Abstract
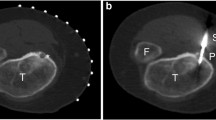
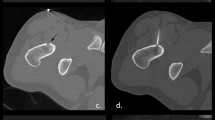
The purpose of this study was to analyze the clinical outcome of osteoid osteoma treated by thermal ablation after drill opening. A total of 17 patients and 20 procedures were included. All patients had typical clinical features (age, pain) and a typical radiograph showing a nidus. In 5 cases, additional histological specimens were acquired. After drill opening of the osteoid osteoma nidus, 12 thermal ablations were induced by laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) (9F Power-Laser-Set; Somatex, Germany) and 8 ablations by radiofrequency ablation (RFA) (RITA; StarBurst, USA). Initial clinical success with pain relief has been achieved in all patients after the first ablation. Three patients had an osteoid osteoma recurrence after 3, 9, and 10 months and were successfully re-treated by thermal ablation. No major complication and one minor complication (sensible defect) were recorded. Thermal ablation is a safe and minimally invasive therapy option for osteoid osteoma. Although the groups are too small for a comparative analysis, we determined no difference between laser- and radiofrequency-induced ablation in clinical outcome after ablation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcove RC, Heelan RT, Huvos AG, et al. (1991) Osteoid osteoma. Diagnosis, localization, and treatment. Clin Orthop 267:197–201
Lindner NJ, Scarborough M, Ciccarelli JM, et al. (1997) CT-controlled thermocoagulation of osteoid osteoma in comparison with traditional methods Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 135(6):522–527
Pfeiffer M, Sluga M, Windhager R et al. (2003) Surgical treatment of osteoid osteoma of the extremities Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 141(3):345–348
Sluga M, Windhager R, Pfeiffer M et al. (2002) Peripheral osteoid osteoma. Is there still a place for traditional surgery? J Bone Joint Surg Br 84(2):249–251
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Wolfe MW et al. (1998) Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(6):815–821
Rosenthal DI, Alexander A, Rosenberg AE et al. (1992) Ablation of osteoid osteomas with a percutaneously placed electrode: a new procedure Radiology 183(1):29–33
Campanacci M, Ruggieri P, Gasbarrini A et al. (1999) Osteoid osteoma. Direct visual identification and intralesional excision of the nidus with minimal removal of bone Bone Joint Surg Br 81(5):814–820
Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF et al. (2003) Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines J Vasc Intervent Radiol 14(9 Pt 2):S199–S202
Omary RA, Bettmann MA, Cardella JF et al. (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for the reporting and archiving of interventional radiology procedures J Vasc Intervent Radiol 14(9 Pt 2):S293–S295
Jaffe HL (1935) Osteoid osteoma: a benign osteoblastic tumor composed of osteoid and atypical bone Arch Surg 31:709–728
Mungo DV, Zhang X, O’Keefe RJ et al. (2002) COX-1 and COX-2 expression in osteoid osteomas J Orthop Res 20(1):159–162
Kneisl JS, Simon MA (1992) Medical management compared with operative treatment for osteoid-osteoma J Bone Joint Surg Am 74(2):179–185
Levy JM, Hubbard JO, Crowe JK (1982) Computed tomography—guided removal of an osteoid osteoma: a case report Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 5(1):14–15
Assoun J, Railhac JJ, Bonnevialle P et al. (1993) Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous resection with CT guidance Radiology 188(2):541–547
Amendola A, Vellet D, Willits K (1994) Osteoid osteoma of the neck of the talus: percutaneous, computed tomography-guided technique for complete excision Foot Ankle Int 15(8):429–432
Erdtmann B, Duda SH, Pereira P et al. (2001) CT-guided therapy of osteoid osteoma by drill trepanation of the nidus. Clinical follow-up results Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 173(8):708–713
Klose KC, Forst R, Vorwerk D et al. (1991) The percutaneous removal of osteoid osteomas via CT-guided drilling Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 155(6):532–537
Kohler R, Rubini J, Postec F et al. (1995) Treatment of osteoid osteoma by CT-controlled percutaneous drill resection. Apropos of 27 cases Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 81(4):317–325
Adam G, Keulers P, Vorwerk D et al. (1995) The percutaneous CT-guided treatment of osteoid osteomas: a combined procedure with a biopsy drill and subsequent ethanol injection Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 162(3):232–235
Adam G, Neuerburg J, Vorwerk D et al. (1997) Percutaneous treatment of osteoid osteomas: combonation of drill biopsy and subsequent ethanol injection Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 1(2):281–284
Sanhaji L, Gharbaoui IS, Hassani RE et al. (1996) A new treatment of osteoid osteoma: percutaneous sclerosis with ethanol under scanner guidance J Radiol 77(1):37–40
Duda SH, Schnatterbeck P, Harer T et al. (1997) Treatment of osteoid osteoma with CT-guided drilling and ethanol instillation Dtsch Med Wochenschr 122(16):507–510
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Torriani M et al. (2003) Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous treatment with radiofrequency energy Radiology 229(1):171–175
Vanderschueren GM, Taminiau AH, Obermann WR et al. (2002) Osteoid osteoma: clinical results with thermocoagulation Radiology 224(1):82–86
Lindner NJ, Ozaki T, Roedl R et al. (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in osteoid osteoma J Bone Joint Surg Br 83(3):391–396
Woertler K, Vestring T, Boettner F et al. (2001) Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and follow-up in 47 patients J Vasc Intervent Radiol 12(6):717–722
Cioni R, Armillotta N, Bargellini I, et al. (2004) CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol 14(7):1203–1208
Gangi A, Dietemann JL, Clavert JM et al. (1998) Treatment of osteoid osteoma using laser photocoagulation. Apropos of 28 cases Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 84(8):676–684
Witt JD, Hall-Craggs MA, Ripley P et al. (2000) Interstitial laser photocoagulation for the treatment of osteoid osteoma J Bone Joint Surg Br 82(8):1125–1128
Ghanem I, Collet LM, Kharrat K et al. (2003) Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma in children and adolescents J Pediatr Orthop B 12(4):244–252
Gallazzi MB, Arborio G, Garbagna PG et al. (2001) Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: technique and preliminary results Radiol Med (Torino) 102(5–6):329–334
Barei DP, Moreau G, Scarborough MT et al. (2000) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma Clin Orthop (373):115–124
Venbrux AC, Montague BJ, Murphy KP et al. (2003) Image-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for osteoid osteomas J Vasc Intervent Radiol 14(3):375–380
Sequeiros RB, Hyvonen P, Sequeiros AB et al. (2003) MR imaging-guided laser ablation of osteoid osteomas with use of optical instrument guidance at 0.23 T Eur Radiol 13(10):2309–2314
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gebauer, B., Tunn, PU., Gaffke, G. et al. Osteoid Osteoma: Experience with Laser- and Radiofrequency-Induced Ablation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29, 210–215 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0166-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0166-6