Abstract
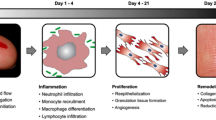
Hypertrophic scars, resulting from alterations in the normal processes of cutaneous wound healing, are characterized by proliferation of dermal tissue with excessive deposition of fibroblast-derived extracellular matrix proteins, especially collagen, over long periods, and by persistent inflammation and fibrosis. Hypertrophic scars are among the most common and frustrating problems after injury. As current aesthetic surgical techniques become more standardized and results more predictable, a fine scar may be the demarcating line between acceptable and unacceptable aesthetic results. However, hypertrophic scars remain notoriously difficult to eradicate because of the high recurrence rates and the incidence of side effects associated with available treatment methods. This review explores the various treatment methods for hypertrophic scarring described in the literature including evidence-based therapies, standard practices, and emerging methods, attempting to distinguish those with clearly proven efficiency from anecdotal reports about therapies of doubtful benefits while trying to differentiate between prophylactic measures and actual treatment methods. Unfortunately, the distinction between hypertrophic scar treatments and keloid treatments is not obvious in most reports, making it difficult to assess the efficacy of hypertrophic scar treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acikel, C., Ergun, O., Ulkur, E., Servet, E., Celikoz, B.: Camouflage of self-inflicted razor blade incision scars with carbon dioxide laser resurfacing and thin skin grafting. Plast Reconstr Surg 116, 798 (2005)
Akita, S., Akino, K., Imaizumi, T., Tanaka, K., et al.: The quality of pediatric burn scars is improved by early administration of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Burn Care Res 27, 333 (2006)
Allison, K.P., Kiernan, M.N., Waters, R.A., Clement, R.M.: Pulsed dye laser treatment of burn scars: Alleviation or irritation? Burns 29, 207 (2003)
Apfelberg, D.B., Maser, M.R., White, D.N., Lash, H.: Failure of carbon dioxide laser excision of keloids. Lasers Surg Med 9, 382 (1989)
Alster, T.: Laser scar revision: Comparison study of 585- nm pulsed-dye laser with and without intralesional corticosteroids. Dermatol Surg 29, 25 (2003)
Alster, T.S.: Laser treatment of hypertrophic scars, keloids, and striae. Dermatol Clin 15, 419 (1997)
Alster, T.S., Handrick, C.: Laser treatment of hypertrophic scars, keloids, and striae. Semin Cutan Med Surg 19, 287 (2000)
Alster, T.S., Nanni, C.A.: Pulsed-dye laser treatment of hypertrophic burn scars. Plast Reconstr Surg 102, 2190 (1998)
Alster, T.S., West, T.B.: Treatment of scars: A review. Ann Plast Surg 39, 418 (1997)
Amicucci, G., Schietroma, M., Rossi, M., Mazzotta, C.: Silicone occlusive sheeting vs silicone cushion for the treatment of hypertrophic and keloid scars: A prospective randomized study. Ann Ital Chir 76, 79 (2005)
Apikian, M., Goodman, G.: Intralesional 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of keloid scars. Australas J Dermatol 45, 140 (2004)
Asilian, A., Darougheh, A., Shariati, F.: New combination of triamcinolone, 5-fluorouracil, and pulsed-dye laser for treatment of keloid and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg 32, 907 (2006)
Atiyeh, B.S., Al-Amm, C.A., El-Musa, K.: Improved scar quality following primary and secondary healing of cutaneous wounds. Aesth Plast Surg 27, 411 (2003)
Atiyeh, B.S., Al-Amm, C.A., El-Musa, K.A., Sawwaf, A., Dham, R.: Scar quality and physiologic barrier function restoration following moist and moist exposed dressings of partial thickness wounds. Dematol Surg 29, 14 (2003)
Atiyeh, B.S., Costagliola, M., Hayek, S.N.: Keloid or hypertrophic scar: The controversy: Review of the Literature. Ann Plast Surg 54, 676 (2005)
