Abstract
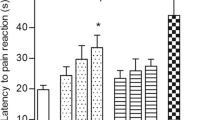
In this study ibuprofen (50.0 mg/kg, i.p.), rofecoxib (10.0 mg/kg, i.p.) and thalidomide (50.0 mg/kg, oral) were shown to prevent vincristine-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. Sprague-Dawley rats were injected every other day with vincristine (0.1 mg/kg) over 13 days. The animals were cotreated daily with vehicle (saline), ibuprofen, rofecoxib or thalidomide throughout the period of vincristine treatment. Mechanical withdrawal threshold to punctuate and radiant heat stimuli were determined prior to and then on alternate days throughout the treatment period. Vincristine vehicle-treated animals developed marked mechanical hyperalgesia from day 5 of chemotherapy and this lasted until the end of the experiment. Thermal thresholds were not altered by the administration of vincristine vehicle. Animals in the vincristine vehicle group neither gained nor lost weight during the treatment period. All three active drugs showed an antihyperalgesic effect on the responses to mechanical stimulation of the hind paw that was significant from day 5 for ibuprofen and thalidomide and from day 7 for rofecoxib. Thermal thresholds increased after the administration of both the NSAIDs and thalidomide. Rofecoxib was the only drug to show any beneficial effect in protecting the animals from failure to gain body weight.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam-Klages S, Adam D, Wiegmann K, Struve S, Waldemar K, Schneider-Mergener J, Kronke M (1996) FAN, a novel WD-repeat protein, couples the p55 TNF-receptor to neutral sphingomyelinase. Cell 86:937–947
Aley KO, Reichling DB, Levine JD (1996) Vincristine hyperalgesia in the rat: a model of painful vincristine neuropathy in humans. Neuroscience 73:259–265
Allan SM (2000) The role of pro- and antiinflammatory cytokines in neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 917:84–93
Bao L, Zhu Y, Elhassan AM, Wu Q, Xiao B, Zhu J, Lindgren JU (2001) Adjuvant-induced arthritis: IL-1 beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha are up- regulated in the spinal cord. Neuroreport 12:3905–3908
Bennett GJ (1999) Does a neuroimmune interaction contribute to the genesis of painful peripheral neuropathies? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7737–7738
Bennett GJ (2000) A neuroimmune interaction in painful peripheral neuropathy. Clin J Pain 16:S139–S143
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorder of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Bove SE, Calcaterra SL, Brooker RM, Huber CM, Guzman RE, Juneau PL, Schrier DJ, Kilgore KS (2003) Weight bearing as a measure of disease progression and efficacy of anti-inflammatory compounds in a model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11:821–830
Bradley WG, Lassman LP, Pearce GW, Walton JN (1970) The neuromyopathy of vincristine in man. Clinical, electrophysiological and pathological studies. J Neurol Sci 10:107–131
Breitbart W, McDonald MV, Rosenfeld B, Passik SD, Hewitt D, Thaler H, Portenoy RK (1996) Pain in ambulatory AIDS patients. I: Pain characteristics and medical correlates. Pain 68:315–321
Calabrese L, Fleischer AB (2000) Thalidomide: current and potential clinical applications. Am J Med 108:487–495
Casey EB, Jellife AM, Le Quesne PM, Millet YL (1973) Vincristine neuropathy. Clinical and electrophysiological observations. Brain 96:69–86
Chacur M, Milligan ED, Gazda LS, Armstrong C, Wang H, Tracey KJ, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2001) A new model of sciatic inflammatory neuritis (SIN): induction of unilateral and bilateral mechanical allodynia following acute unilateral peri-sciatic immune activation in rats. Pain 94:231–244
