Abstract
Purpose
The linea aspera can be used as a landmark to assess the rotation of the distal femoral epiphysis when performing an endoprostheses. However, no study has assessed the reliability of this landmark. We therefore asked whether the linea aspera could be used as a rotational landmark for positioning distal femoral knee megaprostheses.
Materials
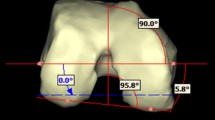
This is an anatomic MRI-based study of 50 femurs (27 subjects). For each femur, multiple axial sections were obtained from the intercondylar line at the knee joint to the lesser trochanter; each axial section was superposed with that where the posterior condyles were seen and the R angle was measured. The R angle is the angle measured medially where the line passing through the linea aspera and the line tangent to the posterior condyles intersects.
Results
There were considerable differences between and within subjects with a maximum R angle ranging from 100° to 120°. Regression models showed that the R angle was significantly associated with distance from knee joint and subjects.
Conclusion
Surgeons should have the R angle measured before performing a distal femoral reconstruction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6):716–723
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:46–55
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Bhattee G, Moonot P, Govindaswamy R, Pope A, Fiddian N, Harvey A (2014) Does malrotation of components correlate with patient dissatisfaction following secondary patellar resurfacing? Knee 21(1):247–251
Biau D, Faure F, Katsahian S, Jeanrot C, Tomeno B, Anract P (2006) Survival of total knee replacement with a megaprosthesis after bone tumor resection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(6):1285–1293
Capanna R, Morris HG, Campanacci D, Del Ben M, Campanacci M (1994) Modular uncemented prosthetic reconstruction after resection of tumours of the distal femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br 76(2):178–186
Davidian M, Giltinian DM (1995) Nonlinear models for repeated measurement data. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Davila J, Malkani A, Paiso JM (2001) Supracondylar distal femoral nonunions treated with a megaprosthesis in elderly patients: a report of two cases. J Orthop Trauma 15(8):574–578
Eckardt JJ, Kabo JM, Kelly CM, Ward WG Sr, Cannon CP (2003) Endoprosthetic reconstructions for bone metastases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 415(Suppl):S254–S262
Fitzpatrick CK, Baldwin MA, Clary CW, Wright A, Laz PJ, Rullkoetter PJ (2012) Identifying alignment parameters affecting implanted patellofemoral mechanics. J Orthop Res 30(7):1167–1175
Harrison RJ Jr, Thacker MM, Pitcher JD, Temple HT, Scully SP (2006) Distal femur replacement is useful in complex total knee arthroplasty revisions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 446:113–120
Höll S, Schlomberg A, Gosheger G, Dieckmann R, Streitbuerger A, Schulz D, Hardes J (2012) Distal femur and proximal tibia replacement with megaprosthesis in revision knee arthroplasty: a limb-saving procedure. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(12):2513–2518
Incavo SJ, Wild JJ, Coughlin KM, Beynnon BD (2007) Early revision for component malrotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 458:131–136
Katz MA, Beck TD, Silber JS, Seldes RM, Lotke PA (2001) Determining femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty: reliability of techniques. J Arthroplasty 16(3):301–305
Liao JG, Lipsitz SR (2002) A type of restricted maximum likelihood estimator for variance components in generalized linear mixed models. Biometrika 89:401–409
Malawer MM (2001) Distal femoral resection with endoprosthetic reconstruction. In: Malawer MM, Sugarbaker P (eds) Musculoskeletal cancer surgery treatment of sarcomas and allied diseases. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Berlin, pp 457–481
Malo M, Vince KG (2003) The unstable patella after total knee arthroplasty: etiology, prevention, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 11(5):364–371
Park DH, Jaiswal PK, Al-Hakim W, Aston WJ, Pollock RC, Skinner JA, Cannon SR, Briggs TW (2007) The use of massive endoprostheses for the treatment of bone metastases. Sarcoma 2007:62151
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and S-Plus. Springer Verlag, New York
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org. Accessed 10 Mar 2016
Sawaguchi N, Majima T, Ishigaki T, Mori N, Terashima T, Minami A (2010) Mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty improves patellar tracking and patellofemoral contact stress: in vivo measurements in the same patients. J Arthroplasty 25(6):920–925
Schwartz AJ, Kabo JM, Eilber FC, Eilber FR, Eckardt JJ (2010) Cemented distal femoral endoprostheses for musculoskeletal tumor: improved survival of modular versus custom implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(8):2198–2210
Sharma S, Turcotte RE, Isler MH, Wong C (2006) Cemented rotating hinge endoprosthesis for limb salvage of distal femur tumors. Clin Orthop Relat Res 450:28–32
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86(2):420–428
Sikorski JM (2008) Alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(9):1121–1127
Siston RA, Patel JJ, Goodman SB, Delp SL, Giori NJ (2005) The variability of femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(10):2276–2280
Springer BD, Sim FH, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG (2004) The modular segmental kinematic rotating hinge for nonneoplastic limb salvage. Clin Orthop Relat Res 421:181–187
Su EP, Su SL, Della Valle AG (2010) Stiffness after TKR: how to avoid repeat surgery. Orthopedics 33(9):658
Thompson JA, Hast MW, Granger JF, Piazza SJ, Siston RA (2011) Biomechanical effects of total knee arthroplasty component malrotation: a computational simulation. J Orthop Res 29(7):969–975
Vaishya R, Singh AP, Hasija R, Singh AP (2011) Treatment of resistant nonunion of supracondylar fractures femur by megaprosthesis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1137–1140
Vanbiervliet J, Bellemans J, Verlinden C, Luyckx JP, Labey L, Innocenti B, Vandenneucker H (2011) The influence of malrotation and femoral component material on patellofemoral wear during gait. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(10):1348–1354
Verlinden C, Uvin P, Labey L, Luyckx JP, Bellemans J, Vandenneucker H (2010) The influence of malrotation of the femoral component in total knee replacement on the mechanics of patellofemoral contact during gait: an in vitro biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(5):737–742
Wakabayashi H, Naito Y, Hasegawa M, Nakamura T, Sudo A (2012) A tumor endoprosthesis is useful in elderly rheumatoid arthritis patient with acute intercondylar fracture of the distal femur. Rheumatol Int 32(5):1411–1413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reple, G., Felden, A., Feydy, A. et al. The linea aspera as a rotational landmark: an anatomical MRI-based study. Surg Radiol Anat 38, 1069–1074 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1661-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1661-6