Atiyeh, B.S., Ioannovich, J., Al-Amm, C.A., El-Musa, K.A., Dham, R.: Improving scar quality: A prospective clinical study. Aesth Plast Surg 26, 470 (2002)
Atkinson, J.A., McKenna, K.T., Barnett, A.G., McGrath, D.J., Rudd, M.A.: Randomized, controlled trial to determine the efficacy of paper tape in preventing hypertrophic scar formation in surgical incisions that traverse Langer's skin tension lines. Plast Reconstr Surg 116, 1648 (2005)
Baisch, A., Riedel, F.: Hyperplastic scars and keloids: Part I. Basics and prevention. HNO 54, 893 (2006)
Baum, T.M., Busuito, M.J.: Use of a glycerin-based gel sheeting in scar management. Adv Wound Care 11, 40 (1998)
Baumann, L.S., Spencer, J.: The effects of topical vitamin E on the cosmetic appearance of scars. Dermatol Surg 25, 311 (1999)
Bayat, A., McGrouther, D.A.: Clinical management of skin scarring. Skinmed 4, 165 (2005)
Behroozan, D.S., Goldberg, L.H., Dai, T., Geronemus, R.G., Friedman, P.M.: Fractional photothermolysis for the treatment of surgical scars: A case report. J Cosmet Laser Ther 8, 35 (2006)
Bellew, S.G., Weiss, M.A., Weiss, R.A.: Comparison of intense pulsed light to 595-nm long-pulsed pulsed dye laser for treatment of hypertrophic surgical scars: A pilot study. J Drugs Dermatol 4, 448 (2005)
Berman, B., Dunan, M.R.: Short-term keloid treatment in vivo with human interferon \(\alpha \)2b results in a selective and persistent normalization of keloid fibroblast collagen, glycosaminoglycan, and collagenase production in vitro. J Am Acad Dermatol 21, 694 (1989)
Berman, B., Flores, F.: Comparison of a silicone gel-filled cushion and silicon gel sheeting for the treatment of hypertrophic or keloid scars. Dermatol Surg 25, 484 (1999)
Berman, B., Flores, F.: Recurrence rates of excised keloids treated with postoperative triamcinolone acetonide injections or interferon alfa-2b injections. J Am Acad Dermatol 37, 755 (1997)
Berman, B., Flores, F.: The treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Eur J Dermatol 8, 591 (1998)
Beuth, J., Hunzelmann, N., Van Leendert, R., Basten, R., et al.: Safety and efficacy of local administration of contractubex to hypertrophic scars in comparison to corticosteroid treatment: Results of a multicenter, comparative epidemiological cohort study in Germany. Vivo 20, 277 (2006)
Bock, O., Schmid-Ott, G., Malewski, P., Mrowietz, U.: Quality of life of patients with keloid and hypertrophic scarring. Arch Dermatol Res 297, 433 (2006)
Bombaro, K.M., Engrav, L.H., Carrougher, G.J., Wiechman, S.A., et al.: What is the prevalence of hypertrophic scarring following burns? Burns 29, 299 (2003)
Bonte, F., Dumas, M., Chaudagne, C., Meybeck, A.: Asiaticoside and madecassoside activity on human fibroblast type I and III collagen. Ann Pharm Franc 53, 38 (1995)
Borgognoni, L., Reali, U.M.: Intralesional hyaluronic acid treatment of pathological scars. Ann Plast Surg 38, 308 (1997)
Bosse, J.P., Papillon, J., Frenette, G., Dansereau, J., et al.: Clinical study of a new antikeloid agent. Ann Plast Surg 3, 13 (1979)
Boutli-Kasapidou, F., Tsakiri, A., Anagnostou, E., Mourellou, O.: Hypertrophic and keloidal scars: An approach to polytherapy. Int J Dermatol 44, 324 (2005)
Boyce, D.E., Bantick, G., Murison, M.S.: The use of ADCONT/ N glycosaminoglycan gel in the revision of tethered scars. Br J Plast Surg 53, 403 (2000)
Branagan, M., Chenery, D.H., Nicholson, S.: Use of the infrared attenuated total reflectance spectroscopy for the in vivo measurement of hydration level and silicone distribution in the stratum corneum following skin coverage by polymeric dressings. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol 13, 157 (2000)
Brissett, A.E., Sherris, D.A.: Scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. Facial Plast Surg 17, 263 (2001)
Brown, C.A.: A comparison of the outcomes of two clinical audits of burn pressure garment satisfaction and compliance in Saudi Arabia. Burns 27, 342 (2001)