Chan C-C, Boyce S, Charleson S, Cromlish W, Ethier D, Evans J, Ford-Hutchinson WA, Forrest MJ, Gauthier JY, Gordon R, Gresser M, Guay J, Kargman S, Kennedy BLY, Leger S, Mancini J, O’Neill GP, Ouellet M, Patrick D, Percival MD, Perrier H, Prasit P, Rodger I, Tagari P, Therien M, Vickers P, Visco P, Wang Z, Webb J, Wong E, Xu L-J, Young RN, Zamboni R, Riendieau D (1999) Rofecoxib [Vioxx, MK-0966; 4-(4’-Methylsulfonylphenyl)-3-phenyl-2-(5H)-furanone]: a potent and orally active cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Pharmacological and biochemical profiles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:551–560
Cornblath DR, McArthur JC (1988) Predominantly sensory neuropathy in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Neurology 38:794–796
Dougherty PM, Cata JP, Cordella JV, Burton A, Weng H-R (2004) Taxol-induced sensory disturbance is characterized by preferential impairment of myelinated fiber function in cancer patients. Pain 109:132–142
Dougherty PM, Cordella JV, Weng HR (2001) Chemotherapy-induced hypersensitivity is accompanied by a decrease in spontaneous locomotor activity. Neurosci Abstr 27
Dyck PJ, Dyck PJB, Velosa JA, Larson TS, O’Brien PC, The Nerve Growth Factor Study Group (2000) Patterns of quantitative sensation testing of hypoesthesia and hyperalgesia are predictive of diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 23:510–517
Ferrua B, Doglio MS, Shaw A, Sonthonnax S, Limouse M, Schaffar L (1990) Stimulation of human interleukin 1 production and specific mRNA expression by microtubule-disrupting drugs. Cell Immunol 131:391–397
Finck BN, Johnson RW (1997) Anorexia, weight loss and increased plasma interleukin-6 caused by chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of interleukin-1b in the rat. Brain Res 761:333–337
Garrison CJ, Dougherty PM, Carlton SM (1994) GFAP expression in lumbar spinal cord of naive and neuropathic rats treated with MK-801. Exp Neurol 129:237–243
Gelber DA, Pfeifer MA, Broadstone VL, Munster EW, Peterson M, Arezzo JC, Shamoon H, Zeidler A, Clements R, Greene DA, Porte D Jr, Laudadio C, Bril V (1995) Components of variance for vibratory and thermal threshold testing in normal and diabetic subjects. J Diabetes Comp 9:170–176
George A, Marziniak M, Schafers M, Toyka KV, Sommer C (2000) Thalidomide treatment in chronic constrictive neuropathy decreases endoneurial tumor necrosis factor-alpha, increases interleukin-10 and has long-term effects on spinal cord dorsal horn met-enkephalin. Pain 88:267–275
Green SV, Donoso JA, Heller-Bettinger IE, Samson FE (1977) Axonal transport disturbances in vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy. Ann Neurol 1:255–262
Hargreaves KM, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Holland JF, Scharlau C, Gailani S, Krant MJ, Olson KB, Horton J, Shnider BI, Lynch JJ, Owens A, Carbone PP, Colsky J, Grob D, Miller SP, Hall TC (1973) Vincristine treatment of advanced cancer: a cooperative study of 392 cases. Cancer Res 33:1258–1264
Honore P, Menning PM, Rogers SD, Nichols ML, Mantyh PW (2000) Neurochemical plasticity in persistent inflammatory pain. Prog Brain Res 129:357–363
Kajander KC, Bennett GJ (1992) Onset of a painful neuropathy in rat: a partial and differential deafferentation and spontaneous discharge in AB and Ad primary afferent neurons. J Neurophysiol 68:734–744
Keifer JA, Guttridge DC, Ashburner BP, Baldwin AS (2001) Inhibition of NF-kB activity by thalidomide through suppression of IkB kinase activity. J Biol Chem 276:22382–22387
Kim SH, Chung JM (1992) An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 50:355–364
Kimura T, Iwase M, Kondo G, Watanabe H, Ohashi M, Ito D, Nagumo M (2003) Suppressive effect of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor on cytokine release in human neutrophils. Int Immunopharmacol 3:1519–1528
Laird JM, Bennett GJ (1993) An electrophysiological study of dorsal horn neurons in the spinal cord of rats with an experimental peripheral neuropathy. J Neurophysiol 69:2072–2085
Lashbrook JM, Ossipov MH, Hunter JC, Raffa RB, Tallarida RJ, Porreca F (1999) Synergistic antiallodynic effects of spinal morphine with ketorolac and selective COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors in nerve injured rats. Pain 82:65–72
