Abstract
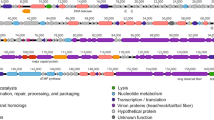
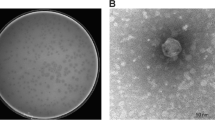
Phage therapy is an alternative approach to overcome the problem of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Here, a novel bacteriophage AhyVDH1, which infects Aeromonas hydrophila 4572, was isolated and its morphology, one-step growth curve, lytic activity, stability under various conditions, and genome were investigated. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that AhyVDH1 has an icosahedral head 49 nm in diameter and a contractile tail 127 nm in length, suggesting that it belongs to the family Myoviridae. AhyVDH1 showed strong adsorption to the surface of A. hydrophila 4572 (90% in 10 min). The latent period of AhyVDH1 was shown to be 50 min, and the burst size was 274 plaque-forming unit/infected cell. AhyVDH1 was stable at 30 °C for 1 h and lost infectivity after20 min of heating at 60 °C. Infectivity remained unaffected at pH 6–7 for 1 h, while the bacteriophage was inactivated at pH < 4 or > 11. AhyVDH1 has a 39,175-bp genome, with a 58% G + C content and 59 open reading frames. BLAST analysis indicated that the genome sequence of phage AhyVDH1 was related to that of Aeromonas phage Ahp2. Both time and MOI-dependent in vitro A. hydrophila growth inhibition were observed with AhyVDH1.Re-growth of the host bacteria appeared about 12 h after treatment, suggesting its potential therapeutic value in treating A. hydrophila infections, but phage cocktails should be developed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batra P, Mathur P, Misra MC (2016) Aeromonas spp.: an emerging nosocomial pathogen. J Lab Phys 8(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2727.176234
Danaher PJ, Mueller WP (2011) Aeromonas hydrophilaseptic arthritis. Mil Med 176(12):1444–1446. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-11-00211
Lai CC, Shiao CC, Lu GD, Ding LW (2007) Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria bacteremia: rare pathogens of infection in a burn patient. Burns 33(2):255–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2006.06.003
Liakopoulos V, Arampatzis S, KourtiP TT, Zarogiannis S, Eleftheriadis T et al (2011) Aeromonas hydrophila as a causative organism in peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis: case report and review of the literature. Clin Nephrol 75:65–68. https://doi.org/10.2379/CNP75065
Joseph SW, Carnahan A (1994) The isolation, identification, and systematics of the Motile Aeromonas species. Annu Rev Fish Dis 4:315–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-8030(94)90033-7
Wang JB, Lin NT, Tseng YH, Weng SF (2016) Genomic characterization of the novel Aeromonas hydrophilaphage Ahp1 suggests the derivation of a new subgroup from phiKMV-Like family. PLoS ONE 11(9):e0162060. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162060
Jun JW, Kim JH, Shin SP, Han JE, Chai JY, Park SC (2013) Protective effects of the Aeromonas phages pAh1-C and pAh6-C against mass mortality of the cyprinid loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) caused by Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 416–417:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.09.045
Huang C, Shi J, Ma W, Li Z, Wang J, Li J, Wang X (2018) Isolation, characterization, and application of a novel specific Salmonella bacteriophage in different food matrices. Food Res Int 111:631–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.071
Chen L, Yuan S, Liu Q, Mai G, Yang J, Deng D, Zhang B, Liu C, Ma Y (2018) In vitro design and evaluation of phage cocktails against Aeromonas salmonicida. Front Microbiol 9:1476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01476
Easwaran M, Dananjaya SHS, Park SC, Lee J, Shin HJ, De Zoysa M (2017) Characterization of bacteriophage pAh-1 and its protective effects on experimental infection of Aeromonas hydrophila in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Fish Dis 40(6):841–846. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12536
Hoang AH, Tran TTX, Le PN, Dang THO (2019) Selection of phages to control Aeromonas hydrophila– an infectious agent in striped catfish. Biocontrol Sci 24(1):23–28. https://doi.org/10.4265/bio.24.23
Chandrarathna HPSU, Nikapitiya C, Dananjaya SHS, De Silva BCJ, Heo G-J, De Zoysa M, Lee J (2020) Isolation and characterization of phage AHP-1 and its combined effect with chloramphenicol to control Aeromonas hydrophila. Braz J Microbiol 51(1):409–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00178-z
Kabwe M, Brown T, Speirs L, Ku H, Leach M, Chan HT, Petrovski S, Lock P, Tucci J (2020) Novel bacteriophages capable of disrupting biofilms from clinical strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. Front Microbiol 11:194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00194
Akmal M, Rahimi-Midani A, Hafeez-ur-Rehman M, Hussain A, Choi T-J (2020) Isolation, characterization, and application of a bacteriophage infecting the fish pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila. Pathogens 9(3):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9030215
Bai M, Cheng YH, Sun XQ, Wang ZY, Wang YX, Cui XL, Xiao W (2019) Nine novel phages from a plateau lake in Southwest China: insights into Aeromonas phage diversity. Viruses 11(7):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070615
Zhang S, Fan C, Xia Y, Li M, Wang Y, Cui X, Xiao W (2019) Characterization of a novel bacteriophage specific to Exiguobacterium indicum isolated from a plateau eutrophic lake. J Basic Microbiol 59(2):206–214. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201800184