Burd, A., Huang, L.: Hypertrophic response and keloid diathesis: Two very different forms of scar. Plast Reconstr Surg 116, 150e (2005)
Carney, S.A., Cason, C.G., Gowar, J.P., Stevenson, J.H., et al.: Cica care gel sheeting in the management of hypertrophic scarring. Burns 20, 163 (1994)
Chan, H.H., Wong, D.S., Ho, W.S., Lam, L.K., Wei, W.: The use of pulsed-dye laser for the prevention and treatment of hypertrophic scars in Chinese persons. Dermatol Surg 30, 987 (2004)
Chan, K.Y., Lau, C.L., Adeeb, S.M., Somasundaram, S., Nasir-Zahari, M.: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, prospective clinical trial of silicone gel in prevention of hypertrophic scar development in median sternotomy wound. Plast Reconstr Surg 116, 1013 (2005)
Chang, C.C., Kuo, Y.F., Chiu, H., Lee, J.L., et al.: Hydration, not silicone, modulates the effects of keratinocytes on fibroblasts. J Surg Res 59, 705 (1995)
Chang, P., Laubenthal, K.N., Lewis, R.W., Rosenquist, M., et al.: Prospective, randomized study of the efficacy of pressure garment therapy in patients with burns. J Burn Care Rehabil 16, 473 (1995)
Chen, M.A., Davidson, T.M.: Scar management: Prevention and treatment strategies. Curr Opinion Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13, 242 (2005)
Cheng, J.C.Y., Evans, J.H., Leung, K.S., Clark, J.A., et al.: Pressure therapy in the treatment of postburn hypertrophic scar: A clinical look into its usefulness and fallacies by pressure monitoring. Burns 10, 154 (1984)
Chowdri, N.A., Masarat, M., Mattoo, A., Darzi, M.A.: Keloids and hypertrophic scars: Results with intraoperative and serial postoperative corticosteroid injection therapy. Aust N Z J Surg 69, 655 (1999)
Chung, V.Q., Kelley, L., Marra, D., Jiang, S.B.: Onion extract gel versus petrolatum emollient on new surgical scars: A prospective double-blinded study. Dermatol Surg 32, 193 (2006)
Collins, J.: Pressure techniques for the prevention of hypertrophic scar. Clin Plast Surg 19, 733 (1992)
Copcu, E., Sivrioglu, N., Oztan, Y.: Combination of surgery and intralesional verapamil injection in the treatment of the keloid. J Burn Care Rehab 25, 1 (2004)
Costa, A.M., Peyrol, S., Porto, L.C., Comparin, J.P., et al.: Mechanical forces induce scar remodeling study in non-pressure- treated versus pressure-treated hypertrophic scars. Am J Pathol 155, 1671 (1999)
Costagliola M, Rougé D, Gavroy JP, Ster F (1994) Quantitative and qualitative aspect of the vitro pressure test. 9e`me Congre's de l'International Society for Burn Injury, Paris
Cruz-Korchin, N.I.: Effectiveness of silicone sheets in the prevention of hypertrophic breast scars. Ann Plast Surg 37, 345 (1996)
Davey, R.B., Wallis, K.A., Bowering, K.: Adhesive contact media: An update on graft fixation and burn scar management. Burns 17, 313 (1991)
De Cubber, J.: A silicone elastomer manipulation technique for the production of medical devices. J Facial Somato Prosthetics 4, 15 (1998)
De Cuyper, C.: Permanent make-up: Indications and complications. Kosmet Med 27, 56 (2006)
De Groot, A.C., Berretty, P.M.J., Ginkel, G.J.W., den Henjst, C.W., et al.: Allergic contact dermatitis from tocopheryl acetate in cosmetic creams. Contact Dermatitis 25, 302 (1991)
De Oliveira, G.V., Nunes, T.A., Magna, L.A., Cintra, M.L., et al.: Silicone versus nonsilicone gel dressings: A controlled trial. Dermatol Surg 27, 721 (2001)
Desmoulière, A., Regard, M., Darby, I., Gabbiani, G.: Apoptosis mediates the decrease in cellularity during the transition between granulation tissue and scar. Am J Pathol 146, 56 (1995)
Dinh, Q., Veness, M., Richards, S.: Role of adjuvant radiotherapy in recurrent earlobe keloids. Australas J Dermatol 45, 162 (2004)
Dolynchuk, K.N., Ziesmann, M., Serletti, J.M.: Topical putrescine (Fibrostat) in treatment of hypertrophic scars: Phase II study. Plast Reconstr Surg 97, 117 (1996)
