Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the expression of ser-miRNAs at different periods during treatment and analyze their relationship with therapeutic response and prognosis in HER2-positive breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with trastuzumab (NCCT).
Methods
Venous blood was drawn from patients at different periods during NCCT. The expression of ser-miRNAs was assessed by qRT-PCR and their relation to treatment response and survival was analyzed.
Results
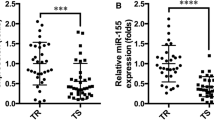
The results showed the expression of miR-10b, -21, -34a, -125b, -145, -155, and -373 in patients before the start of treatment was significantly higher, ser-miR-210 was lower, and ser-miR-122 was comparable to the levels in healthy controls. Changes in ser-miR-21 levels during NCCT were significantly correlated to clinical response and survival and, however, were not associated with pathology response. The expression levels of ser-miR-21 were decreased from the start of NCCT to the end of the second cycle and from the start to the end of NCCT in clinical responders; however, there was no significant difference in non-responders. The patients with decreased ser-miR-21 expression from the start to the end of the second cycle and from the start to the end of NCCT had better overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) than those with elevated ser-miR-21 expression.
Conclusion
These results showed that changes in ser-miR-21 levels were significantly related to NCCT clinical response and prognosis. Ser-miR-21 may serve as a non-invasive biomarker to predict NCCT response in HER2-positive breast cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Du F, Yuan P, Zhao ZT, Yang Z, Wang T, Zhao JD, Luo Y, Ma F, Wang JY, Fan Y, Cai RG, Zhang P, Li Q, Song YM, Xu BH (2016) A miRNA-based signature predicts development of disease recurrence in HER2 positive breast cancer after adjuvant trastuzumab-based treatment. Sci Rep 6:33825. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33825
Parra-Palau JL, Morancho B, Peg V, Escorihuela M, Scaltriti M, Vicario R, Zacarias-Fluck M, Pedersen K, Pandiella A, Nuciforo P, Serra V, Cortés J, Baselga J, Perou CM, Prat A, Rubio IT, Arribas J (2014) Effect of p95HER2/611CTF on the response to trastuzumab and chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/dju291
De Mattos-Arruda L, Bottai G, Nuciforo PG, Di Tommaso L, Giovannetti E, Peg V, Losurdo A, Pérez-Garcia J, Masci G, Corsi F, Cortés J, Seoane J, Calin GA, Santarpia L (2015) MicroRNA-21 links epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammatory signals to conferresistance to neoadjuvant trastuzumab and chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancerpatients. Oncotarget 6:37269–37280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5495
Jung EJ, Santarpia L, Kim J, Esteva FJ, Moretti E, Buzdar AU, Di Leo A, Le XF, Bast RC Jr, Park ST, Pusztai L, Calin GA (2012) Plasma microRNA 210 levels correlate with sensitivity to trastuzumab and tumor presence inbreast cancer patients. Cancer 118:2603–2614. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26565
Bai WD, Ye XM, Zhang MY, Zhu HY, Xi WJ, Huang X, Zhao J, Gu B, Zheng GX, Yang AG, Jia LT (2014) MiR-200c suppresses TGF-beta signaling and counteracts trastuzumab resistance and metastasis by targeting ZNF217 and ZEB1 in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 135:1356–1368. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28782
Gong C, Yao Y, Wang Y, Liu B, Wu W, Chen J, Su F, Yao H, Song E (2011) Up-regulation of miR-21 mediates resistance to trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. J Biol Chem 286:19127–19137. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m110.216887
Ye X, Bai W, Zhu H, Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang L, Yang A, Zhao J, Jia L (2014) MiR-221 promotes trastuzumab-resistance and metastasis in HER2-positive breast cancers by targeting PTEN. BMB Rep 47:268–273
Joyce DP, Kerin MJ, Dwyer RM (2016) Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast cancer. Int J Cancer 139:1443–1448. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30179
Zhang L, Xu Y, Jin X, Wang Z, Wu Y, Zhao D, Chen G, Li D, Wang X, Cao H, Xie Y, Liang Z (2015) A circulating miRNA signature as a diagnostic biomarker for non-invasive early detection of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 154:423–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3591-0
