Abstract
Cancer is a serious and life-eliminating disease. Majority of anticancer agents are non-selective. Along with the cancerous cells they also target the normal ones. An important aspect is to hit the developing mechanism of the tumor, which is highlighted by in silico drug designing. On the basis of novel molecular targets, in silico (computational approach) drug discovery has emerged as today’s need. Histone deacetylases are an important therapeutic target for many human cancers. The first and only approved (in 2006) histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) is Zolinza. Depending on the types of the histone deacetylase (HDAC) enzymes, discovery of type-specific inhibitors is important. With continued research and development, in near future HDACIs are likely to figure prominently in cancer treatment plans. This review presents the overview of HDACs, their role in cancer, their structural classes, activity, catalytic domain and the inhibitors of HDACs for cancer therapy. Also it helps in understanding the open directions in this area of research and highlights the importance of computational approaches in discovering specific drugs for cancer therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Q, Xu W (2005) Novel anticancer targets and drug discovery in post genomic age. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 5:53–63
Seddon BM, Workman P (2003) The role of functional and molecular imaging in cancer drug discovery and development. Br J Radiol 76:S128–S138
Sikora K, Advani S, Koroltchouk V, Magrath I, Levy L, Pinedo H, Schwartsmann G, Tattersall M, Yan S (1999) Essential drugs for cancer therapy: a World Health Organization consultation. Ann Oncol 10:385–390
Gelmon KA, Eisenhauer EA, Harris AL, Ratain MJ, Workman P (1999) Anticancer agents targeting signalling molecules and cancer cell environment: challenges for drug development. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1281–1287
Walkinshaw DR, Yang XJ (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as novel anticancer therapeutics. Curr Oncol 15:237–243
Chen JS, Faller DV, Spanjaard RA (2003) Short-chain fatty acid inhibitors of histone deacetylases: promising anticancer therapeutics. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 3:219–236
Marks P, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Miller T, Kelly WK (2001) Histone deacetylases and cancer: causes and therapies. Nat Rev Cancer 1:194–202
Kelly WK, Connor OAO, Marks PA (2002) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: from target to clinical trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 11:1695–1713
Marks PA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Rifkind RA (2001) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as new cancer drugs. Curr Opin Oncol 13:477–483
Marks PA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Rifkind RA (2001) Inhibitors of histone deacetylase are potentially effective anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 7:759–760
Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther MJ, Lazar MA, Klein PS (2001) Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogen. J Biol Chem 76:36734–36741
Meinke PT, Liberator P (2001) Histone deacetylase: a target for antiproliferative and antiprotozoal agents. Curr Med Chem 8:211–235
Juvale DC, Kulkarni VV, Deokar HS, Wagh NK, Padhye SB, Kulkarni VM (2006) 3D-QSAR of histone deacetylase inhibitors: hydroxamate analogues. Org Biomol Chem 4:2858–2868
Minucci S, Pelicci PG (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:38–51
Karagiannis TC, El-Osta A (2007) Will broad-spectrum histone deacetylase inhibitors be superseded by more specific compounds. Leukemia 21:61–65
Hideshima T, Bradner JE, Wong J, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Schreiber SL, Anderson KC (2005) Small-molecule inhibition of proteasome and aggresome function induces synergistic antitumor activity in multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8567–8572
Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ (1997) Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 389:251–260
Lenfant F, Mann RK, Thomsen B, Ling X, Grunstein M (1996) All four core histone N-termini contain sequences required for the repression of basal transcription in yeast. EMBO J 15:3974–3985
Kouraklis G, Misiakos EP, Theocharis S (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as a potential therapeutic agent for human cancer treatment. Target Oncol 1:34–41
Chen Y, Jiang YJ, Zhou JW, Yu QS, You QD (2008) Identification of ligand features essential for HDACs inhibitors by pharmacophore modeling. J Mol Graph Model 26:1160–1168