Eberlein, A., Schepler, H., Spilker, G., Altmeyer, P., Hartmann, B.: Erbium:YAG laser treatment of post-burn scars: Potentials and limitations. Burns 31, 15 (2005)
Espana, A., Solano, T., Quintanilla, E.: Bleomycin in the treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars by multiple needle punctures. Dermatol Surg 27, 23–27 (2001)
Esselman, P.C., Thombs, B.D., Magyar-Russell, G., Fauerbach, J.A.: Burn rehabilitation: State of the science. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 85, 383 (2006)
Feng, X., Tan, J., Pan, Y., Wu, Q., et al.: Control of hypertrophic scar from inception by using xenogenic (porcine) acellular dermal matrix (ADM) to cover deep second-degree burn. Burns 32, 293 (2006)
Field, T., Peck, M., Hernandez-Rief, M., Krugman, S., et al.: Postburn itching, pain, and psychological symptoms are reduced with massage therapy. J Burn Care Rehabil 21, 189 (2000)
Field, T., Peck Krugman, S., Tuchel, T., Schanberg, S., et al.: Burn injuries benefit from massage therapy. J Burn Care Rehabil 19, 241 (1998)
Fitzpatrick, R.E.: Treatment of inflamed hypertrophic scars using intralesional 5-FU. Dermatol Surg 25, 224 (1999)
Fricke, N.B., Omnell, M.L., Dutcher, K.A., Hollender, L.G., Engrav, L.H.: Skeletal and dental disturbances in children after facial burns and pressure garment use: A 4 year follow up. J Burn Care Rehabil 20, 239 (1999)
Fulton Jr., J.E.: Silicone gel sheeting for the prevention and management of evolving hypertrophic and keloid scars. Dermatol Surg 21, 947 (1995)
Gailloud-Matthieu, M.C., Raffoul, W., Egloff, D.V.: Hypertrophic scars and keloids: Which therapeutic options today? Rev Med Suisse Romande 119, 721 (1999)
George, W.M.: Linear lymphatic hypopigmentation after intralesional corticosteroid injection: Report of two cases. Cutis 64, 61 (1999)
Gerasimenko, MIu, Iusova, ZhIu, Zenger, V.G., Kazantseva, I.A.: Differentiated approach to medicine phonophoresis in complex treatment of cicatrical deformations. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk 6, 29 (2005)
Gerow, F.J., Hardy, S.B., Spira, M., Law, S.W.: Immersion treatment for burns: An experimental study. Surg Forum 14, 32 (1963)
Ghahary, A., Shen, Y.J., Scott, P.G., Tredget, E.E.: Immunolocalization of TGF-beta 1 in human hypertrophic scar and normal dermal tissues. Cytokine 7, 184 (1995)
Gibbons, M., Zuker, R., Brown, M., Candlish, S., et al.: Experience with silastic gel sheeting in pediatric scarring. J Burn Care Rehabil 15, 69 (1994)
Gilman, T.H.: Silicone sheet for treatment and prevention of hypertrophic scar: A new proposal for the mechanism of efficacy. Wound Rep Reg 11, 235–236 (2003)
Giele, H.P., Liddiard, K., Currie, K., Wood, F.M.: Direct measurement of cutaneous pressures generated by pressure garments. Burns 23, 137 (1997)
Giele, H., Liddiard, K., Booth, K., Wood, F.: Anatomical variations in pressures generated by pressure garments. Plast Reconstr Surg 101, 399 (1998)
Giugliano, G., Pasquali, D., Notaro, A., Brongo, S., et al.: Verapamil inhibits interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor production in primary cultures of keloid fibroblasts. Br J Plast Surg 56, 804 (2003)
Gold, M.H.: A controlled clinical trail of topical silicone gel sheeting in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. J Am Acad Dermatol 30, 506 (1994)
Gold, M.H., Foster, T.D., Adair, M.A., Burlison, K., Lewis, T.: Prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids by the prophylactic use of topical silicone gel sheets following a surgical procedure in an office setting. Dermatol Surg 27, 641 (2001)
Gopinath, D., Ahmed, M.R., Gomathi, K.: Dermal wound healing processes with curcumin induced collagen films. Biomaterials 25, 1911 (2004)