Li Q, Liu M, Ma F, Luo Y, Cai R, Wang L, Xu N, Xu B (2014) Circulating miR-19a and miR-205 in serum may predict the sensitivity of luminal A subtype of breast cancerpatients to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with epirubicin plus paclitaxel. PLoS One 9:e104870. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104870
Al-Khanbashi M, Caramuta S, Alajmi AM, Al-Haddabi I, Al-Riyami M, Lui WO, Al-Moundhri MS (2016) Tissue and serum miRNA profile in locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) in response to neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) treatment. PLoS One 11:e0152032. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152032
Müller V, Gade S, Steinbach B, Loibl S, von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Schwedler K, Lübbe K, Schem C, Fasching PA, Mau C, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H (2014) Changes in serum levels of miR-21, miR-210, and miR-373 in HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy: a translational research project within the Geparquinto trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 147:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3079-3
Yadav P, Mirza M, Nandi K, Jain SK, Kaza RC, Khurana N, Ray PC, Saxena A (2016) Serum microRNA-21 expression as a prognostic and therapeutic biomarker for breast cancer patients. Tumour Biol 37:15275–15282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5361-y
Yoruker EE, Aydoğan F, Gezer U, Saip P, Dalay N (2015) Analysis of circulating microRNAs during adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with luminal A breast cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 3:954–958. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2015.567
Wu X, Somlo G, Yu Y, Palomares MR, Li AX, Zhou W, Chow A, Yen Y, Rossi JJ, Gao H, Wang J, Yuan YC, Frankel P, Li S, Ashing-Giwa KT, Sun G, Wang Y, Smith R, Robinson K, Ren X, Wang SE (2012) De novo sequencing of circulating miRNAs identifies novel markers predicting clinical outcome of locallyadvanced breast cancer. J Transl Med 10:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-42
Wang H, Tan G, Dong L, Cheng L, Li K, Wang Z, Luo H (2012) Circulating miR-125b as a marker predicting chemoresistance in breast cancer. PLoS One 7:e34210. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034210
Sun Y, Wang M, Lin G, Sun S, Li X, Qi J, Li J (2012) Serum microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track disease in breast cancer. PLoS One 7:e47003. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047003
Liu B, Su F, Chen M, Li Y, Qi X, Xiao J, Li X, Liu X, Liang W, Zhang Y, Zhang J (2017) Serum miR-21 and miR-125b as markers predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy response and prognosis in stage II/III breast cancer. Hum Pathol 64:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.03.016
Liu B, Su F, Li Y, Qi X, Liu X, Liang W, You K, Zhang Y, Zhang J (2017) Changes of serum miR34a expression during neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict the treatment response and prognosis in stage II/III breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 88:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.133
Hu Z, Dong J, Wang LE, Ma H, Liu J, Zhao Y, Tang J, Chen X, Dai J, Wei Q, Zhang C, Shen H (2012) Serum microRNA profiling and breast cancer risk: the use of miR-484/191 as endogenous controls. Carcinogenesis 33:828–834. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs030
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Symmans WF, Peintinger F, Hatzis C, Rajan R, Kuerer H, Valero V, Assad L, Poniecka A, Hennessy B, Green M, Buzdar AU, Singletary SE, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2007) Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 25:4414–4422. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.10.6823
Fan C, Liu N (2019) Identification of dysregulated microRNAs associated with diagnosis and prognosis in triple–negative breast cancer: an in silico study. Oncol Rep 41:3313–3324. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7094
Shi M, Guo N, Falkenberg N, Anastasov N, Rappl K, Braselmann H, Auer G, Walch A, Huber M, Höfig I, Schmitt M, Höfler H, Atkinson MJ, Aubele M (2013) MiR-221/-222 differentiate prognostic groups in advanced breast cancers and influence cell invasion. Br J Cancer 109:2714–2723. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.625
Rexer BN, Arteaga CL (2012) Intrinsic and acquired resistance to HER2-targeted therapies in HER2 gene-amplified breast cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications. Crit Rev Oncog 17:1–16