Leem JG, Bove GM (2002) Mid-axonal tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces ectopic activity in a subset of slowly conducting cutaneous and deep afferent neurons. J Pain 3:45–49
Lindholm D, Heumann R, Meyer M, Thoenen H (1987) Interleukin-1 regulates synthesis of nerve growth factor in non-neuronal cells of rat sciatic nerve. Nature 30:658–659
Lokensgard RJ, Hu S, van Fenema EM, Sheng WS, Peterson PK (2000) Effect of thalidomide on chemokine production by human microglia. J Infect Dis 182:983–987
Ma W, Du W, Eisenach JC (2002) Role for both spinal cord COX-1 and COX- 2 in maintenance of mechanical hypersensitivity following peripheral nerve injury. Brain Res 937:94–99
Ma W, Eisenach JC (2002) Morphological and pharmacological evidence for the role of peripheral prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurosci 15:1037–1047
Mantovani G, Maccio A, Madeddu C (2001) Managing cancer-related anorexia/cachexia. Drugs 61:499–514
Mazario J, Gaitan G, Herrero JF (2001) Cyclooxygenase-1 versus cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in the induction of antinociception in rodent withdrawal reflexes. Neuropharmacology 40:937–946
Meade EA, Smith WL, DeWitt DL (1993) Differential inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) isoenzymes by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem 268:6610–6614
Moos PJ, Muskardin DT, Fitzpatrick FA (1999) Effect of taxol and taxotere on gene expression in macrophages: induction of the prostaglandin H synthase-2 isoenzyme. J Immunol 162:467–473
Moreira AL, Sampaio EP, Zmuidzinas A, Frindt P, Smith KA, Kaplan G (1993) Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor a by enhancing mRNA degradation. J Exp Med 177:1675–1680
Morioka N, Inoue A, Hanada T, Kumagai K, Takeda K, Ikoma K, Hide I, Tamura Y, Shiomi H, Dohi T, Nakata Y (2002) Nitric oxide synergistically potentiates interleukin-1b-induced increase of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA levels, resulting in the facilitation of substance P release from primary afferent neurons: involvement of cGMP-independent mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 43:868–876
Neumann S, Doubell TP, Leslie T, Woolf CJ (1996) Inflammatory pain hypersensitivity mediated by phenotypic switch in myelinated primary sensory neurons. Nature 384:360–364
Nozaki-Taguchi N, Chaplan SR, Higuera S, Ajakwe RC, Yaksh TL (2001) Vincristine-induced allodynia in the rat. Pain 93:69–76
Okamoto K, Martin DP, Schmelzer JD, Mitsui Y, Low PA (2001) Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in rat sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 169:386–391
Palecek J, Paleckova V, Dougherty PM, Carlton SM, Willis WD (1992) Responses of spinothalamic tract cells to mechanical and thermal stimulation of the skin in rats with an experimental peripheral neuropathy. J Neurophysiol 67:1562–1573
Parnet P, Kelley KW, Bluthe RM, Dantzer R (2002) Expression and regulation of interleukin-1 receptors in the brain. Role of cytokines-induced sickness behavior. J Neuroimmunol 125:5–14
Perkins BA, Olaleye D, Zinman B, Bril V (2001) Simple screening tests for peripheral neuropathy in the diabetes clinic. Diabetes Care 24:250–255
Pogrebniak HW, Matthews W, Pass HI (1991) Chemotherapy amplifies production of tumor necrosis factor. Surgery 110:231–237
Postma TJ, Benard BA, Huijgens PC, Ossenkoppele GJ, Heimans JJ (1993) Long term effects of vincristine on the peripheral nervous system. J Neurooncol 15:23–27
Rajkumar SV, Fonseca R, Witzig TE (2001) Complete resolution of reflex sympathetic dystrophy with thalidomide treatment. Arch Intern Med 161:2502–2503
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet S, Allchorne A, Poole S, Bonventre J, Woolf CJ (2001) Interleukin-1b-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 410:471–475