Govindarajan, R., Vijayakumar, M., Rao, C., Shirwaikar, A., et al.: Healing potential of Anogeissus latifolia for dermal wounds in rats. Acta Pharm 54, 331 (2004)
Hamanova, H., Broz, L.: Topigel in the treatment of hypertrophic scars after burn injuries. Acta Chir Plast 44, 18 (2002)
Hambleton, J., Shakespeare, P., Pratt, B.: The progress of hypertrophic scars monitored by ultrasound measurements of thickness. Burns 18, 301 (1992)
Hanasono, M.M., Lum, J., Carroll, L.A., Mikulec, A.A., Koch, R.J.: The effect of silicone gel on basic fibroblast growth factor levels in fibroblast cell culture. Arch Facial Plast Surg 6, 88 (2004)
Har-Shai, Y., Amar, M., Sabo, E.: Intralesional cryotherapy for enhancing the involution of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Plast Reconstr Surg 111, 1841 (2003)
Har-Shai, Y., Lindenbaum, E., Tendler, M., Gamliel-Lazarovich, A., et al.: Negatively charged static electricity stimulation as a possible mechanism for enhancing the involution of hypertrophic and keloid scars. Isr Med Assoc J 1, 203 (1999)
Harumi, M., Miyuki, N., Hideo, M., Kiyokazu, K.: Effects of clothing pressure exerted on a trunk on heart rate, blood pressure, skin blood flow, and respiratory function. J Textile Mach Soc Jpn 54, 57 (2001)
Havlik, R.J.: Vitamin E and wound healing: Safety and efficacy reports. Plast Reconstr Surg 100, 1901 (1997)
Hirshowitz, B., Ullmann, Y., Har-Shai, Y., Vilenski, A., Peled, I.J.: Silicone occlusive sheeting (SOS) in the management of hypertrophic scarring, including the possible mode of action of silicone, by static electricity. Eur J Plast Surg 16, 5 (1993)
Ho, W.S., Ying, S.Y., Chan, P.C., Chan, H.H.: Use of onion extract, heparin, allantoin gel in prevention of scarring in Chinese patients having laser removal of tattoos: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Dermatol Surg 32, 891 (2006)
Holme, S.A., Beattie, P.E., Fleming, C.J.: Cosmetic camouflage advice improves quality of life. Br J Dermatol 147, 946 (2002)
Hulsbergen-Henning, J.P., Roskam, Y., van Gemert, M.J.: Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with an argon laser. Lasers Surg Med 6, 72 (1986)
Hubbard, M., Masters, I.B., Williams, G.R., Chang, A.B.: Severe obstructive sleep apnea secondary to pressure garments used in the treatment of hypertrophic burn scars. Eur Respir J 16, 1205 (2000)
Jackson, B.A., Shelton, A.J., McDaniel, D.H.: Pilot study evaluating topical onion extract as treatment for postsurgical scars. Dermatol Surg 25, 267 (1999)
Jaros E, Priborsky J, Klein L (1999) Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with cryotherapy. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) Suppl 42:61
Jenkins, M., Alexander, J.W., Mac Millian, B.G.: Failure of topical steroids and vitamin E to reduce postoperative scar formation following reconstructive surgery. J Burn Care Rehabil 7, 309 (1986)
Johnson, J., Greenspan, B., Gorga, D., Nagler, W., Goodwin, C.: Compliance with pressure garment use in burn rehabilitation. J Burn Care Rehabil 15, 181 (1994)
Jurjus A, Atiyeh BS, Abdallah IM, Jurjus RA, et al. Pharmacological modulation of wound healing in experimental burns. Burns 2007 in press
Kang, N., Sivakumar, B., Sanders, R., Nduka, C., Gault, D.: Intralesional injections of collagenase are ineffective in the treatment of keloid and hypertrophic scars. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59, 693 (2006)
Kapoor, M., Howard, R., Hall, I., Appleton, I.: Effects of epicatechin gallate on wound healing and scar formation in a full thickness incisional wound healing model in rats. Am J Pathol 165, 299 (2004)
Katz, B.E.: Silicone gel sheeting in scar therapy. Cutis 56, 65 (1995)
Khoosal, D., Goldman, R.D.: Vitamin E for treating children's scars: Does it help reduce scarring? Can Family Physician 52, 855 (2006)
Kono, T., Ercocen, A.R., Nakazawa, H., Nozaki, M.: Treatment of hypertrophic scars using a long-pulsed dye laser with cryogen- spray cooling. Ann Plast Surg 54, 487 (2005)