Arteaga CL, Sliwkowski MX, Osborne CK, Perez EA, Puglisi F, Gianni L (2011) Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 9:16–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.177
Ohzawa H, Miki A, Teratani T, Shiba S, Sakuma Y, Nishimura W, Noda Y, Fukushima N, Fujii H, Hozumi Y, Mukai H, Yasuda Y (2017) Usefulness of miRNA profiles for predicting pathological responses to neoadjuvantchemotherapy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. Oncol Lett 13:1731–1740. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.5628
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, Mo Z, Bi X, Liu Z, Fan Y, Chen X, Wu C (2012) Re-expression of miR-21 contributes to migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell characteristics in MCF-7 cells. Mol Cell Biochem 363:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1195-5
Zhao D, Tu Y, Wan L, Bu L, Huang T, Sun X, Wang K, Shen B (2013) In vivo monitoring of angiogenesis inhibition via down-regulation of mir-21 in a VEGFR2-luc murine breast cancer model using bioluminescent imaging. PLoS One 8:e71472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1195-5
Lee JA, Lee HY, Lee ES, Kim I, Bae JW (2011) Prognostic implications of MicroRNA-21 overexpression in invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast. J Breast Cancer 14:269–275. https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2011.14.4.269
Zaman MS, Shahryari V, Deng G, Thamminana S, Saini S, Majid S, Chang I, Hirata H, Ueno K, Yamamura S, Singh K, Tanaka Y, Tabatabai ZL, Dahiya R (2012) Up-regulation of microRNA-21 correlates with lower kidney cancer survival. PLoS One 7:e31060. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031060
Silva-Santos RM, Costa-Pinheiro P, Luis A, Antunes L, Lobo F, Oliveira J, Henrique R, Jerónimo C (2013) MicroRNA profile: a promising ancillary tool for accurate renal cell tumour diagnosis. Br J Cancer 109:2646–2653. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.552
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J, Ford LP (2005) Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cellgrowth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1290–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki200
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K, Banham AH, Pezzella F, Boultwood J, Wainscoat JS, Hatton CS, Harris AL (2008) Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 141:672–675. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07077.x
Toraih EA, Mohammed EA, Farrag S, Ramsis N, Hosny S (2015) Pilot study of serum MicroRNA-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in egyptian breast cancer patients. Mol Diagn Ther 19:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-015-0143-6
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2016) The role of miR-126 in embryonic angiogenesis, adult vascular homeostasis, and vascular repair and its alterations in atherosclerotic disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 97:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.05.007
Wu K, Yang Y, Zhong Y, Ammar HM, Zhang P, Guo R, Liu H, Cheng C, Koroscil TM, Chen Y, Liu S, Bihl JC (2016) The effects of microvesicles on endothelial progenitor cells are compromised in type 2 diabetic patients via downregulation of the miR-126/VEGFR2 pathway. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 310:E828–E837. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00056.2016
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP, Novotny W (2004) Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1381
Acknowledgements
We thank International Science Editing (http://www.internationalscienceediting.com) for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 81372838 and 61801151); the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry; Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (Grant number H2018014); Regional collaborative innovative foundation of Tibetan medicine (Grant number 2018XTCX008); and Hei Long Jiang Postdoctoral Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Su, F., Lv, X. et al. Serum microRNA-21 predicted treatment outcome and survival in HER2-positive breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with trastuzumab. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 84, 1039–1049 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03937-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03937-9