Cress WD, Seto E (2000) Histone deacetylases, transcriptional control, and cancer. J Cell Physiol 184:1e16
Strahl BD, Allis CD (2000) The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403:41e45
Tanner KG, Trievel RC, Kuo MH, Howard RM, Berger SL, Allis CD, Marmorstein R, Denu JM (1999) Catalytic mechanism and function of invariant glutamic acid 173 from the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 transcriptional coactivator. J Biol Chem 274:18157–18160
Gregory PD, Wagner K, Horz W (2001) Histone acetylation and chromatin remodeling. Exp Cell Res 265:195–202
Roth SY, Denu JM, Allis CD (2001) Histone acetyltransferases. Annu Rev Biochem 70:81–120
Pazin MJ, Kadonaga JT (1997) What’s up and down with histone deacetylation and transcription. Cell 89(3):325–328
Grunstein M (1997) Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389:349–352
Struhl K (1998) Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Genes Dev 12:599–606
Mahlknecht U, Hoelzer D (2000) Histone acetylation modifiers in the pathogenesis of malignant disease. Mol Med 6:623–644
Khochbin S, Verdel A, Lemercier C, Seigneurin-Berny D (2001) Functional significance of histone deacetylase diversity. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11:162–166
Lin HY, Chen CH, Lin SP, Weng JR, Chen CH (2006) Targeting histone deacetylase in cancer therapy. Med Res Rev 26(4):397–413
Blander G, Guarente L (2004) The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem 73:417–435
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, Chen D, Su F, Shiloh A, Guarente L, Gu W (2001) Negative control of p53 by Sir2 alpha promotes cell survival under stress. Cell 107(2):137–148
Park JH, Jung Y, Kim TY, Kim SG, Jong HS, Lee JW, Kim DK, Lee JS, Kim NK, Kim TY et al (2004) Class I histone deacetylase selective novel synthetic inhibitors potently inhibit human tumor proliferation. Clin Cancer Res 10:5271–5281
Zhu P, Huber E, Kiefer F, Gottlicher M (2004) Specific and redundant functions of histone deacetylases in regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Cycle 3:1240–1242
Zhang CL, McKinsey TA, Chang S, Antos CL, Hill JA, Olson EN (2002) Class II histone deacetylases act as signal-responsive repressors of cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 110:479–488
Inche A, La Thangue NB (2006) Chromatin control and cancer drug discovery: realising the promise. Drug Discov Today 11:97–109
Somoza JR, Skene RJ, Katz BA, Mol C, Ho JD, Jennings AJ, Luong C, Arvai A, Buggy JJ, Chi E, Tang J, Sang BC, Verner E, Wynands R, Leahy EM, Dougan DR, Snell G, Navre M, Knuth MW, Swanson RV, McRee DE, Tari LW (2004) Structural snapshots of human HDAC8 provide insights into the class I histone deacetylases structure. Structure 12:1325–1334
Vannini A, Volpari C, Filocamo G, Casavola EC, Brunetti M, Renzoni D, Chakravarty P, Paolini C, De Francesco R, Gallinari P, Steinkuhler C, Marco SD (2004) Crystal structure of a eukaryotic zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15064–15069
Chen Y, Li H, Tang W, Zhu C, Jiang Y, Zou J, Yu Q, You Q (2009) 3D-QSAR studies of HDACs inhibitors using pharmacophore-based alignment. Eur J Med Chem 44(7):2868–2876
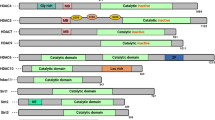
Zhang Y, Gilquin B, Khochbin S, Matthias P (2006) Two catalytic domains are required for protein deacetylation. J Biol Chem 281:2401–2404
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW (2006) Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:769–784
Lagger G, O’Carroll D, Rembold M, Khier H, Tischler J, Weitzer G, Schuettengruber B, Hauser C, Brunmeir R, Jenuwein T, Seiser C (2002) Essential function of histone deacetylase 1 in proliferation control and CDK inhibitor repression. EMBO J 21:2672–2681
Kim SH, Jeong JW, Park JA, Lee JW, Seo JH, Jung BK, Bae MK, Kim KW (2007) Regulation of the HIF-1a stability by histone deacetylases. Oncol Rep 17:647–651
Harms KL, Chen X (2007) Histone deacetylase 2 modulates p53 transcriptional activities through regulation of p53-DNA binding activity. Cancer Res 67:3145–3152
Trivedi CM, Luo Y, Yin Z, Zhang M, Zhu W, Wang T, Floss T, Goettlicher M, Noppinger PR, Wurst W, Ferrari VA, Abrams CS, Gruber PJ, Epstein JA (2007) Hdac2 regulates the cardiac hypertrophic response by modulating Gsk3h activity. Nat Med 13:324–331
Chang S, Young BD, Li S, Qi X, Richardson JA, Olson EN (2006) Histone deacetylase 7 maintains vascular integrity by repressing matrix metalloproteinase 10. Cell 126:321–334
Dokmanovic M, Clarke C, Marks PA (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview and perspectives. Mol Cancer Res 5(10):981–989
