3
Stanford MJ, Dove AP (2010) Stereocontrolled ring-opening polymerisation of lactide. Chem Soc Rev 39:486–494. doi:10.1039/B815104K
Sauer A, Kapelski A, Fliedel C, Dagorne S, Kol M, Okuda J (2013) Structurally well-defined group 4 metal complexes as initiators for the ring-opening polymerization of lactide mon omers. Dalton Trans 42:9007–9023. doi:10.1039/c3dt00010a
Pratt RC, Lohmeijer BGG, Long DA, Waymouth RM, Hedrick JL (2006) Triazabicyclodecene: a simple bifunctional organocatalyst for acyl transfer and ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters. J Am Chem Soc 128:4556–4557. doi:10.1021/ja060662
Kricheldorf HR (2009) Syntheses of biodegradable and biocompatible polymers by means of bismuth catalysts. Chem Rev 109:5579–5594. doi:10.1021/cr900029e
Mecerreyes D, Jerome R, Dubois P (1999) Novel macromolecular architectures based on aliphatic polyesters: Relevance of the “Coordination-Insertion” ring-opening polymerization in advances in polymer science, Springer, New York, 147:1–59
Kharas GB, Sanchez-Riora F, Soverson DK (2004) Polymers of lactic acid. In: Mobley DP (ed) Plastics from microbes. Hanser Publ, Munchen, Germany
Silvernail CM, Yao LJ, Hill LMR, Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2007) Structural and mechanistic studies of bis(phenolato)amine zinc(II) catalysts for the polymerization of ε-caprolactone. Inorg Chem 46:6565–6574. doi:10.1021/ic700581s
Du H, Xuan Pang X, Yu H, Zhuang X, Chen X, Cui D, Wang X, Jing X (2007) Polymerization of rac-lactide using schiff base aluminum catalysts: structure, activity, and stereoselectivity. Macromolecules 40:1904–1913. doi:10.1021/ma062194u
Barakat I, Dubois P, Jérôme R, Teyssié P (1993) Macromolecular engineering of polylactones and polylactides. X. Selective end-functionalization of poly(d, l)-lactide. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 31:505–514. doi:10.1002/pola.1993.080310222
Gregson CKA, Blackmore IJ, Gibson VC, Long NJ, Marshall EL, White AJP (2006) Titanium-salen complexes as initiators for the ring opening polymerisation of rac-lactide. Dalton Trans 3134–3140. doi:10.1039/B518266B
Kricheldorf HR, Hachmann-Thiessen H, Schwartz G (2004) Di-, tri- and tetrafunctional poly(ε-caprolactone)s by Bi(OAc)3-catalyzed ring-opening polymerizations of ε-caprolactone. Macromolecules 37:6340–6345. doi:10.1021/ma030425g
Williams CK, Choi LE, Nam W, Young VG Jr, Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2003) A highly active zinc catalyst for the controlled polymerization of lactide. J Am Chem Soc 125:11350–11359. doi:10.1021/ja0359512
Alcazar-Roman LM, O’ Keefe BJ, Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2003) Electronic influence of ligand substituents on the rate of polymerization of ε-caprolactone by single-site aluminium alkoxide catalysts. Dalton Trans 3082–3087. doi:10.1039/B303760F
O’Keefe BJ, Breyfogle LE, Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2002) Mechanistic comparison of cyclic ester polymerizations by novel iron(III)-alkoxide complexes: single vs multiple site catalysis. J Am Chem Soc 124:4384–4393. doi:10.1021/ja012689t
Chamberlain BM, Cheng M, Moore DR, Ovitt T, Lobkovsky EB, Coates GW (2001) Polymerization of lactide with zinc and magnesium β-diiminate complexes: stereocontrol and mechanism. J Am Chem Soc 123:3229–3238. doi:10.1021/ja003851f
Stevels WM, Ankone MJK, Dijkstra PJ, Feijen J (1996) Kinetics and mechanism of ε-caprolactone polymerization using yttrium alkoxides as initiators. Macromolecules 29:8296–8303. doi:10.1021/ma960701
Chakraborty D, Chen EY-X (2003) Chiral amido aluminum and zinc alkyls: a synthetic, structural, and polymerization study. Organometallics 22:769–774. doi:10.1021/om020889n
