Abstract
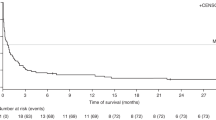
Posttransplantation lymphoproliferation disorder (PTLD) is a life-threatening complication after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Anti-CD20 antibody is the most widely used antibody to eliminate infected B cells. Few studies have focused on prognostic factors predicting the outcome of EBV (Epstein–Barr virus)-PTLD. We conducted a retrospective analysis of 2571 haplo-HSCTs performed between 2010 and 2017 at the Peking University Institute of Hematology; seventy patients who had been treated with rituximab for PTLD were enrolled. The overall EBV-related PTLD frequency was 3.1%. With a median follow-up time of 365 days (range, 54–2659), the overall survival rate was 51.43% (36/70). The cumulative incidence of EBV-PTLD complete remission with anti-CD20 antibody monotherapy was 68.57% (48/70). EBV-PTLD-related mortality was 11.43% (8/70), while the transplantation-related mortality was 38.57% (27/70). Multivariate analysis showed that a decrease in EBV viral load 1 week after therapy was associated with high response rate of EBV-PTLD (p = 0.007, 0.106 (0.021–0.549)), low PTLD-related mortality (p = 0.010, HR 0.058 (0.007–0.503)), and transplantation-related mortality (p = 0.051, HR 0.441 (0.194–1.003)). For EBV-PTLD patients after haplo-HSCT who received rituximab as first-line therapy, non-decreased EBV viral load 1 week after anti-CD20 therapy could be high risk factor for poor outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Dharnidharka VR, Webster AC, Martinez OM, Preiksaitis JK, Leblond V, Choquet S (2016) Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2(56):15088
Kanakry JA, Kasamon YL, Bolaños-Meade J, Borrello IM, Brodsky RA, Fuchs EJ, Ghosh N, Gladstone DE, Gocke CD, Huff CA (2013) Absence of post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder after allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation using post-transplantation cyclophosphamide as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 19(10):1514–1517
Sanz J, Arango M, Senent L, Jarque I, Montesinos P, Sempere A, Lorenzo I, Martín G, Moscardó F, Mayordomo E (2014) EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder after umbilical cord blood transplantation in adults with hematological diseases. Bone Marrow Transplant 49(3):397–402
Baker KS, Defor TE, Burns LJ, Ramsay NKC, Neglia JP, Robison LL (2003) New malignancies after blood or marrow stem-cell transplantation in children and adults: incidence and risk factors. Jclinoncol 21(7):1352
Michael U, Helena W, Mikael S, Ola B, Markus M, Olle R, Jacek W, Per L, Mats R, Jonas M (2014) Risk factors for Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 99(2):346–352
Fox CP, Burns D, Parker AN, Peggs KS, Harvey CM, Natarajan S, Marks DI, Jackson B, Chakupurakal G, Dennis M (2014) EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder following in vivo T-cell-depleted allogeneic transplantation: clinical features, viral load correlates and prognostic factors in the rituximab era. Bone Marrow Transplant 49(2):280–286
Brunstein CG, Weisdorf DJ, Defor T, Barker JN, Tolar J, Burik JAHV, Wagner JE (2006) Marked increased risk of Epstein-Barr virus-related complications with the addition of antithymocyte globulin to a nonmyeloablative conditioning prior to unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation. Blood 108(8):2874–2880
Cohen JM, Sebire NJ, Harvey J, Gaspar HB, Cathy C, Jones A, Rao K, Cubitt D, Amrolia PJ, Davies EG (2007) Successful treatment of lymphoproliferative disease complicating primary immunodeficiency/immunodysregulatory disorders with reduced-intensity allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. Blood 110(6):2209–2214
Mensen A, Na IK, Häfer R, Meerbach A, Schlecht M, Pietschmann ML, Gruhn B (2014) Comparison of different rabbit ATG preparation effects on early lymphocyte subset recovery after allogeneic HSCT and its association with EBV-mediated PTLD. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140(11):1971–1980
Brunstein CG, Weisdorf DJ, Defor T, Barker JN, Tolar J, van Burik JA, Wagner JE (2015) Marked increased risk of Epstein-Barr virus-related complications with the addition of antithymocyte globulin to a nonmyeloablative conditioning prior to unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation. Blood 108(8):2874–2880
Uhlin M, Wikell H, Sundin M, Blennow O, Maeurer M, Ringden O, Winiarski J, Ljungman P, Remberger M, Mattsson J (2014) Risk factors for Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 99(2):346–352
Xu LP, Zhang CL, Mo XD, Zhang XH, Chen H, Han W, Chen YH, Wang Y, Yan CH, Wang JZ (2015) Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder after unmanipulated human leukocyte antigen haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, risk factors, treatment, and clinical outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 21(12):2185–2191
Dierickx D, Tousseyn T, Gheysens O (2015) How I treat posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 126(20):2274–2283
Styczynski J, Velden WVD, Fox CP, Dan E, Camara RDL, Cordonnier C, Ljungman P (2016) Management of Epstein-Barr virus infections and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders in patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Sixth European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL-6) guidelines. Haematologica 101(7):803–811
Rasche L, Kapp M, Einsele H, Mielke S (2013) EBV-induced post transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: a persisting challenge in allogeneic hematopoetic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 49(2):163–167