Riester D, Hildmann C, Grune wald S, Beckers T, Schwienhorst A (2007) Factors affecting the substrate specificity of histone deacetylases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:439–445
Marmorstein R (2001) Structure of histone acetyltransferases. J Mol Biol 311:433–444
Elaut G, Rogiers V, Vanhaecke T (2007) The pharmaceutical potential of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des 13:2584–2620
Sigalotti L, Fratta E, Coral S, Cortini E, Covre A, Nicolay HJ, Anzalone L, Pezzani L, Di Giacomo AM, Fonsatti E, Coalizzi F, Altomonte M, Calabro L, Maio M (2007) Epigenetic drugs as pleiotropic agents in cancer treatment: biomolecular aspects and clinical applications. J Cell Physiol 212:330–344
Garber K (2004) Purchase of Aton spotlights HDAC inhibitors. Nat Biotechnol 22:364–365
Fang JY (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibitors, anti-cancerous mechanism and therapy for gastrointestinal cancers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:988–994
Glaser KB, Staver MJ, Waring JF, Stender J, Ulrich RG, Davidsen SK (2003) Gene expression profiling of multiple histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors: defining a common gene set produced by HDAC inhibition in T24 and MDA carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther 2:151–163
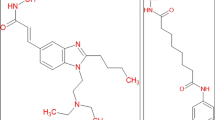
Miller TA, Witter DJ, Belvedere S (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem 46:5097–5116
Bi G, Jiang G (2006) The molecular mechanism of HDAC Inhibitors in anticancer effects. Cell Mol Immunol 3(4):285–290
Jung M, Brosch G, Kölle D, Scherf H, Gerhäuser C, Loid P (1999) Amide analogues of trichostatin A as inhibitors of histone deacetylase and inducers of terminal cell differentiation. J Med Chem 42:4669–4679
Grozinger CM, Schreiber SL (2002) Deacetylase enzymes: biological functions and the use of small-molecule inhibitors. Chem Biol 9:3–16
Yoshida M, Kijima M, Akita M, Beppu T (1990) Potent and specific inhibition of mammalian histone deacetylase both in vivo and in vitro by trichostatin A. J Biol Chem 265:17174–17179
Tsuji N, Kobayashi M, Nagashima K, Wakisaka Y, Koizumi K (1976) A new antifungal antibiotic, trichostatin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 29:1–6
Marks PA, Dokmanovic M (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: discovery and development as anticancer agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14:1497–1511
Wegener D, Hildmann C, Schwienhorst A (2003) Recent progress in the development of assays suited for histone deacetylase inhibitor screening. Mol Genet Metab 80:138–147
Khan N, Jeffers M, Kumar S, Hackett C, Boldog F, Khramtsov N, Qian X, Mills E, Berghs SC, Carey N, Finn PW, Collins LS, Tumber A, Ritchie JW, Jensen PB, Lichenstein HS, Sehested M (2007) Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small molecule HDAC inhibitors. Biochem J 409:581–589. doi:10.1042/BJ20070779
Maia A, Altucci L (2009) Epi-drugs to fight cancer: from chemistry to cancer treatment, the road ahead. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:199–213
Finnin MS, Donigian JR, Cohen A, Richon VM, Rifkind RA, Marks PA, Breslow R, Pavletich NP (1999) Structures of a histone deacetylase homologue bound to the TSA and SAHA inhibitors. Nature 401:188–193
Richon VM, Emiliani S, Verdin E, Webb Y, Breslow R, Rifkind RA, Marks PA (1998) A class of hybrid polar inducers of transformed cell differentiation inhibits histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3003–3007
Mai A, Massa S, Pezzi R, Simeoni S, Rotili D, Nebbioso A, Scognamiglio A, Altucci L, Loidl P, Brosch G (2005) Class II (IIa)-selective histone deacetylase inhibitors. 1. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel (aryloxopropenyl)pyrrolyl hydroxyamides. J Med Chem 48:3344–3353
Paris M, Porcelloni M, Binaschi M, Fattori D (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: from bench to clinic. J Med Chem 51:1505–1529
Kelly WK, Marks PA (2005) Drug insight: histone deacetylase inhibitors—development of the new targeted anticancer agent suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2:150–157
Qian X, Ara G, Mills E, LaRochelle WJ, Lichenstein HS, Jeffers M (2008) Activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat (PXD101) in preclinical models of prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 122:1400–1410
Suzuki T, Ando T, Tsuchiya K, Fukazawa N, Saito A, Mariko Y, Yamashita T, Nakanishi O (1999) Synthesis and histone deacetylase inhibitory activity of new benzamide derivatives. J Med Chem 42:3001–3003
