Abstract
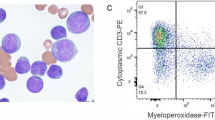
Mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) is an uncommon diagnosis, representing only about 2–5% of acute leukemia cases. The blast cells of MPAL express multilineage immunophenotypic markers and may have a shared B/T/myeloid phenotype. Due to historical ambiguity in the diagnosis of MPAL, the genetics and clinical features of this disease remain poorly characterized. Based on the 2008 and 2016 World Health Organization classifications, myeloid lineage is best determined by presence of myeloperoxidase, while B and T lymphoid lineages are demonstrated by CD19 and cytoplasmic CD3 expression. MPAL typically carries a worse prognosis than either acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or acute lymphoid leukemia (ALL). Given the rarity of MPAL, there is a lack of prospective trial data to guide therapy; treatment generally relies on ALL-like regimens followed by consolidation chemotherapy or hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). Here, we review the updated classification, biology, clinical features, and treatment approach to MPAL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinberg OK, Arber DA (2010) Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: historical overview and a new definition. Leukemia 24(11):1844–1851. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.202
Altman AJ (1990) Clinical features and biological implications of acute mixed lineage (hybrid) leukemias. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 12(2):123–133
Mirro J, Zipf TF, Pui CH, Kitchingman G, Williams D, Melvin S, Murphy SB, Stass S (1985) Acute mixed lineage leukemia: clinicopathologic correlations and prognostic significance. Blood 66(5):1115–1123
Sulak LE, Clare CN, Morale BA, Hansen KL, Montiel MM (1990) Biphenotypic acute leukemia in adults. Am J Clin Pathol 94(1):54–58
Catovsky D, Matutes E, Buccheri V, Shetty V, Hanslip J, Yoshida N, Morilla R (1991) A classification of acute leukaemia for the 1990s. Ann Hematol 62(1):16–21
Bene MC, Bernier M, Casasnovas RO, Castoldi G, Knapp W, Lanza F, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A, Sperling C, van’t Veer MB (1998) The reliability and specificity of c-kit for the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemias and undifferentiated leukemias. The European Group for the Immunological Classification of Leukemias (EGIL). Blood 92(2):596–599
Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A, van’t Veer MB (1995) Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia 9(10):1783–1786
Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein HVJ, Vardiman JW (2001) Pathology and genetics of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 2nd printing, World Health Organization classification of Tumours. IARC Press, Lyon, France
Borowitz MJ, Bene MC, Harris NL, Porwit A, Matutes E (2008) Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. In: WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press, Lyon, France
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M, Vardiman JW (2016) The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 127(20):2391–2405. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544
Shi R, Munker R (2015) Survival of patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemias: a large population-based study. Leuk Res 39(6):606–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2015.03.012
van den Ancker W, Terwijn M, Westers TM, Merle PA, van Beckhoven E, Drager AM, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA (2010) Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage: diagnostic consequences of the WHO2008 classification. Leukemia 24(7):1392–1396. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.119
Yan L, Ping N, Zhu M, Sun A, Xue Y, Ruan C, Drexler HG, Macleod RA, Wu D, Chen S (2012) Clinical, immunophenotypic, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic features in 117 adult patients with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia defined by WHO-2008 classification. Haematologica 97(11):1708–1712. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2012.064485
Pawar RN, Banerjee S, Bramha S, Krishnan S, Bhattacharya A, Saha V, Chakrapani A, Bhave S, Chandy M, Nair R, Parihar M, Arora N, Mishra DK (2017) Mixed-phenotypic acute leukemia series from tertiary care center. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 60(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.4103/0377-4929.200057
Matutes E, Pickl WF, Van't Veer M, Morilla R, Swansbury J, Strobl H, Attarbaschi A, Hopfinger G, Ashley S, Bene MC, Porwit A, Orfao A, Lemez P, Schabath R, Ludwig WD (2011) Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: clinical and laboratory features and outcome in 100 patients defined according to the WHO 2008 classification. Blood 117(11):3163–3171. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-10-314682