Chakraborty D, Chen EY-X (2002) Neutral, three-coordinate, chelating diamide aluminum complexes: catalysts/initiators for synthesis of telechelic oligomers and high polymers. Organometallics 21:1438–1442. doi:10.1021/om011051n
Ni Q, Yu L (1998) Synthesis of novel poly(ε-caprolactone)s functionalized with a thioester end-group via a living ring opening polymerization and their application in chemoselective ligation with compounds containing a cysteine terminal. J Am Chem Soc 120:1645–1646. doi:10.1021/ja9738790
Huang C-H, Wang F-C, Ko B-T, Yu L-T, Lin C–C (2001) Ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone and l-lactide using aluminum thiolates as initiator. Macromolecules 34:356–361. doi:10.1021/ma0014719
Stolt M, Södergård A (1999) Use of monocarboxylic iron derivatives in the ring-opening polymerization of l-lactide. Macromolecules 32:6412–6417. doi:10.1021/ma9902753
Stolt M, Södergård A (1998) Ring-opening polymerization of l-lactide by means of different iron compounds. Macromol Symp 130:393–402. doi:10.1002/masy.19981300133
Kricheldorf HR, Damrau D-O (1997) Polylactones, 38. Polymerization of l-lactide with Fe(II) lactate and other resorbable Fe(II) salts. Macromol Chem Phys 198:1767–1774. doi:10.1002/macp.1997.021980606
Kricheldorf HR, Serra A (1958) Polylactones in polymer bulletin. Springer, New York, 14:497–502
Yang N, Xin L, Gao W, Zhang J, Luo X, Liu X, Mu Y (2012) Al and Zn complexes bearing N, N, N-tridentate quinolinyl anilidoimine ligands: synthesis, characterization and catalysis in l-lactide polymerization. Dalton Trans 41:11454–11463. doi:10.1039/c2dt30594a
Roberts CC, Barnett BR, Green DB, Fritsch JM (2012) Synthesis and structures of tridentate ketoiminate zinc complexes that act as l-lactide ring-opening polymerization catalysts. Organometallics 31:4133–4141. doi:10.1021/om200865w
Ma W-A, Wang Z-X (2011) Zinc and aluminum complexes supported by quinoline-based N, N, N-chelate ligands: synthesis, characterization, and catalysis in the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone and rac-lactide. Organometallics 30:4364–4373. doi:10.1021/om200423g
Wheaton CA, Hayes PG, Ireland BJ (2009) Complexes of Mg, Ca and Zn as homogeneous catalysts for lactide polymerization. Dalton Trans 4832–4846. doi:10.1039/b819107g
Helou M, Miserque O, Brusson J-M, Carpentier J-F, Guillaume SM (2009) Poly(trimethylene carbonate) from biometals-based initiators/catalysts: highly efficient immortal ring-opening polymerization processes. Adv Synth Catal 351:1312–1324. doi:10.1002/adsc.200800788
Labourdette G, Lee DJ, Patrick O, Ezhova MB, Mehrkhodavandi P (2009) Unusually stable chiral ethyl zinc complexes: reactivity and polymerization of lactide. Organometallics 28:1309–1319. doi:10.1021/om800818v
Chen M-T, Chang P-J, Huang C-A, Peng K-F, Chen, C-T (2009) Magnesium complexes containing bis-amido-oxazolinate ligands as efficient catalysts for ring-opening polymerisation of l-lactide. Dalton Trans 9068–9074. doi:10.1039/B907549F
Helou M, Miserque O, Brusson J-M, Carpentier J-F, Guillaume SM (2008) Ultraproductive, zinc-mediated, immortal ring-opening polymerization of trimethylene carbonate. Chem Eur J 14:8772–8775. doi:10.1002/chem.200801416
Jeske RC, DiCiccio AM, Coates GW (2007) Alternating copolymerization of epoxides and cyclic anhydrides: an improved route to aliphatic polyesters. J Am Chem Soc 129:11330–11331. doi:10.1021/ja0737568
Marshall EL, Gibson VC, Rzepa HS (2005) A computational analysis of the ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide initiated by single-site β-diketiminate metal complexes: defining the mechanistic pathway and the origin of stereocontrol. J Am Chem Soc 127:6048–6051. doi:10.1021/ja043819b