Kopp, J., Wang, G.Y., Kulmburg, P., Schultze-Mosgau, S., et al.: Accelerated wound healing by in vivo application of keratinocytes overexpressing KGF. Mol Ther 10, 86 (2004)
Kosaka, M.: The current therapy and prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Skin Res 3, 628 (2004)
Kosaka, M., Kamiishi, H.: New concept of balloon-compression wear for the treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Plast Reconstr Surg 108, 1454 (2001)
Kuhn, M.A., Moffit, M.R., Smith, P.D., Lyle, W.G., et al.: Silicone sheeting decreases fibroblast activity and downregulates TGFbeta2 in hypertrophic scar model. Int J Surg Invest 2, 467 (2001)
Larrabee Jr., W.F., East, C.A., Jaffe, H.S., Stephenson, C., Petrson, K.E.: Intralesional interferon [gamma] treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116, 1159 (1990)
Larson, D.L., Abston, S., Evans, E.B., Dobrkovsky, M., Linares, H.A.: Techniques for decreasing scar formation and contractures in the burned patient. J Trauma 11, 807 (1971)
Larson, D.L., Abston, S., Willis, B., Linares, H.A., et al.: Contracture and scar formation in the burned patient. Clin Plast Surg 1, 653 (1974)
Lebwohl, M.: From the literature: Intralesional 5-FU in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids: Clinical experience. J Am Acad Dermatol 42, 677 (2000)
Lee, D.K., Serkin, A.L.: Carbon dioxide laser and Apligraf for a painful plantar hypertrophic scar. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 94, 61 (2004)
Lee, J.P., Jalili, R.B., Tredget, E.E., Demare, J.R., Ghahary, A.: Antifibrogenic effects of liposome-encapsulated IFN-alpha2b cream on skin wounds in a fibrotic rabbit ear model. J Interferon Cytokine Res 25, 627 (2005)
Lee, S.M., Ngim, C.K., Chan, Y.Y., Ho, M.J.: A comparison of Sil-K and Epiderm in scar management. Burns 22, 483 (1996)
LeVier, R.R., Harrison, M.C., Cook, R.R., Lane, T.H.: What is silicone? Plast Reconstr Surg 92, 163 (1993)
Leung, K., Cheng, J., Ma, G., Clark, J., Leung, P.: Complications of pressure therapy for postburn hypertrophic scar. Burns 10, 434 (1984)
Leung, P.C., Ng, M.: Pressure therapy for hypertrophic scars resulting from burns. Burns 6, 244 (1980)
Leung, P., Ng, M.: Pressure treatment for hypertrophic scars resulting from burns. Burns 6, 244 (1980)
Linares, H.A.: From wound to scar. Burns 22, 339 (1996)
Linares, H.A., Larson, D.L., Willis-Galstaun, B.A.: Historical notes on the use of pressure in the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. Burns 19, 17 (1993)
Loladze, M., Alibegashvili, M., Turmanidze, T.S., Iashvili, B., et al.: Use of bilidase for the treatment of experimental hypertrophic postburn cicatrices. Bull Exp Biol Med 139, 98 (2005)
Lu, L., Saulis, A.S., Liu, W.R., Roy, N.K., et al.: The temporal effects of anti-TGF-beta1, -2, and -3 monoclonal antibody on wound healing and hypertrophic scar formation. J Am College Surg 201, 391 (2005)
Lupton, J.R., Alster, T.S.: Laser scar revision. Dermatol Clin 20, 55 (2002)
Macintyre, L., Baird, M.: Pressure garments for use in the treatment of hypertrophic scars: A review of the problems associated with their use. Burns 32, 10 (2006)
Magliaro, A., Gianfaldoni, R., Cervadoro, G.: Treatment of burn scars with a gel based on allantoin and sulfomucopolysaccharides. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 134, 153 (1999)
Majan, J.I.: Evaluation of a self-adherent soft silicone dressing for the treatment of hypertrophic postoperative scars. J Wound Care 15, 193 (2006)
Malaker, K., Vijayraghavan, K., Hodson, I., Al Yafi, T.: Retrospective analysis of treatment of unresectable keloid with primary radiation over 25 years. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 16, 290 (2004)
Malick, M.H., Carr, J.A.: Flexible elastomer molds in burn scar control. Am J Occup Ther 34, 603 (1980)
