Abstract
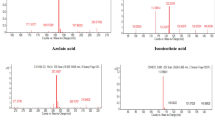
Astragalus adsurgens (A. adsurgens), which is considered a forage in China, grows widely in Eurasia and North America. However, Alternaria gansuense (A. gansuense) (synonym: Embellisia astragali) systematically infects A. adsurgens, producing swainsonine (SW), which poisons domesticated animals. In this study, we hypothesized that the A. gansuense SW-producing fungus is morphologically and molecularly related to the locoweed endophyte, Alternaria oxytropis (A. oxytropis), which systematically grows in host plants. Therefore, pure cultures of the fungi from diseased plants or endophytic interactions were collected from fields and assayed for SW via high-performance liquid chromatography linked to mass spectroscopy (HPLC–MS). The production of SW was also detected in A. adsurgens, A. oxytropis and diseased plants by assaying for the presence of the β-ketoacyl synthase (KS) gene, which is required for SW synthesis. Diseased A. adsurgens and pure cultures of A. gansuense have SW and the healthy-looking A. adsurgens plants also contained SW, probably because they were infected with A. gansuense. Therefore, A. adsurgens-infected A. gansuense are not safe for livestock consumption.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun K, Romero J, Liddell C, Creamer R (2003) Production of swainsonine by fungal endophytes of locoweed. Biol Rev 107:980–988. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095375620300813X
Carroll GC (1988) Fungal endophytes in stems and leaves: from latent pathogen to mutualistic symbiont. Ecology 69:2–9
Chen SS (2004) The systematic analysis and pharmacological activity research of Oxytropis glabra DC. Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, Yangling
Colegate SM, Dorling PR, Allen JG, Huxtable CR (2010) Plant associated toxins: agricultural, phytochemical and ecological aspects. Aust Vet J 73:119–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1996.tb09998.x
Cook D, Dale RG, Kevin DW, Jessie MR, Michael HR, Benedict TG (2009) Quantitative PCR method to measure the fungal endophyte in locoweeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57:6050–6054. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf901028z
Cook D, Ralphs MH, Welch KD, Stegelmeier BL (2009) Locoweed poisoning in livestock. Soc Range Manag 31:16–21. https://doi.org/10.2111/1551-501X-31.1.16
Cook D, Gardner DR, Grum D, Pfister JA, Ralphs MH, Welch KD, Green BT (2011) Swainsonine and endophyte relationships in Astragalus mollissimus and Astragalus lentiginosus. J Agric Food Chem 59:1281–1287. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf103551t
Cook D, Gardner DR, Pfister JA (2014) Swainsonine-containing plants and their realationship to endophytic fungi. Agric Food Chem 62:7326–7334. https://doi.org/10.2527/jam2016-1769
Cook D, Bgg D, Creamer R, Baucom DL, Gardner DR, Pan J, Moore N, Krasnoff SB, Jaromczyk JW, Schardl CL (2017) Swainsonine biosynthesis genes in diverse symbiotic and pathogenic fungi. G3-Genes Genomes Genet 7:1791–1797. https://doi.org/10.2527/jam2016-1769
Cui ZH, Zhao XH, Li QF, Wang JH, Geng GX (2008) Determination of swainsonine in Astragalus locoweed by internal standard gas chromatography. J Northwest SCi Tech Univ Agirc For 36:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-1508(08)60080-7
Donnell JO, Dickinson CH (1980) Pathogenicity of Alternaria and Cladosporium isolates on Phaseolus. Trans British Mycol Soc 74:335–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(80)80164-1
