Abstract
Purpose
Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4), a member of the polo-like kinase family, plays several important roles in mitotic regulation, including centrosome duplication, spindle formation, and cytokinesis. PLK4 overexpression is frequently detected in many human cancers, including ovarian cancer, and the inhibition of PLK4 activity results in cancer cell mitotic arrest and apoptosis. Therefore, PLK4 might be a valid therapeutic target for antitumor therapy. In the present study, we aimed to determine if YLZ-F5, a potent small-molecule inhibitor of PLK4, inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth.
Methods and results
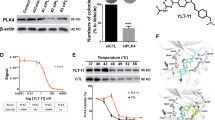
MTT assay showed that YLZ-F5 inhibited ovarian cancer cell proliferation in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. The results of colony formation assays were consistent with those of the MTT assay results. In addition, YLZ-F5 induced ovarian cancer cell apoptosis that was associated with activation of caspase-3/caspase-9. Moreover, YLZ-F5 caused aberrant in centriole duplication that was associated with the inhibition of PLK4 phosphorylation. Notably, we showed that YLZ-F5 promoted the accumulation of ovarian cancer cells with mitotic defects (> 4 N DNA content) in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, YLZ-F5 markedly inhibited the migration of A2780 cells.
Conclusion
Taken together, these findings suggest that YLZ-F5 is a potential drug candidate for human ovarian cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PLK4:
-
Polo-like kinase 4
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-di-phenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- ESI–MS:
-
Electrospray ionisation-mass spectrometry
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- DAPI:
-
2-(4-Amidinophenyl)-6-indolecarbamidine dihydrochloride
- 7-AAD:
-
7-Aminoactinomycin D
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- GEPIA:
-
Gene expression profiling interactive analyze
- FIGO:
-
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Cress RD, Chen YS, Morris CR, Petersen M, Leiserowitz GS (2015) Characteristics of long-term survivors of epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol 126(3):491. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000000981
Lheureux S, Gourley C, Vergote I, Oza AM (2019) Epithelial ovarian cancer. Lancet 393(10177):1240–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32552-2
Matulonis UA, Sood AK, Fallowfield L, Howitt BE, Sehouli J, Karlan BY (2016) Ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16061. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.61
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N (2011) Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 474(7353):609–615. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10166
de Carcer G, Manning G, Malumbres M (2011) From Plk1 to Plk5: functional evolution of polo-like kinases. Cell Cycle 10(14):2255–2262. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.10.14.16494
Barr FA, Silljé HH, Nigg EA (2004) Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(6):429. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1401
Archambault V, Glover DM (2009) Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(4):265. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2675
Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J, Miyakawa I (2005) Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene 24(2):287–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208272
Lens SM, Voest EE, Medema RH (2010) Shared and separate functions of polo-like kinases and aurora kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10(12):825. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2964
Archambault V, Lepine G, Kachaner D (2015) Understanding the Polo Kinase machine. Oncogene 34(37):4799–4807. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.451
Strebhardt K (2010) Multifaceted polo-like kinases: drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):643. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3184
Leung GC, Hudson JW, Kozarova A, Davidson A, Dennis JW, Sicheri F (2002) The Sak polo-box comprises a structural domain sufficient for mitotic subcellular localization. Nat Struct Biol 9(10):719–724. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb848
Sillibourne JE, Bornens M (2010) Polo-like kinase 4: the odd one out of the family. Cell Div 5(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-1028-5-25
Habedanck R, Stierhof Y-D, Wilkinson CJ, Nigg EA (2005) The Polo kinase Plk4 functions in centriole duplication. Nat Cell Biol 7(11):1140. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1320
