Abstract
Aim
We decided to study the relationship between brain volume and cranial capacity and the relationship between brain volume and age on a series of CT from healthy adults.
Methods
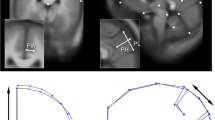
Fifty-eight healthy volunteers (27 women, 31 men, age range 18–95 years) were examined using our imaging protocols. The volunteers had no present or past neuropsychiatric illness and no abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs.
Results
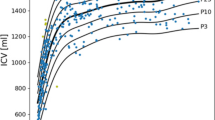
Mean intracranial volume was 1,384.6 cm3 (standard deviation = 135.27, range 1,106–1,656) and mean brain volume was 1,201.0 cm3 (standard deviation = 142.52, range 791–1,500). Linear regression between brain volume and cranial capacity yielded this formula: brain volume = 182.3 + 0.7 × cranial capacity. Multivariate analysis yielded a relationship between cranial capacity, brain volume and age as follows: brain volume = 396.5–3.5 × age + 0.7 × cranial capacity.
Conclusion
This study could be supplemented by the collection of data such as, the size of the individuals in order to study the relationship between size of the brain and stature because this relation remains unclear.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott AH, Netherway DJ, Niemann DB, Clark B, Yamamoto M, Cole J, Hanieh A, Moore MH, David DJ (2000) CT-determined intracranial volume for a normal population. J Craniofac Surg 11:211–223
Allen JS, Damasio H, Grabowski TJ (2002) Normal neuroanatomical variation in the human brain: an MRI-volumetric study. Am J Phys Anthropol 118:341–358
Blatter DD, Bigler ED, Gale SD, Johnson SC, Anderson CV, Burnett BM, Parker N, Kurth S, Horn SD (1995) Volumetric analysis of brain IRM. Normative database spanning 5 decades of life. Am J Neuroradiol 16:241–251
Paul Broca (1879) Méthode des moyennes. Bull Soc Anthropol 2:756–820
Buckner RL, Head D, Parker J, Fotenos AF, Marcus D, Morris JC, Snyder AZ (2004) A unified approach for morphometric and functional data analysis in young, old, and demented adults using automated atlas-based head size normalization. Neuroimage 23:724–738
Coffey CE, Lucke JF, Saxton JA (1998) Sex differences in brain aging: a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol 55:169–179
Conroy GC, Vannier MW (1984) Noninvasive three-dimensional computer imaging of matrix-filled fossil skulls by high-resolution tomography. Science 26:456–458
Courchesne E, Chisum HJ, Townsend J, Cowles A, Covington J, Egaas B, Harwood M, Hinds S, Press GA (2000) Normal brain development and aging: quantitative analysis at in vivo MR imaging in healthy volunteers. Radiology 216:672–682
Davis PJM, Wright EA (1977) A new method for measuring cranial cavity volume and its application to the assessment of cerebral atrophy. Neuropath Appl Neuro 3:341–358
Dekaban AS, Sadowsky M (1978) Changes in brain weights during the span of humain life: relation of brain weights to body heights and body weights. Ann Neurol 4:345–356
Ge Y, Groosman I, Bobb JS, Robin ML, Mannon LJ, Kolson L (2002) Age related toral gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: volumetric MR imaging analysis. Am J Neuroradiol 23:1327–1333
Ho KC, Roessmann U, Straumfjord JV, Monroe G (1980) Analysis of brain weight. Adult brain weight in relation to sex, race and age. Arch Pathol Lab Med 104:635–639
Holloway RL, Broadfield DC, Yua MS et al (2004) The human fossil record. Volume 3. Brain endocasts. The paleoneurological Evidence. Wiley, New York
Kruggel F (2006) MRI-based volumetry of head compartments: normative values of healthy adlults. NeuroImage 30:1–11
Mazonakis M, Karampekios S, Damilakis J, Voloudaki A, Gourtsoyiannis N (2004) Stereological estimation of intracranial volume on CT image. Eur Radiol 14:1285–1290
Mueller EA, Moore MM, Kerr DCR (1998) Brain volume preserved in healthy edrely through the eleventh decade. Neurology 51:1555–1562
Olivier G (1960) Pratique Anthropologique. Vigot frères Editeurs, Paris
Pakkenberg H, Voight J (1964) Brain weight of the Danes: forensic material. Acta Anat 56:297–307
Peters M, Jäncke L, Staiger JF, Schlaug G, Huang Y, Steinmetz H (1998) Unsolved problems in comparing brain sizes in Homo sapiens. Brain Cognition 37:254–285
Pfefferbaum A, Mathalon DH, Sullivan EV, Rawles JM, Zipusky RB, Lim KO (1994) A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study of changes in brain morphology from infancy to late adulthood. Arch Neurol 51:874–887
Sahin B, Acer N, Sonmez OF, Emirzeoglu M, Basaloglu H, Uzun A, Bilgic S (2007) Comparison of four methods for the estimation of intracranial volume: a gold standard study. Clin Anat 20:766–773
Topinard P (1888) Le poids de l’Encéphale d’après les registres de Paul Broca. Mémoires de la société d’anthropologie 3:33–41
Whitwell JL, Crum WR, Watt HC, Fox NC (2001) Normalization of cerebral volumes by use of intracranial volume: implications for longitudinal quantitative MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 22:1483–1489
Witelson SF, Beresh H, Kigar DL (2006) Intelligence and brain size in 100 postmortem brains: sex, lateralization and age factors. Brain 129:386–398
Wolf H, Kruggel F, Hensel A (2003) The relationship between head size and intracranial volume in elderly subjects. Brain Res 973:74–80
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G (2006) User 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 31:116–128
Zilles K (1972) Biometric analysis of fresh volumes of various prosencephalic brain regions in 78 human adult brains. Gegenbaurs Morphologishes Jahrbuch 118:234–273
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricard, AS., Desbarats, P., Laurentjoye, M. et al. On two equations about brain volume, cranial capacity and age. Surg Radiol Anat 32, 989–995 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0650-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0650-4