Chen M, Attygalle AB, Lobkovsky EB, Coates GW (1999) Single-site catalysts for ring-opening polymerization: synthesis of heterotactic poly(lactic acid) from rac-lactide. J Am Chem Soc 121:11583–11584. doi:10.1021/ja992678o
Wu J-C, Huang B-H, Hsueh M-L, Lai S-L, Lin C-C (2005) Ring-opening polymerization of lactide initiated by magnesium and zinc alkoxides. Polymer 46:9784–9792. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.08.009
Chen H-Y, Huang B-H, Lin C-C (2005) A highly efficient initiator for the ring-opening polymerization of lactides and ε-caprolactone: a kinetic study. Macromolecules 38:5400–5405. doi:10.1021/ma050672f
Chen H-Y, Tang H-Y, Lin C-C (2006) Ring-opening polymerization of lactides initiated by zinc alkoxides derived from NNO-tridentate ligands. Macromolecules 39:3745–3752. doi:10.1021/ma060471r
Ajellal N, Carpentier J-F, Guillaume C, Guillaume SM, Helou M, Poirier V, Sarazin Y, Trifonov (2010) A metal-catalyzed immortal ring-opening polymerization of lactones, lactides and cyclic carbonates. Dalton Trans 39:8363–8376. doi:10.1039/C001226B
Sarazin Y, Poirier V, Roisnel T, Carpentier J-F (2010) Discrete, base-free, cationic alkaline-earth complexes–access and catalytic activity in the polymerization of lactide. Eur J Inorg Chem 3423–3428. doi:10.1002/ejic.201000558
Wang L, Ma H (2010) Zinc complexes supported by multidentate aminophenolate ligands: synthesis, structure and catalysis in ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide. Dalton Trans 39:7897–7910. doi:10.1039/C0DT00250J
Huang Y, Hung W-C, Liao M-Y, Tsai T-E, Peng Y-L, Lin C-C (2009) Ring-opening polymerization of lactides initiated by magnesium and zinc complexes based on NNO-tridentate ketiminate ligands: activity and stereoselectivity studies. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 47:2318–2329. doi:10.1002/pola.23314
Chen H-Y, Liu M-Y, Sutar AK, Lin C-C (2010) Synthesis and structural studies of heterobimetallic alkoxide complexes supported by bis(phenolate) ligands: efficient catalysts for ring-opening polymerization of l-lactide. Inorg Chem 49:665–674. doi:10.1021/ic901938e
Li C-Y, Chen P-S, Hsu S-J, Lin C-H, Huang H-Y, Ko B-T (2012) Mono-aluminum, di-magnesium and tri-zinc complexes supported by bisphenolate ligand: synthesis, characterization and catalytic studies for ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters. J Organomet Chem 716:175–181. doi:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2012.06.019
Poirier V, Roisnel T, Carpentier J-F, Sarazin Y (2009) Versatile catalytic systems based on complexes of zinc, magnesium and calcium supported by a bulky bis(morpholinomethyl)phenoxy ligand for the large-scale immortal ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic esters. Dalton Trans 44:9820–9827. doi:10.1039/b917799j
Liu B, Roisnel T, Guegan J-P, Carpentier J-F, Sarazin Y (2012) Heteroleptic silylamido phenolate complexes of calcium and the larger alkaline earth metals: β-agostic Ae···Si-H stabilization and activity in the ring-opening polymerization of l-lactide. Chem Eur J 18:6289–6301. doi:10.1002/chem.201103666
Dobrzynski P, Kasperczyk J, Bero M (1999) Application of calcium acetylacetonate to the polymerization of glycolide and copolymerization of glycolide with ε-caprolactone and l-lactide. Macromolecules 32:4735–4737. doi:10.1021/ma981969z
Chen J, Gorczynski JL, Zhang G, Fraser CL (2010) Iron tris(dibenzoylmethane-polylactide). Macromolecules 43:4909–4920. doi:10.1021/ma100333e
O’Keefe BJ, Monnier SM, Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2001) Rapid and controlled polymerization of lactide by structurally characterized ferric alkoxides. J Am Chem Soc 123:339–340. doi:10.1021/ja003537l