Holland AJ, Lan W, Niessen S, Hoover H, Cleveland DW (2010) Polo-like kinase 4 kinase activity limits centrosome overduplication by autoregulating its own stability. J Cell Biol 188(2):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200911102
Takai N, Miyazaki T, Fujisawa K, Nasu K, Hamanaka R, Miyakawa I (2001) Expression of polo-like kinase in ovarian cancer is associated with histological grade and clinical stage. Cancer Lett 164(1):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00703-5
Weichert W, Denkert C, Schmidt M, Gekeler V, Wolf G, Kobel M, Dietel M, Hauptmann S (2004) Polo-like kinase isoform expression is a prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma. Br J Cancer 90(4):815–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601610
He Y, Wang H, Yan M, Yang X, Shen R, Ni X, Chen X, Yang P, Chen M, Lu X et al (2018) High LIN28A and PLK4 coexpression is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Med Rep 18(6):5327–5336. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9562
Liu Z, Lei Q, Wei W, Xiong L, Shi Y, Yan G, Gao C, Ye T, Wang N, Yu L (2017) Synthesis and biological evaluation of (E)-4-(3-arylvinyl-1H-indazol-6-yl)pyrimidin-2-amine derivatives as PLK4 inhibitors for the treatment of breast cancer. RSC Adv 7(44):27737–27746. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02518A
Lei Q, Xiong L, Xia Y, Feng Z, Gao T, Wei W, Song X, Ye T, Wang N, Peng C et al (2018) YLT-11, a novel PLK4 inhibitor, inhibits human breast cancer growth via inducing maladjusted centriole duplication and mitotic defect. Cell Death Dis 9(11):1066. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1071-2
Holland AJ, Cleveland DW (2014) Polo-like kinase 4 inhibition: a strategy for cancer therapy? Cancer Cell 26(2):151–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.017
Mason JM, Lin DC, Wei X, Che Y, Yao Y, Kiarash R, Cescon DW, Fletcher GC, Awrey DE, Bray MR et al (2014) Functional characterization of CFI-400945, a polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor, as a potential anticancer agent. Cancer Cell 26(2):163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.006
Nigg EA, Raff JW (2009) Centrioles, centrosomes, and cilia in health and disease. Cell 139(4):663–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.036
Zhao Y, Wang X (2019) PLK4: a promising target for cancer therapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145(10):2413–2422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02994-0
Kazazian K, Go C, Wu H, Brashavitskaya O, Xu R, Dennis JW, Gingras A-C, Swallow CJ (2017) Plk4 promotes cancer invasion and metastasis through Arp2/3 complex regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Can Res 77(2):434–447. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2060
Tian X, Zhou D, Chen L, Tian Y, Zhong B, Cao Y, Dong Q, Zhou M, Yan J, Wang Y (2018) Polo-like kinase 4 mediates epithelial–mesenchymal transition in neuroblastoma via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 9(2):54. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0088-2
Press MF, Xie B, Davenport S, Zhou Y, Guzman R, Nolan GP, O'Brien N, Palazzolo M, Mak TW, Brugge JS et al (2019) Role for polo-like kinase 4 in mediation of cytokinesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(23):11309–11318. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818820116
Kawakami M, Mustachio LM, Zheng L, Chen Y, Rodriguez-Canales J, Mino B, Kurie JM, Roszik J, Villalobos PA, Thu KL et al (2018) Polo-like kinase 4 inhibition produces polyploidy and apoptotic death of lung cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(8):1913–1918. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719760115
Liao Z, Zhang H, Fan P, Huang Q, Dong K, Qi Y, Song J, Chen L, Liang H, Chen X, Zhang Z, Zhang B (2019) High PLK4 expression promotes tumor progression and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol 54(2):479–490. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4659
Kazazian K, Go C, Wu H, Brashavitskaya O, Xu R, Dennis JW, Gingras AC, Swallow CJ (2017) Plk4 promotes cancer invasion and metastasis through Arp2/3 complex regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Res 77(2):434–447. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2060
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [Grant number 2019M652543] and Sichuan Provincial Science and technology program for Key research and development, China (No. 2018SZ0007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Liu, Z., Qu, Y. et al. YLZ-F5, a novel polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor, inhibits human ovarian cancer cell growth by inducing apoptosis and mitotic defects. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 86, 33–43 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04098-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04098-w