Abstract.
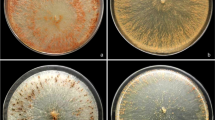
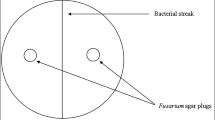
The growth of the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici race 2 (FOL 2) was observed in dual culture with two soil fungi as biocontrol agents, Trametes versicolor and Pleurotus eryngii. In both cases, an interaction zone with the pathogen was found with the Fusarium’s hyphae becoming free of cytoplasmic content. The enzymatic complex of fungi, studied as biocontrol agents, showed β-(1,3)-glucanase activity, and no other important glucanase activities were noted in all of the media studied. As the principal components of F. oxysporum cell walls are glucans, the results of the positive attack on the cell walls of FOL 2 by the T. versicolor and P. eryngii enzymatic complex demonstrated the contribution of glucanases in the degradation of the hyphal cell walls of F. oxysporum. The lack of cellulase and xylanase activities (acting on plant cell wall polysaccharides) in T. versicolor makes this species a better alternative for the potential control of diseases caused by Fusarium spp.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Dueñas, F., Martínez, M. Enzymatic Activities of Trametes versicolor and Pleurotus eryngii Implicated in Biocontrol of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici . Curr Microbiol 32, 151–155 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900027
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900027