Gowda RR, Chakraborty D (2010) Zinc acetate as a catalyst for the bulk ring opening polymerization of cyclic esters and lactide. J Mol Catal A Chem 333:167–172. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2010.10.013
Gowda RR, Chakraborty D (2011) Copper acetate catalyzed bulk ring opening polymerization of lactides. J Mol Catal A Chem 349:86–93. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2011.08.024
Gowda RR, Chakraborty D (2009) Environmentally benign process for bulk ring opening polymerization of lactones using iron and ruthenium chloride catalysts. J Mol Catal A Chem 301:84–92. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2008.11.010
Okamoto Y (1991) Cationic ring-opening polymerization of lactones in the presence of alcohol. Makromolekulare Chemie. Macromol Symp 42/43:117–133. doi:10.1002/masy.19910420109
Searles S, Tamres M, Barrow GM (1953) Hydrogen-bonding of esters and lactones. Site of bonding and effect of ring size. J Am Chem Soc 75:71–73. doi:10.1021/ja01097a019
Gowda RR, Chakraborty D, Ramkumar V (2009) New aryloxy and benzyloxy derivatives of titanium as catalysts for bulk ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone and δ-valerolactone. Eur J Inorg Chem 2981–2993. doi:10.1002/ejic.200900280
Gowda RR, Chakraborty D, Ramkumar V (2010) Aryloxy and benzyloxy compounds of hafnium: synthesis, structural characterization and studies on solvent-free ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone and δ-valerolactone. Polymer 51:4750–4759. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2010.08.031
Gowda RR, Ramkumar V, Chakraborty D Indian Patent: 2550/CHE/2010
Idage BB, Idage SB, Kasegaonkar AS, Jadhav RV (2010) Ring opening polymerization of dilactide using salen complex as catalyst. Mater Sci Eng B 168:193–198. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2009.10.037
Kricheldorf HR, Damrau D-O (1998) Polylactones. 44. Polymerizations of l-lactide catalyzed by manganese salts. JMS Pure Appl Chem 35:1875–1887. doi:10.1080/10601329808000558
Mazarro R, Cabezas LI, Lucas AD, Gracia I, Rodríguez JF (2009) Study of different catalysts and initiators in bulk copolymerization of d, l-lactide and glycolide. JMS Pure Appl Chem 46:1049–1059. doi:10.1080/10601320903252090
Breyfogle LE, Williams CK, Young VG., Hillmyer MA, Tolman WB (2006) Comparison of structurally analogous Zn2, Co2, and Mg2 catalysts for the polymerization of cyclic esters. Dalton Trans 928–936. doi:10.1039/B507014G
Wu G-P, Wei S-H, Ren W-M, Lu X-B, Xu T-Q, Darensbourg DJ (2011) Perfectly alternating copolymerization of CO2 and epichlorohydrin using cobalt(III)-based catalyst systems. J Am Chem Soc 133:15191–15199. doi:10.1021/ja206425j
Adamo R, Saksena R, Kovák P (2006) Studies towards a conjugate vaccine for anthrax: synthesis of the tetrasaccharide side chain of the bacillus anthracis exosporium. Helv Chim Acta 89:1075–1089. doi:10.1002/hlca.200690106
Frisch MJ., Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T. CT (2010)
de Geus M, Peters R, Koning CE, Heise A (2008) Insights into the initiation process of enzymatic ring-opening polymerization from monofunctional alcohols using liquid chromatography under critical conditions. Biomacromolecules 9:752–757. doi:10.1021/bm701158y
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajashekhar, B., Chakraborty, D. Co(II) and Mn(II) catalyzed bulk ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters. Polym. Bull. 71, 2185–2203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1180-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1180-8