Wang DF, Helquist P, Wiech NL, Wiest O (2005) Toward selective histone deacetylase inhibitor design: homology modeling, docking studies, and molecular dynamics simulations of human class I histone deacetylases. J Med Chem 48:6936–6947
Saito A, Yamashita T, Mariko Y, Nosaka Y, Tsuchiya K, Ando T, Suzuki T, Tsuruo T, Nakanishi O (1999) A synthetic inhibitor of histone deacetylase, MS-27–275, with marked in vivo antitumor activity against human tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4592–4597
Hu E, Dul E, Sung CM, Chen Z, Kirkpatrick R, Zhang GF, Johanson K, Liu R, Lago A, Hofmann G, Macarron R, Los Frailes MD, Perez P, Krawiec J, Winkler J, Jaye M (2003) Identification of novel isoformselective inhibitors within class I histone deacetylases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:720–728
Pan L, Lu J, Huang B (2007) HDAC inhibitors: a potential new category of anti-tumor agents. Cell Mol Immunol 4(5):337–343
Johnstone RW (2002) Histone-deacetylase inhibitors: novel drugs for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:287–299
Finzer P, Stohr M, Seibert N, Rosl F (2003) Phenylbutyrate inhibits growth of cervical carcinoma cells independent of HPV type and copy number. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:107–113
Acharya MR, Sparreboom A, Venitz J, Figg WD (2005) Rational development of histone deacetylase inhibitors as anti-cancer agents: a review. Mol Pharmacol 68:917–932
Batova A, Shao LE, Diccianni MB, Yu AL, Tanaka T, Rephaeli A, Nudelman A, Yu J (2002) The histone deacetylase inhibitor AN-9 has selective toxicity to acute leukemia and drug-resistant primary leukemia and cancer cell lines. Blood 100:3319–3324
Gore SD, Weng LJ, Figg WD, Zhai S, Donehower RC, Dover G, Grever MR, Griffin C, Grochow LB, Hawkins A, Burks K, Zabelena Y, Miller CB (2002) Impact of prolonged infusions of the putative differentiating agent sodium phenylbutyrate on myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 8:963–970
Gore SD, Weng LJ, Zhai S, Figg WD, Donehower RC, Dover GJ, Grever M, Griffin CA, Grochow LB, Rowinsky EK, Zabalena Y, Hawkins AL, Burks K, Miller CB (2001) Impact of the putative differentiating agent sodium phenylbutyrate on myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 7:2330–2339
Kijima M, Yoshida M, Sugita K, Horinouchi S, Beppu T (1993) Trapoxin, an antitumor cyclic tetrapeptide, is an irreversible inhibitor of mammalian histone deacetylase. J Biol Chem 268:22429–22435
Nakajima H, Kim YB, Terano H, Yoshida M, Horinouchi S (1998) FR901228, a potent antitumor antibiotic, is a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Exp Cell Res 241:126–133
Andrianov V, Gailite V, Lola D, Loza E, Semenikhina V, Kalvinsh I, Finn P, Petersen KD, Ritchie JWA, Khan N, Tumber A, Collins LS, Vadlamudi SM, Börkling F, Sehested M (2009) Novel amide derivatives as inhibitors of histone deacetylase: design, synthesis and SAR. Euro J Med Chem 44:1067–1085
Kapetanovic IM (2008) Computer-aided drug discovery and development (CADDD): in silico-chemico-biological approach. Chem Biol Interact 171(2):165–176
Garrett MD, Workman P (1999) Discovering novel chemotherapeutic drugs for the third millennium. Eur J Cancer 35:2010–2030
Workman P (2001) New drug targets for genomic cancer therapy: successes, limitations, opportunities and future challenges. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 1:33–47
Anderson AC (2003) The process of structure-based drug design. Chem Biol 10:787–797
Lengauer T, Zimmer R (2000) Protein structure prediction methods for drug design. Brief Bioinform 1(3):275–288
Dallavalle S, Cincinelli R, Nannei R, Merlini L, Morini G, Penco S, Pisano C, Vesci L, Barbarino M, Zuco V, Cesare MD, Zunino F (2009) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of biphenyl-4-yl-acrylohydroxamic acid derivatives as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.11.005
Pratt WB, Ruddon RW, Ensminger WD, Maybaum J (1994) Some milestones in the development of cancer chemotherapy. In: The anticancer drugs, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 17–25
Liu R, Hsieh CY, Lam KS (2004) New approaches in identifying drugs to inactivate oncogene products. Semin Cancer Biol 14:13–21
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noureen, N., Rashid, H. & Kalsoom, S. Identification of type-specific anticancer histone deacetylase inhibitors: road to success. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66, 625–633 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1324-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1324-y