Orkin SH, Zon LI (2008) Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology. Cell 132(4):631–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.025
Regalo G, Leutz A (2013) Hacking cell differentiation: transcriptional rerouting in reprogramming, lineage infidelity and metaplasia. EMBO Mol Med 5(8):1154–1164. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201302834
Simmons S, Knoll M, Drewell C, Wolf I, Mollenkopf HJ, Bouquet C, Melchers F (2012) Biphenotypic B-lymphoid/myeloid cells expressing low levels of Pax5: potential targets of BAL development. Blood 120(18):3688–3698. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-03-414821
Hsu CL, King-Fleischman AG, Lai AY, Matsumoto Y, Weissman IL, Kondo M (2006) Antagonistic effect of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein-alpha and Pax5 in myeloid or lymphoid lineage choice in common lymphoid progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(3):672–677. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510304103
De Obaldia ME, Bell JJ, Wang X, Harly C, Yashiro-Ohtani Y, DeLong JH, Zlotoff DA, Sultana DA, Pear WS, Bhandoola A (2013) T cell development requires constraint of the myeloid regulator C/EBP-alpha by the Notch target and transcriptional repressor Hes1. Nat Immunol 14(12):1277–1284. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2760
Li S, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Chung SS, Sanders MA, Hricik T, Rapaport F, Patel J, Dillon R, Vijay P, Brown AL, Perl AE, Cannon J, Bullinger L, Luger S, Becker M, Lewis ID, To LB, Delwel R, Lowenberg B, Dohner H, Dohner K, Guzman ML, Hassane DC, Roboz GJ, Grimwade D, Valk PJ, D'Andrea RJ, Carroll M, Park CY, Neuberg D, Levine R, Melnick AM, Mason CE (2016) Distinct evolution and dynamics of epigenetic and genetic heterogeneity in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 22(7):792–799. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4125
Heesch S, Neumann M, Schwartz S, Bartram I, Schlee C, Burmeister T, Hanel M, Ganser A, Heuser M, Wendtner CM, Berdel WE, Gokbuget N, Hoelzer D, Hofmann WK, Thiel E, Baldus CD (2013) Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage in adults: molecular and clinical characterization. Ann Hematol 92(6):747–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1694-4
Al-Seraihy AS, Owaidah TM, Ayas M, El-Solh H, Al-Mahr M, Al-Ahmari A, Belgaumi AF (2009) Clinical characteristics and outcome of children with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica 94(12):1682–1690. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.009282
Park JA, Ghim TT, Bae K, Im HJ, Jang SS, Park CJ, Chi HS, Seo JJ (2009) Stem cell transplant in the treatment of childhood biphenotypic acute leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53(3):444–452. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.22105
Owaidah TM, Al Beihany A, Iqbal MA, Elkum N, Roberts GT (2006) Cytogenetics, molecular and ultrastructural characteristics of biphenotypic acute leukemia identified by the EGIL scoring system. Leukemia 20(4):620–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404128
Rubnitz JE, Onciu M, Pounds S, Shurtleff S, Cao X, Raimondi SC, Behm FG, Campana D, Razzouk BI, Ribeiro RC, Downing JR, Pui CH (2009) Acute mixed lineage leukemia in children: the experience of St Jude Children’s Research Hospital. Blood 113(21):5083–5089. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-10-187351
Manola KN (2013) Cytogenetic abnormalities in acute leukaemia of ambiguous lineage: an overview. Br J Haematol 163(1):24–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12484
Hoehn D, Medeiros LJ, Chen SS, Tian T, Jorgensen JL, Ahmed Y, Lin P (2012) CD117 expression is a sensitive but nonspecific predictor of FLT3 mutation in T acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T/myeloid acute leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol 137(2):213–219. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCPR3N3JMSYLPFG
Kern W, Grossmann V, Roller A, Weissmann S, Alpermann T, Schoeck U, Haferlach C, Schnittger S, Haferlach T, Kohlmann A (2012) Mixed phenotype acute leukemia, T/myeloid, NOS (MPAL-TM) has a high <em>DNMT3A</em> mutation frequency and carries further genetic features of both AML and T-ALL: results of a comprehensive next-generation sequencing study analyzing 32 genes. Blood 120(21):403–403
Kotrova M, Musilova A, Stuchly J, Fiser K, Starkova J, Mejstrikova E, Stary J, Zuna J, Hrusak O, Trka J, Zaliova M (2016) Distinct bilineal leukemia immunophenotypes are not genetically determined. Blood 128(18):2263–2266. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-07-725861
Eckstein OS, Wang L, Punia JN, Kornblau SM, Andreeff M, Wheeler DA, Goodell MA, Rau RE (2016) Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) exhibits frequent mutations in DNMT3A and activated signaling genes. Exp Hematol 44(8):740–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2016.05.003