Eisenstark A (1967) Bacteriophage techniques. In: Maramorsch K, Koprowski H (eds) Methods in virology. Academic Press, New York, pp 449–524
Stenholm AR, Dalsgaard I, Middelboe M (2008) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages infecting the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(13):4070–4078. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00428-08
Fu CQ, Zhao Q, Li ZY, Wang YX, Zhang SY, Lai YH, Xiao W, Cui XL (2016) A novel Halomonas ventosae-specific virulent halovirus isolated from the Qiaohou salt mine in Yunnan, Southwest China. Extremophiles 20(1):101–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0802-x
Lu Z, Breidt F, Fleming HP et al (2003) Isolation and characterization of a Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriophage, ΦJL-1, from a cucumber fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 84(2):225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00111-9
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
John B, Alexandre L, Mark B (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29(12):2607–2618. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.12.2607
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Laslett D, Canback B (2004) ARAGORN, a program for the detection of transfer RNA and transfer-messenger RNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh152
Sudhir K, Glen S, Koichiro T (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27(7):1009–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Muturi P, Yu J, Maina AN, Kariuki S, Mwaura FB, Wei H (2019) Bacteriophages isolated in China for the control of Pectobacterium carotovorum causing potato soft rot in Kenya. Virol Sin 34(3):287–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-019-00091-7
Rodriguez I, Novoa B, Figueras A (2008) Immune response of zebrafish (Danio rerio) against a newly isolated bacterial pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25(3):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.05.002
Lee SW, Wendy W (2017) Antibiotic and heavy metal resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila and Edwardsiella tarda isolated from red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) coinfected with motile aeromonas septicemia and edwardsiellosis. Vet World 10(7):803–807. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2017.803-807
Yang Y, Miao P, Li H, Tan S, Yu H, Yu H (2017) Antibiotic susceptibility and molecular characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila from grass carp. J Food Saf 38(1):e12393. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12393
Jun JW, Kim JH, Gomez D, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Park SC (2010) Occurrence of tetracycline-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Korean cyprinid loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). African J Microbiol Res 4(9):849–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2009.12.017
Yuan SJ, Chen L, Liu Q, Zhou Y, Yang JF, Deng D et al (2018) Characterization and genomic analyses of Aeromonas hydrophila phages AhSzq-1 and AhSzw-1, isolates representing new species within the T5virus genus. Arch Virol 163(7):1985–1988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3805-y
El-Araby DA, El-Didamony G, Megahed MTH (2016) New approach to use phage therapy against Aeromonas hydrophilainduced motile aeromonas septicemia in Nile Tilapia. J Mar Sci Res Dev 6(3):194. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9910.1000194
Kim JH, Son JS, Choi YJ, Choresca CH, Shin SP, Han JE et al (2012) Isolation and characterization of a lytic Myoviridae bacteriophage PAS-1 with broad infectivity in Aeromonas salmonicida. Curr Microbiol 64(5):418–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-012-0091-x
Housby JN, Mann NH (2009) Phage therapy. Drug Discov Today 14:536–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2009.03.006
Lu WK, Yu LX, Ou XK, Li FR (2017) Relationship between occurrence frequency of cyanobacteria bloom and meteorological factors in Lake Dianchi. J Lake Sci 29:534–545. https://doi.org/10.18307/2017.0302
Altamirano FLG, Barr JJ (2019) Phage therapy in the postantibiotic era. Clin Microbiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00066-18
Vincent AT, Paquet VE, Bernatchez A, Tremblay DM, Moineau S, Charette SJ (2017) Characterization and diversity of phages infecting Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. Sci Rep 7(1):7054. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07401-7
Luo X, Liao G, Liu C, Jiang X, Lin M, Zhao C, Tao J, Huang Z (2018) Characterization of bacteriophage HN48 and its protective effects in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus against Streptococcus agalactiae infections. J Fish Dis 41(10):1477–1484. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12838
Le TS, Nguyen TH, Vo HP, Doan VC, Nguyen HL, Tran MT, Tran TT, Southgate PC, Kurtböke Dİ (2018) Protective effects of bacteriophages against Aeromonas hydrophila causing Motile Aeromonas Septicemia (MAS) in striped catfish. Antibiotics 7(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics701001
Funding
This funding was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Nos. 31660042, 31660001, 31660089, 32071570] and Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department [Grant No. 2018IA100].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Gao, D., Xia, Y. et al. Characterization of Novel Bacteriophage AhyVDH1 and Its Lytic Activity Against Aeromonas hydrophila. Curr Microbiol 78, 329–337 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02279-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02279-7