Styczynski J, Gil L, Tridello G, Ljungman P, Donnelly JP, van der Velden W, Omar H, Martino R, Halkes C, Faraci M, Theunissen K, Kalwak K, Hubacek P, Sica S, Nozzoli C, Fagioli F, Matthes S, Diaz MA, Migliavacca M, Balduzzi A, Tomaszewska A, Camara Rde L, van Biezen A, Hoek J, Iacobelli S, Einsele H, Cesaro S (2013) Response to rituximab-based therapy and risk factor analysis in Epstein Barr Virus-related lymphoproliferative disorder after hematopoietic stem cell transplant in children and adults: a study from the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 57(6):794–802. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit391
Patriarca F, Medeot M, Isola M, Battista ML, Sperotto A, Pipan C, Toffoletti E, Dozzo M, Michelutti A, Gregoraci G (2013) Prognostic factors and outcome of Epstein-Barr virus DNAemia in high-risk recipients of allogeneic stem cell transplantation treated with preemptive rituximab. Transpl Infect Dis 15(3):259–267
Wj VDV, Mori T, Stevens WB, de Haan AF, Stelma FF, Blijlevens NM, Donnelly JP (2013) Reduced PTLD-related mortality in patients experiencing EBV infection following allo-SCT after the introduction of a protocol incorporating pre-emptive rituximab. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(11):1465–1471
Garcíacadenas I, Castillo N, Martino R, Barba P, Esquirol A, Novelli S, Orti G, Garrido A, Saavedra S, Moreno C (2015) Impact of Epstein Barr virus-related complications after high-risk allo-SCT in the era of pre-emptive rituximab. Bone Marrow Transplant 50(4):579–584
Meyer SC, Medinger M, Halter JP, Baldomero H, Hirsch HH, Tzankov A, Dirnhofer S, Passweg JR, Tichelli A (2014) Heterogeneity in clinical course of EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorder after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Hematology 19(5):280–285
Jiang X, Xu L, Zhang Y, Huang F, Liu D, Sun J, Song C, Liang X, Fan Z, Zhou H, Dai M, Liu C, Jiang Q, Xu N, Xuan L, Wu M, Huang X, Liu Q (2016) Rituximab-based treatments followed by adoptive cellular immunotherapy for biopsy-proven EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Oncoimmunology 5(5):e1139274. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2016.1139274
Lu DP, Dong L, Wu T, Huang XJ, Zhang MJ, Han W, Chen H, Liu DH, Gao ZY, Chen YH (2006) Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood 107(8):3065–3073
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, Thomas ED (1995) 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 15(6):825–828
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, Martin P, Chien J, Przepiorka D, Couriel D (2015) National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 11(12):945–956
Xiao-Jun H, Lan-Ping X, Kai-Yan L, Dai-Hong L, Yu W, Huan C, Yu-Hong C, Wei H, Jing-Zhi W, Yao C (2009) Partially matched related donor transplantation can achieve outcomes comparable with unrelated donor transplantation for patients with hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 15(14):4777–4783
Cesaro S, Pegoraro A, Tridello G, Calore E, Pillon M, Varotto S, Abate D, Barzon L, Mengoli C, Carli M (2010) A prospective study on modulation of immunosuppression for Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in pediatric patients who underwent unrelated hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 89(12):1533–1540
Kobayashi S, Sano H, Mochizuki K, Ohara Y, Takahashi N, Ohto H, Kikuta A (2017) Pre-emptive rituximab for Epstein-Barr virus reactivation after haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Int 59(9):973–978. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.13336
Liu Q, Xuan L, Liu H, Huang F, Zhou H, Fan Z, Zhao K, Wu M, Xu L, Zhai X (2013) Molecular monitoring and stepwise preemptive therapy for Epstein-Barr virus viremia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol 88(7):550–555
Stevens SJ, Verschuuren EA, Pronk I, Van DBW, Harmsen MC, The TH, Meijer CJ, Aj VDB, Middeldorp JM (2001) Frequent monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in unfractionated whole blood is essential for early detection of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in high-risk patients. Blood 97(5):1165–1171
Ahmad I, Cau NJ, Maaroufi Y, Meuleman N, Aoun M, Lewalle P, Martiat P, Crokaert F, Bron D (2009) Preemptive management of Epstein-Barr virus reactivation after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 87(8):1240–1245
Omar H, Hägglund H, Gustafsson-Jernberg A, Leblanc K, Mattsson J, Remberger M, Ringdén O, Sparrelid E, Sundin M, Winiarski J (2010) Targeted monitoring of patients at high risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease by quantitative Epstein-Barr virus polymerase chain reaction. Transpl Infect Dis 11(5):393–399
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81870140, 81670166, 81873445, 81530046), the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81621001), the Project of Health Collaborative Innovation of Guangzhou City (No. 201704020214), the Scientific Research Foundation for Capital Medicine Development (No. 2018-2-4084), Peking University Clinical Scientist Program (BMU2019LCKXJ003), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Peking University People’s Hospital. Informed consent was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, XY., Mo, XD., Xu, LP. et al. A retrospective analysis on anti-CD20 antibody–treated Epstein–Barr virus–related posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder following ATG-based haploidentical T-replete hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 99, 2649–2657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04003-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-020-04003-8