Neumann M, Heesch S, Schlee C, Schwartz S, Gokbuget N, Hoelzer D, Konstandin NP, Ksienzyk B, Vosberg S, Graf A, Krebs S, Blum H, Raff T, Bruggemann M, Hofmann WK, Hecht J, Bohlander SK, Greif PA, Baldus CD (2013) Whole-exome sequencing in adult ETP-ALL reveals a high rate of DNMT3A mutations. Blood 121(23):4749–4752. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-11-465138
Zhang J, Ding L, Holmfeldt L, Wu G, Heatley SL, Payne-Turner D, Easton J, Chen X, Wang J, Rusch M, Lu C, Chen SC, Wei L, Collins-Underwood JR, Ma J, Roberts KG, Pounds SB, Ulyanov A, Becksfort J, Gupta P, Huether R, Kriwacki RW, Parker M, McGoldrick DJ, Zhao D, Alford D, Espy S, Bobba KC, Song G, Pei D, Cheng C, Roberts S, Barbato MI, Campana D, Coustan-Smith E, Shurtleff SA, Raimondi SC, Kleppe M, Cools J, Shimano KA, Hermiston ML, Doulatov S, Eppert K, Laurenti E, Notta F, Dick JE, Basso G, Hunger SP, Loh ML, Devidas M, Wood B, Winter S, Dunsmore KP, Fulton RS, Fulton LL, Hong X, Harris CC, Dooling DJ, Ochoa K, Johnson KJ, Obenauer JC, Evans WE, Pui CH, Naeve CW, Ley TJ, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, Downing JR, Mullighan CG (2012) The genetic basis of early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 481(7380):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10725
Coustan-Smith E, Mullighan CG, Onciu M, Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Pei D, Cheng C, Su X, Rubnitz JE, Basso G, Biondi A, Pui CH, Downing JR, Campana D (2009) Early T-cell precursor leukaemia: a subtype of very high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 10(2):147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70314-0
Weir EG, Ali Ansari-Lari M, Batista DA, Griffin CA, Fuller S, Smith BD, Borowitz MJ (2007) Acute bilineal leukemia: a rare disease with poor outcome. Leukemia 21(11):2264–2270. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404848
Killick S, Matutes E, Powles RL, Hamblin M, Swansbury J, Treleaven JG, Zomas A, Atra A, Catovsky D (1999) Outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica 84(8):699–706
Xu XQ, Wang JM, Lu SQ, Chen L, Yang JM, Zhang WP, Song XM, Hou J, Ni X, Qiu HY (2009) Clinical and biological characteristics of adult biphenotypic acute leukemia in comparison with that of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case series of a Chinese population. Haematologica 94(7):919–927. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2008.003202
Legrand O, Perrot JY, Simonin G, Baudard M, Cadiou M, Blanc C, Ramond S, Viguie F, Marie JP, Zittoun R (1998) Adult biphenotypic acute leukaemia: an entity with poor prognosis which is related to unfavourable cytogenetics and P-glycoprotein over-expression. Br J Haematol 100(1):147–155
Lee JH, Min YH, Chung CW, Kim BK, Yoon HJ, Jo DY, Shin HJ, Bang SM, Won JH, Zang DY, Kim HJ, Chi HS, Lee KH, Cheong JW, Kim JS, Kim SH, Park S, Park SY, Chung JS, Lee JH, Park CJ, Korean Society of Hematology AMLMDSWP (2008) Prognostic implications of the immunophenotype in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 49(4):700–709. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428190701843247
Zhang Y, Wu D, Sun A, Qiu H, He G, Jin Z, Tang X, Miao M, Fu Z, Han Y (2011) Clinical characteristics, biological profile, and outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia: a case series. Acta Haematol 125(4):210–218. https://doi.org/10.1159/000322594
Deffis-Court M, Alvarado-Ibarra M, Ruiz-Arguelles GJ, Rosas-Lopez A, Barrera-Lumbreras G, Aguayo-Gonzalez A, Lopez-Karpovitch X, Lopez-Hernandez M, Velazquez-Sanchez de Cima S, Zamora-Ortiz G, Crespo-Solis E (2014) Diagnosing and treating mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a multicenter 10-year experience in Mexico. Ann Hematol 93(4):595–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1919-6
Zheng C, Wu J, Liu X, Ding K, Cai X, Zhu W (2009) What is the optimal treatment for biphenotypic acute leukemia? Haematologica 94(12):1778–1780; author reply 1780. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.014829
Weinberg OK, Seetharam M, Ren L, Alizadeh A, Arber DA (2014) Mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a study of 61 cases using World Health Organization and European Group for the immunological classification of leukaemias criteria. Am J Clin Pathol 142(6):803–808. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCPPVUPOTUVOIB5
Wolach O, Stone RM (2015) How I treat mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Blood 125(16):2477–2485. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-10-551465
Porwit A, Bene MC (2015) Acute leukemias of ambiguous origin. Am J Clin Pathol 144(3):361–376. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCPSTU55DRQEGTE
Pomerantz A, Rodriguez-Rodriguez S, Demichelis-Gomez R, Barrera-Lumbreras G, Barrales-Benitez O, Lopez-Karpovitch X, Aguayo-Gonzalez A (2016) Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: suboptimal treatment when the 2008/2016 WHO classification is used. Blood Res 51(4):233–241. https://doi.org/10.5045/br.2016.51.4.233