Sampaio EP, Sarno EN, Galilly R, Cohn AZ, Kaplan G (1991) Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med 173:699–703
Sandler SG, Tobin W, Henderson ES (1969) Vincristine-induced neuropathy. A clinical study of fifty leukemic patients. Neurology 19:367–374
Schäfers M, Svensson CI, Sommer C, Sorkin LS (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-a induces mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation by activation of p38 MAPK in primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 23:2517–2521
Seltzer Z, Dubner R, Shir Y (1990) A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain 43:205–218
Shelanski ML, Wisniewski K (1969) Neurofibrillary degeneration. Arch Neurol 20:199–206
Singh RK, Sodhi A, Singh SM (1991) Production of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by cisplatin- treated murine peritoneal macrophages. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul 10:105–116
So YT, Holtzman D, Abrams DI, Olney KO (1988) Peripheral neuropathy associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Neurol 45:945–948
Sodhi A, Pai K (1992) Increased production of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes treated in vitro with cisplatin or other biological response modifiers. Immunol Lett 34:183–188
Sommer C, Marziniak M, Myers RR (1998) The effect of thalidomide treatment on vascular pathology and hyperalgesia caused by chronic constriction injury of rat nerve. Pain 74:83–91
Sorkin LS, Doom CM (2000) Epineurial application of TNF elicits an acute mechanical hyperalgesia in the awake rat. J Peripher Nerv Syst 5:96–100
Sorkin LS, Xaio W-H, Wagner R, Myers RR (1997) Tumour necrosis factor-a induces ectopic activity in nociceptive primary afferent fibres. Neuroscience 81:255–262
Subbaramaiah K, Hart JC, Norton L, Dannenberg JA (2000) Microtubule-interfering agents stimulate the transcription of cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 275:14838–14845
Svensson CI, Yaksh TL (2002) The spinal phospholipase-cyclooxygenase-prostanoid cascade in nociceptive processing. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:553–583
Swiergiel AH, Dunn AJ (2002) Distinct roles for cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 in interleukin-1-induced behavioral changes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:1031–1036
Syriatowicz J-P, Hu D, Walker JS, Tracey DJ (1999) Hyperalgesia due to nerve injury: role of prostaglandins. Neuroscience 94:587–594
Tanner KD, Levine JD, Topp KS (1998) Microtubule disorientation and axonal swelling in unmyelinated sensory axons during vincristine-induced painful neuropathy in rat. J Comp Neurol 395:481–492
Tanner KD, Reichling DB, Levine JD (1998) Nociceptor hyper-responsiveness during vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat. J Neurosci 18:6480–6491
Watkins LR, Wiertelak EP, Goehler LE, Mooney-Heiberger K, Martinez J, Furness L, Smith KP, Maier SF (1994) Neurocircuitry of illness-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res 639:283–299
Watkins LR, Wiertelak EP, Goehler LE, Smith KP, Martin D, Maier SF (1994) Characterization of cytokine-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res 654:15–26
Weiss HD, Walker MD, Wiernik PH (1974) Neurotoxicity of commonly used antineoplastic agents. N Engl J Med 291:127–133
Weng H-R, Cordella JV, Dougherty PM (2002) Changes in sensory processing in the spinal dorsal horn accompany vincristine-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia. Pain 103:131–138
Wiertelak EP, Smith KP, Furness L, Mooney-Heiberger K, Mayr T, Maier SF, Watkins LR (1994) Acute hyperalgesic responses to illness. Pain 56:227–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cata, J.P., Weng, HR. & Dougherty, P.M. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors and thalidomide ameliorate vincristine-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 54, 391–397 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0809-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0809-y