Dorling PR, Huxtable CR, Vogel P (1978) Lysosomal storage in Swainsona spp. toxicosis: an induced mannosidosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 4:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb00547.x
Dorling PR, Huxtable CR, Colegate SM (1980) Inhibition of lysosomal-mannosidase by swainsonine, an indolizidine alkaloid isolated from Swainsona canescens. Biochem J 191:649–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-0101(83)90163-0
Elbein AD, Solf R, Dorling PR, Vosbeck K (1981) Swainsonine: an inhibitor of glycoprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7393–7397
Gardner DR, Molyneux RJ, Ralphs MH (2001) Analysis of swainsonine: extraction methods, detection, and measurement in populations of locoweeds (Oxytropis spp.). Agric Food Chem 49:4573–4580. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010596p
Gu BQ, Duan DX, Cui ZL, R., C.G. (1990) Clinicopatholog of poisoning of Oxytropis kansuensis in goats. J Northwest Agric Univ 18:62–68
Hamaguchi J, Nakagawa H, Takahashi M, Kudo T, Kamiyama N, Sun B, Oshima T, Sato Y, Deguchi K, Todo S (2007) Swainsonine reduces 5-fluorouracil tolerance in the multistage resistance of colorectal cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer 6:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-6-58
Hino M, Nakayama O, Tsurumi Y, Adachi K, Shibata T, Terano H, Kohsaka M, Aoki H, Imanaka H (1985) Studies of an immunomodulator, swainsonine. I. enhancement of immune response by swainsonine in vitro. J Antibiot 38:926–935. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.38.926
James LF (1972) Syndromes of locoweed poisoning in livestock. Clin Toxicol 5:567–573
James LF, Hartley WJ, Kampen KRV (1981) Syndromes of Astragalus poisoning. J Am Vet Med Assoc 178:146–150
Li JR (2018) Identification of Alternaria Section Undifilum gansuence and detection of LAAO, KS genes in Alternaria Section Undifilum spp. Ningxia University, Ningxia
Li YZ (2007) Studies of yellow stunt and root rot of standing milk-vetch(Astragalus adsuegens Pall.). Lanzhou University, Lanzhou
Li YZ, Nan ZB (2007) A new species, Embellisia astragali sp. nov., causing standing milk-vetch disease in China. Mycologia 99:406–411. https://doi.org/10.3852/mycologia.99.3.406
Li YZ, Creamer R, Baucom D, Nan Z (2011) Pathogenic Embellisia astragali on Astragalus adsurgens is very closely related to locoweed endophyte. Phytopathology 101:S102–S103
Li YZ, Nan ZB, Zhang ZX, Liu YR, Gao XY, Zhen JX (2011) Distribution of damage caused by yellow stunt and rot root of Astragalus adsurgens in five north provinces of China. Acta Pratacul Sin 20:39–45
Liu H (2019) Study on the charcteristics of locoweed endophyte in 3 species of Oxytropis from seeds to plants. Lanzhou University, Lanzhou
Liu JL, Li YZ, Creamer R (2016) A re-examination of the taxonomic status of Embellisia astragali. Curr Microbiol 72:404–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0962-z
Lu H, Chen JP, Lu W, Ma Y, Zhao BY, Wang JY (2012) Isolation and identification of swainsonine-producting fungi found in locoweeds and their rhizosphere soil. Afr J Microbiol Res 6:4959–4969. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.1572
Lu P (2007) Studies on correlated factors to swainsonine in three Oxytropis species in Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Inner Mongolia
Molyneux R, James L (1982) Loco intoxication: indolizidine alkaloids of spotted locoweed (Astragalus lentiginosus). Science 216:190–191. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1801763
Molyneux, R.J., James, L.F. 1991. Swainsonine, the locoweed toxin: analysis and distribution. In handbook of natural toxins toxicology of plant and fungal compounds. NewYork.
