Abstract
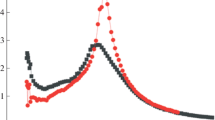
Methylcellulose (MC), a hydrophobically modified cellulose derivative, in an aqueous solution undergoes sol-to-gel and gel-to-sol transitions on heating and cooling, respectively. Using differential scanning calorimetry, MC in light (H2O) and heavy (D2O) water solutions has been investigated to elucidate the solvent isotope effect on the transitions. As a result, their transition temperatures are higher in H2O by about 4 °C than D2O. This phenomenon is rationalized in terms of the strength of the hydrophobic attractive interaction; the strength is enhanced by D2O. We discuss the reason for the enhancement and the difference in the isotope effect between MC and a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) polymer which shows an opposite trend to MC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lodish H, Baltimore D, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaira P, Darnell J (1995) Molecular cell biology, 3rd edn. Scientific American Books, New York
Haque A, Morris ER (1993) Thermogelation of methylcellulose. Part I: molecular structures and processes. Carbohydr Polym 22:161–173
Kobayashi K, Huang C, Lodge TP (1999) Thermoreversible gelation of aqueous methylcellulose solutions. Macromolecules 32:7070–7077
Li L, Shan H, Yue CY, Lam YC, Tam KC, Hu X (2002) Thermally induced association and dissociation of methylcellulose in aqueous solutions. Langmuir 18:7291–7298
Haque A, Richardson RK, Morris ER, Gidley MJ, Caswell DC (1993) Thermogelation of methylcellulose. Part II: effect of hydroxypropyl substituents. Carbohydr Polym 22:175–186
Sarkar N, Walker LC (1995) Hydration–dehydration properties of methylcellulose and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose. Carbohydr Polym 27:177–185
Winnik FM (1989) Association of hydrophobic polymers in H2O and D2O: fluorescence studies with (hydroxypropyl) cellulose. J Phys Chem 93:7452–7457
Joshi SC (2011) Sol–gel behavior of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) in ionic media including drug release. Materials 4:1861–1905
Takahashi M, Shimazaki M, Yamamoto J (2001) Thermoreversible gelation and phase separation in aqueous methyl cellulose solutions. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 39:91–100
Xu Y, Li L (2005) Thermoreversible and salt-sensitive turbidity of methylcellulose in aqueous solution. Polymer 46:7410–7417
Li L, Thangamathesvaran PM, Yue CY, Tam KC, Hu X, Lam YC (2001) Gel network structure of methylcellulose in water. Langmuir 17:8062–8068
Chevillard C, Axelos MAV (1997) Phase separation of aqueous solution of methylcellulose. Colloid Polym Sci 275:537–545
Hirrien M, Chevillard C, Desbriéres J, Axelos MAV, Rinaudo M (1998) Thermogelation of methylcellulose: new evidence for understanding the gelation mechanism. Polymer 39:6251–6259
Desbriéres J, Hirrien M, Rinaudo M (1998) A calorimetric study of methylcellulose gelation. Carbohydr Polym 37:145–152
Xu Y, Wang C, Tam KC, Li L (2004) Salt-assisted and salt-suppressed sol–gel transitions of methylcellulose in water. Langmuir 20:646–652
Zheng P, Li L, Hu X, Zhao X (2004) Sol–gel transition of methylcellulose in phosphate buffer saline solutions. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 42:1849–1860
Kundu PP, Kundu M (2001) Effect of salts and surfactant and their doses on the gelation of extremely dilute solutions methyl cellulose. Polymer 42:2015–2020
Li L, Liu E, Lim CH (2007) Micro-DSC and rheological studies of interactions between methylcellulose and surfactants. J Phys Chem 111:6410–6416
Efimova YM, Haemers S, Wierczinski B, Norde W, van Well AA (2006) Stability of globular protein in H2O and D2O. Biopolymers 85:264–273
Sasisanker P, Oleinikova A, Weingärtner H, Ravindra R, Winter R (2004) Solvation properties and stability of ribonuclease A in normal and deuterated water studied by dielectric relaxation and differential scanning/pressure perturbation calorimetry. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:1899–1905
Guzzi R, Sportelli L, La Rosa C, Milardi D, Grasso D (1998) Solvent isotope effects on azurin thermal unfolding. J Phys Chem B 102:1021–1028
Wang X, Wu C (1999) Light-scattering study of coil-to-globule transition of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) chain in deuterated water. Macromolecules 32:4299–4301
Kujawa P, Winnik FM (2001) Volumetric studies of aqueous polymer solution using pressure perturbation calorimetry: a new look at the temperature-induced phase transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in water and D2O. Macromolecules 34:4130–4135
Tiktopulo EI, Bychkova VE, Rička J, Ptitsyn OB (1994) Cooperativity of the coil–globule transition in a homopolymer: microcalorimetric study of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Macromolecules 27:2879–2882
Shirota H, Kuwabara N, Ohkawa K, Horie K (1999) Deuterium isotope effect on volume phase transition of polymer gel: temperature dependence. J Phys Chem B 103:10400–10408
Mao H, Li C, Zhang Y, Furyk S, Cremer PS, Bergbreiter DE (2004) High-throughput studies of the effects of polymer structure and solution components on the phase separation of thermoresponsive polymers. Macromolecules 37:1031–1036
Kresheck GC, Schneider H, Scheraga HA (1965) The effect of D2O on the thermal stability of proteins. Thermodynamic parameters for the transfer of model compounds from H2O to D2O. J Phys Chem 69:3132–3144
Némethy G, Scheraga HA (1964) Structure of water and hydrophobic bonding in proteins. IV. The thermodynamic properties of liquid deuterium oxide. J Chem Phys 41:680–698
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, Y. Solvent isotope effect on sol–gel transition of methylcellulose studied by DSC. Polym. Bull. 71, 1441–1448 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1134-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-014-1134-1