Aribi A, Bueso-Ramos C, Estey E, Estrov Z, O'Brien S, Giles F, Faderl S, Thomas D, Kebriaei P, Garcia-Manero G, Pierce S, Cortes J, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F (2007) Biphenotypic acute leukaemia: a case series. Br J Haematol 138(2):213–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06634.x
Lee JY, Lee SM, Lee JY, Kim KH, Choi MY, Lee WS (2016) Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia treated with decitabine. Korean J Intern Med 31(2):406–408. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2014.353
Tian H, Xu Y, Liu L, Yan L, Jin Z, Tang X, Han Y, Fu Z, Qiu H, Sun A, Wu D (2016) Comparison of outcomes in mixed phenotype acute leukemia patients treated with chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation versus chemotherapy alone. Leuk Res 45:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2016.04.002
Shimizu H, Saitoh T, Machida S, Kako S, Doki N, Mori T, Sakura T, Kanda Y, Kanamori H, Miyawaki S, Okamoto S, Kanto Study Group for Cell T (2015) Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: results of a matched-pair analysis. Eur J Haematol 95(5):455–460. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.12516
Munker R, Brazauskas R, Wang HL, de Lima M, Khoury HJ, Gale RP, Maziarz RT, Sandmaier BM, Weisdorf D, Saber W, Center for International B, Marrow Transplant R (2016) Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(6):1024–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.02.013
Liu QF, Fan ZP, Wu MQ, Sun J, Wu XL, Xu D, Jiang QL, Zhang Y, Huang F, Wei YQ, Zhao J, Yu GP, Meng FY (2013) Allo-HSCT for acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage in adults: the comparison between standard conditioning and intensified conditioning regimens. Ann Hematol 92(5):679–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1662-4
Wolach O, Stone RM (2017) Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: current challenges in diagnosis and therapy. Curr Opin Hematol 24(2):139–145. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOH.0000000000000322
DeAngelo DJ, Stevenson KE, Dahlberg SE, Silverman LB, Couban S, Supko JG, Amrein PC, Ballen KK, Seftel MD, Turner AR, Leber B, Howson-Jan K, Kelly K, Cohen S, Matthews JH, Savoie L, Wadleigh M, Sirulnik LA, Galinsky I, Neuberg DS, Sallan SE, Stone RM (2015) Long-term outcome of a pediatric-inspired regimen used for adults aged 18-50 years with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 29(3):526–534. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.229
Larson RA, Dodge RK, Burns CP, Lee EJ, Stone RM, Schulman P, Duggan D, Davey FR, Sobol RE, Frankel SR et al (1995) A five-drug remission induction regimen with intensive consolidation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: cancer and leukemia group B study 8811. Blood 85(8):2025–2037
Shimizu H, Yokohama A, Hatsumi N, Takada S, Handa H, Sakura T, Nojima Y (2014) Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia in the imatinib era. Eur J Haematol 93(4):297–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.12343
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Basavapathruni A, Jin L, Boriack-Sjodin PA, Allain CJ, Klaus CR, Raimondi A, Scott MP, Waters NJ, Chesworth R, Moyer MP, Copeland RA, Richon VM, Pollock RM (2013) Potent inhibition of DOT1L as treatment of MLL-fusion leukemia. Blood 122(6):1017–1025. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-04-497644
Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Majer CR, Sneeringer CJ, Song J, Johnston LD, Scott MP, Smith JJ, Xiao Y, Jin L, Kuntz KW, Chesworth R, Moyer MP, Bernt KM, Tseng JC, Kung AL, Armstrong SA, Copeland RA, Richon VM, Pollock RM (2011) Selective killing of mixed lineage leukemia cells by a potent small-molecule DOT1L inhibitor. Cancer Cell 20(1):53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.009
Fung TK, Gandillet A, So CW (2012) Selective treatment of mixed-lineage leukemia leukemic stem cells through targeting glycogen synthase kinase 3 and the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Curr Opin Hematol 19(4):280–286. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283545615
Zhao XF, Gojo I, York T, Ning Y, Baer MR (2009) Diagnosis of biphenotypic acute leukemia: a paradigmatic approach. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 3(1):75–86
Carbonell F, Swansbury J, Min T, Matutes E, Farahat N, Buccheri V, Morilla R, Secker-Walker L, Catovsky D (1996) Cytogenetic findings in acute biphenotypic leukaemia. Leukemia 10(8):1283–1287
Buccheri V, Matutes E, Dyer MJ, Catovsky D (1993) Lineage commitment in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Leukemia 7(6):919–927
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Siddiqi, R. & Naqvi, K. An update on classification, genetics, and clinical approach to mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL). Ann Hematol 97, 945–953 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3297-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3297-6