Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to discuss the distribution characteristics and the anatomical angioarchitecture of cutaneous branches arising from the second dorsal metacarpal artery for the repair of small tissue defects in the hand or fingers using the second dorsal metacarpal artery chain-link flap.
Methods
Fifteen fresh human cadaveric hands were studied using three methods: latex perfusion for microanatomical analysis, denaturation of material and vinyl chloride mixed packing for cast specimens, and latex perfusion creating pellucid specimens. Cutaneous perforators with a diameter of 0.2 mm or greater were evaluated using statistical analysis. Cluster analysis was conducted to determine the overall distribution of the perforators.
Results
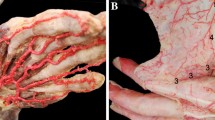
Two main clusters of perforators distributed at a relative distance of 40.8 and 68.6 % from the second web space edge to the midpoint of the second metacarpal bone as a unit. The Chi-square analysis revealed no significant differences in either the radial or ulnar side distribution of the cutaneous perforators from the second dorsal metacarpal artery (p = 0.779). Chain-links formed among adjacent perforators were parallel to the axis of the second metacarpal bone on the dorsum of the hand. Based on the anatomic characteristic, we designed the second dorsal metacarpal artery chain-link flap to recover the defect in the index finger. As a result, the patient was satisfied with the appearance and function.
Conclusion
This study indicates that there are two main clusters of arterioles in the distal second dorsal metacarpal artery that can be helpful for the second dorsal metacarpal artery pedicle cutaneous chain-link perforator flaps in the repair of defects in the fingers.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldabagh B, Cook JL (2014) Reconstruction of scalp wounds with exposed calvarium using a local flap and a split-thickness skin graft: case series of 20 patients. Dermatol Surg 40:257–265
Bailey SH, Andry D, Saint-Cyr M (2010) The dorsal metacarpal artery perforator flap: a case report utilizing a Quaba flap harvested from a previously skin-grafted area for dorsal 5th digit coverage. Hand (N Y) 5:322–325
Checcucci G, Galeano M, Zucchini M, Zampetti PG, Ceruso M (2013) Reverse flow first dorsal metacarpal artery flap for covering the defect of distal thumb. Microsurgery 34:283–286
Chen C, Zhang W, Tang P (2013) Direct and reversed dorsal digito-metacarpal flaps: a review of 24 cases. Injury 45:805–812
Comert A, Altun S, Unlu RE, Orbay H, Tekdemir I (2011) Perforating arteries of the anteromedial aspect of the thigh: an anatomical study regarding anteromedial thigh flap. Surg Radiol Anat 33:241–247
Dautel G, Merle M (1992) Direct and reverse dorsal metacarpal flaps. Br J Plast Surg 45:123–130
Dautel G, Merle M (1991) Dorsal metacarpal reverse flaps. Anatomical basis and clinical application. J Hand Surg Br 16:400–405
Earley MJ, Milner RH (1987) Dorsal metacarpal flaps. Br J Plast Surg 40:333–341
Guo L, Pribaz JR, Pribaz JJ (2008) Nasal reconstruction with local flaps: a simple algorithm for management of small defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 122:130–139
Hallock GG (2003) Direct and indirect perforator flaps: the history and the controversy. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:855–866
Karacalar A, Ozcan M (1997) A new approach to the reverse dorsal metacarpal artery flap. J Hand Surg Am 22:307–310
Lai-jin L, Xu G (2006) The reverse dorsal metacarpal flap: experience with 153 cases. Ann Plast Surg 56:614–617
Lai-Jin L, Xu G, Jian-Li C, Xi-Guang S (2008) A modified approach of the reverse dorsal metacarpal island flap: anatomical basis and application in 24 cases. Ann Plast Surg 61:392–395
Le Nen D, Rizzo C, Hu W, Gerard R, Oana D, Lefevre C, Senecail B (2009) The island hemisoleus flap on distal vascular pedicle: anatomical bases and clinical applications. Surg Radiol Anat 31:715–721
Mei J, Morris SF, Ji W, Li H, Zhou R, Tang M (2013) An anatomic study of the dorsal forearm perforator flaps. Surg Radiol Anat 35:695–700
Ozaksar K, Toros T, Sugun TS, Bal E, Ademoğlu Y, Kaplan I (2010) Reconstruction of finger pulp defects using homodigital dorsal middle phalangeal neurovascular advancement flap. J Hand Surg Eur 35:125–129
Quaba AA, Davison PM (1990) The distally-based dorsal hand flap. Br J Plast Surg 43:28–39
Rozen WM, Niumsawatt V, Ross R, Leong JC, Ek EW (2013) The vascular basis of the hemi-hamate osteochondral free flap. Part 1: vascular anatomy and clinical correlation. Surg Radiol Anat 35:585–594
Schaverien M, Saint-Cyr M (2008) Perforators of the lower leg: analysis of perforator locations and clinical application for pedicled perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 122:161–170
Stecco C, Tiengo C, Stecco A, Porzionato A, Macchi V, Stern R, De Caro R (2013) Fascia redefined: anatomical features and technical relevance in fascial flap surgery. Surg Radiol Anat 35:369–376
Strauch B, Moura WJ (1990) Arterial system of the fingers. J Hand Surg Am 15:148–154
Sun C, Hou ZD, Wang B, Ding ZH (2013) An anatomical study on the characteristics of cutaneous branches-chain perforator flap with ulnar artery pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 131:329–336
Taylor GI, Palmer JH (1987) The vascular territories (angiosomes) of the body: experimental study and clinical applications. Br J Plast Surg 40:113–141
Yang D, Morris SF (2001) Vascular basis of dorsal digital and metacarpal skin flaps. J Hand Surg Am 26:142–146
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Medical Scientific Research Fund Project in Guangdong Province in 2012 (Project No. A2012661).
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that there is no conflict of interest associated with this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Qin, X., Zhang, H. et al. The second dorsal metacarpal artery chain-link flap: an anatomical study and a case report. Surg Radiol Anat 37, 349–356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-014-1372-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-014-1372-9