Noor AI, Neyaz M, Cook D, Creamer R (2020) Molecular characterization of a fungal ketide synthase gene among swainsonine-producing Alternaria species in the USA. Curr Microbiol 77:2554–2563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02111-2
Petrini O, Mu¨ller E, Luginbuhl M (1979) Pilze als Endophyten von gru¨ nen Pflanzen. Naturwissenschaften 66:262–263
Pryor BM, Creamer R, Shoemaker RA, McLain-Romero J, Hambleton S (2009) Undifilum, a new genus for endophytic Embellisia oxytropis and parasitic Helminthosporium bornmuelleri on legumes. Botany 87:178–194. https://doi.org/10.1139/B08-130
Ralphs MH, Creamer R, Baucom D, Gardner DR, Welsh SL, Graham JD, Hart C, Cook D, Stegelmeier BL (2008) Relationship between the endophyte Embellisia spp. and the toxic alkaloid swainsonine in major locoweed species (Astragalus and Oxytropis). J Ecol 34:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-007-9399-6
Santos FM, Latorre AO, Hueza IM, Sanches DS, Lippi LL, Gardner DR, Spinosa HS (2011) Increased antitumor efficacy by the combined administration of swainsonine and cisplatin in vivo. Phytomedicine Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol 18:1096–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2011.06.005
Smith GS, Allred KW, Kiehl DE (1992) Swainsonine content of New Mexican locoweeds. J Anim Sci 43:405–407
Stegelmeier BL, James LF, Panter KE, Gardner DR, Pfister JA, Ralphs MH, Molyneux RJ (1999) Dose response of sheep poisoned with locoweed (Oxytropis Sericea). J Vet Diagn Invest 11:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063879901100510
Sun QZ, Gui R, Na RS, Na DMD, Zhai ZH (1999) Study on productivity of Astragalus adsurgens Pall. with different growth periods. Grassland China 5:29–30
Wang BZ, Han XG, Liu YJ, Zhang YM (2015) Effects of salicylic acid on salt tolerance of Astragalus adsurgens Pall.seedings. Hubei Agric Sci 54:4525–4528
Wang S, Wu S, Chen GY, Hu JJ, Zhang L, Ma CH (2012) Determination of coumarin in serum of rabbits by α- mannose enzyme. China Herbiv Sci 32:41–45
Wang S, Zhang L, Chen SY, Wu S, Ma C (2012) Effects of sawainsonine on the antioxydic function of liver in mice. Xingjiang Agric Sci 49:2304–2309
Wees S, Chang HS, Zhu T, Glazebrook J (2003) Characterization of the early response of Arabidopsis to Alternaria brassicicola infection using expression profiling. Plant Physiol 132:606–617. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.022186
Williams MC, James LF (1975) Toxicity of nitro-containing Astragalus to sheep and chicks. J Range Manag 28:260–263. https://doi.org/10.2307/3897770
Woudenberg JHC, Groenewald JZ, Binder M, Crous PW (2013) Alternaria redefined. Stud Mycol 75:171–212. https://doi.org/10.3114/sim0015
Xu N (2017) Study on toxic substance of Astragalus adsurgens infected by Alternaria gansuense. Lanzhou University, Lanzhou
Yu YT (2006) Studies on the toxicity and major cheminal constitutients of Oxytropis serioopetela Yang Ling. North West Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang
Yu YT, Li JR, Zhao QM, He SH, Chen J, Yang Q, Mao YN (2018) Isolation and Identification of swainsonine-producing fungi from Astragalus adsurgens Pall. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica 8:1770–1780
Zeng CY (2016) Study on the resistance mechanism of nine Astragalus adsurgens varieties to yellow stunt root and rot and comprehensive evaluation for germplasm characteristics. Lanzhou University, Lanzhou
Zhang JJ, Han M, Wang Y, Bai Y (2014) Effect of swainsonine of Oxytropis glabra DC. on α-mannosidase gene relative expression in mouse liver. Chin Anim Husb Veterinary Med 41:50–54
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (32061123004), National Key R & D Program of China (2022YFD1401103), National Forestry and Grassland Administration (20220104) and China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-34).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and Y-ZL designed and performed the experiments. MS analyzed the data. Y-ZL conceived and supervised the project. MS and Y-ZL wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, M., Li, YZ. Alternaria gansuense, a Plant Systematic Fungal Pathogen Producing Swainsonine in Vivo and in Vitro. Curr Microbiol 80, 232 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03341-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03341-w