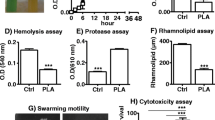
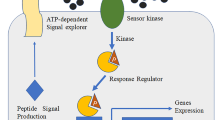
Abstract
In recent years, the occurrence of peritoneal dialysis (PD)-associated peritonitis (PDAP) with Escherichia coli infection has gradually increased. The presence of quorum sensing (QS) among bacteria facilitates the expansion of antibiotic resistance. Brominated furanone (BMF), a halogenated furanone compound isolated from macroalgae, is a new type of quorum-sensing inhibitor that can inhibit bacterial quorum sensing and reduce bacterial resistance. In this study, we established an in vitro peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis biofilm model. After intervention with BMF, the biofilm was destroyed, as shown by scanning electron microscopy, and the number of viable bacteria was reduced. Crystal violet semiquantitative determination showed that biofilm absorption significantly decreased, and RT–PCR showed that luxS expression was downregulated after drug intervention. Therefore, we propose that BMF can effectively inhibit E. coli QS by disrupting the bacterial biofilm and downregulating QS gene expression to reduce the bacterial resistance, providing a direction for the development of novel antibacterial drugs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang YN et al (2019) Chronic kidney disease: biomarker diagnosis to therapeutic targets. Clin Chimica Acta 499:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2019.08.030
Szeto CC, Li PK (2019) Peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 14(7):1100–1105. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.14631218
Zeng Y, Jiang L, Lu Y, Wang Z, Song K, Shen H, Feng S (2021) Peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by gram-negative organisms: ten-years experience in a single center. Ren Fail 43(1):993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2021.1939050
An YL, Ooi GS, Vaithilingam I (2021) Factors predicting clinical outcomes of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis—a single centre study. Med J Malaysia 76(3):382–389
Christaki E, Marcou M, Tofarides A (2020) Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J Mol Evol 88(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-019-09914-3
Azimi S, Klementiev AD, Whiteley M et al (2020) Bacterial quorum sensing during infection. Annu Rev Microbiol 8(74):201–219. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-032020-093845
Azam MW, Khan AU (2019) Updates on the pathogenicity status of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Drug Discov Today 24(1):350–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2018.07.003
Xu G (2020) Evolution of LuxR solos in bacterial communication: receptors and signals. Biotech Lett 42(2):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02763-6
Wang Y, Liu B, Grenier D, Yi L (2019) Regulatory Mechanisms of the LuxS/AI-2 system and bacterial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63(10):e01186-e1219. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01186-19
Torres-Cerna CE, Morales JA, Hernandez-Vargas EA (2019) Modeling quorum sensing dynamics and interference on Escherichia coli[J]. Front Microbiol 10:1835. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01835
Quan Y et al (2017) Regulation of bacteria population behaviors by AI-2 “consumer cells” and “supplier cells.” BMC Microbiol 17(1):198. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-017-1107-2
Proctor CR, McCarron PA, Ternan NG (2020) Furanone quorum-sensing inhibitors with potential as novel therapeutics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 69(2):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.001144
Vinothkannan R, Tamizh MM, Raj CD et al (2018) Fructose furoic acid ester: an effective quorum sensing inhibitor against uropathogenic Escherichia coli[J]. Bioorg Chem 79:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.05.009
He Z, Kong X, Shao T et al (2019) Alterations of the gut microbiota associated with promoting efficacy of prednisone by bromofuranone in MRL/lpr mice[J]. Front Microbiol 10:978. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00978
Han T, Li Y, Shan Q, Liang W, Hao W, Li Y, Tan X, Gu J (2017) Characterization of S-adenosylhomocysteine/Methylthioadenosine nucleosidase on secretion of AI-2 and biofilm formation of Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog 108:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.05.015
Husain A, Alam MM, Shaharyar M et al (2010) Antimicrobial activities of some synthetic butenolides and their pyrrolone derivatives[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 25(1):54–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756360902940860
Horký P, Voráčová M, Konečná K, Sedlák D, Bartůněk P, Vacek J, Kuneš J, Pour M (2018) Nontoxic combretafuranone analogues with high in vitro antibacterial activity. Eur J Med Chem 143:843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.078
Markus V, Golberg K, Teralı K, Ozer N, Kramarsky-Winter E, Marks RS, Kushmaro A (2021) Assessing the molecular targets and mode of action of furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Molecules 26(6):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061620
Chang Y, Wang PC et al (2019) Design, synthesis and evaluation of halogenated furanone derivatives as quorum sensing inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Pharm Sci 140:105058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105058
Sharafutdinov IS, Ozhegov GD et al (2020) Increasing susceptibility of drug-resistant candida albicans to fluconazole and terbinafine by 2(5H)-Furanone derivative. Molecules 25(3):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030642
Sharafutdinov IS, Trizna EY et al (2017) Antimicrobial effects of sulfonyl derivative of 2(5H)-furanone against planktonic and biofilm associated methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 8:2246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02246
Cheng Y, Zhao X, Liu X, Sun W, Ren H, Gao B, Wu J (2015) Antibacterial activity and biological performance of a novel antibacterial coating containing a halogenated furanone compound loaded poly(L-lactic acid) nanoparticles on microarc-oxidized titanium. Int J Nanomedicine 10:727–737. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S75706
Park JS, Ryu EJ, Li L, Choi BK, Kim BM (2017) New bicyclic brominated furanones as potent autoinducer-2 quorum-sensing inhibitors against bacterial biofilm formation. Eur J Med Chem 137:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.05.037
Husain A, Khan SA, Iram F et al (2019) Insights into the chemistry and therapeutic potential of furanones: a versatile pharmacophore[J]. Eur J Med Chem 171:66–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.021
Teren M, Turonova Michova H, Vondrakova L, Demnerova K (2018) Molecules Autoinducer 2 and cjA and Their Impact on gene expression in Campylobacter jejuni. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 28(5):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495411
Ren D, Bedzyk LA, Ye RW, Thomas SM, Wood TK (2004) Differential gene expression shows natural brominated furanones interfere with the autoinducer-2 bacterial signaling system of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 88(5):630–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20259
Wang Y, Wang Y, Sun L, Grenier D, Yi L (2018) The LuxS/AI-2 system of Streptococcus suis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(17):7231–7238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9170-7
Li T, HU SM, et al (2020) The marine-derived furanone reduces intracellular lipid accumulation in vitro by targeting LXRα and PPARα[J]. J Cell Mol Med 24(6):3384–3398. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15012
Cheng Y et al (2021) Long-term antibacterial activity of a composite coating on titanium for dental implant application. J Biomater Appl 35(6):643–654. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328220963934
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Han Jiahui at The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University for his help in analyzing the data. Thanks to teacher Zhen from Guangxi Medical University for helping us with the electron microscope.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Fund of Guangxi, P.R (2018GXNSFAA050084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Wang designed and organized the study and revised the manuscript. Dr. Li and Dr. Wei established the in vitro static biofilm model, detected carrier biofilms by SEM, identified biofilms by crystal violet staining, detected luxS gene expression by RT–PCR, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. Dr. Song and Dr. Li critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no confict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University[Approval Number: NO.2022-KY-E-(059)], Nanning, China.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wei, X., Song, Y. et al. In Vitro Study of the Effect of Inhibition of Quorum Sensing by Brominated Furanone on Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis Associated with Escherichia Coli Infection. Curr Microbiol 79, 337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-03040-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-03040-y