Manuskiatti, W., Fitzpatrick, R.E.: Treatment response of keloidal and hypertrophic sternotomy scars: Comparison among intralesional corticosteroid, 5-fluorouracil, and 585-nm flashlamp- pumped pulsed-dye laser treatments. Arch Dermatol 138, 1149 (2002)
Martin, A.: The use of antioxidants in healing. Dermatol Surg 22, 156 (1996)
McCraw, J.B., McCraw, J.A., McMellin, A., Bettencourt, N.: Prevention of unfavorable scars using early pulse-dye laser treatments: A preliminary report. Ann Plast Surg 42, 7 (1999)
Meier, K., Nanney, L.B.: Emerging new drugs for scar reduction. Expert Opin Emerging Drugs 11, 39 (2006)
Meshkinpour, A., Ghasri, P., Pope, K., Lyubovitsky, J.G., et al.: Treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids with a radiofrequency device: A study of collagen effects. Lasers Surg Med 37, 343 (2005)
Miller, J., Hardy, S.B., Spira, M.: Treatment of burns of the hand with silicone dressing and early motion: Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg 47, 938 (1965)
Miller, M.C., Nanchahal, J.: Advances in the modulation of cutaneous wound healing and scarring. BioDrugs 19, 363 (2005)
Mizutani, H., Yoshida, T., Nouchi, N., Hamanaka, H., Shimizu, M.: Topical tocoretinate improved hypertrophic scar, skin sclerosis in systemic sclerosis, and morphea. J Dermatol 26, 11–17 (1999)
Murison, M., James, W.: Preliminary evaluation of the efficacy of Dermatix silicone gel in the reduction of scar elevation and pigmentation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 59, 437 (2006)
Musgrave, M., Umraw, N., Fish, J., Gomez, M., et al.: The effect of silicone gel sheets on perfusion of hypertrophic burn scars. J Burn Care Rehab 23, 208 (2002)
Mustoe, T.A., Cooter, R.D., Gold, M.H., Hobbs, F.D., et al.: International clinical recommendations on scar management. Plast Reconstr Surg 110, 560 (2002)
Mutalik, S.: Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 71, 3 (2005)
Nachbar, F., Korting, H.C.: The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin. J Mol Med 73, 7 (1995)
Naeini, F.F., Najafian, J., Ahmadpour, K.: Bleomycin tattooing as a promising therapeutic modality in large keloids and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg 32, 1023 (2006)
Nakaoka, H., Miyauchi, S., Miki, Y.: Proliferating activity of dermal fibroblasts in keloids and hypertrophic scars. Acta Derm Venereol 75, 102 (1995)
Nedelec, B., Ghahary, A., Scott, P., Tredget, E.: Control of wound contraction: Basic and clinical features. Hand Clin 16, 289 (2000)
Niessen, F., Spauwen, P., Robinson, P., Fidler, V., Kon, M.: The use of silicone occlusive sheeting (Sil-K) and silicone occlusive gel (Epiderm) in the prevention of hypertrophic scar formation. Plast Reconstr Surg 102, 1962 (1998)
Niessen, F.B., Spauwen, P.H.M., Schalkwijk, J., Kon, M.: On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: A review. Plast Reconstr Surg 104, 1435 (1999)
Nikkonen, M.M., Pitkanen, J.M., Al-Qattan, M.M.: Problems associated with the use of silicone gel sheeting for hypertrophic scars in the hot climate of Saudi Arabia. Burns 27, 498 (2001)
Norris, J.E.: The effect of carbon dioxide laser surgery on the recurrence of keloids. Plast Reconstr Surg 87, 44 (1991)
Norris, J.E.C.: Superficial X-ray therapy in keloid management: A retrospective study of 24 cases and literature review. Plast Reconstr Surg 95, 1051 (1995)
Nouri, K., Vidulich, K., Rivas, M.P.: Lasers for scars: A review. J Cosmet Dermatol 5, 14 (2006)
O'Brien L, Pandit A (2006) Silicon gel sheeting for preventing and treating hypertrophic and keloid scars. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 25(1):CD003826
Ogawa, R., Mitsuhashi, K., Hyakusoku, H., Miyashita, T.: Postoperative electron-beam irradiation therapy for keloids and hypertrophic scars: Retrospective study of 147 cases followed for more than 18 months. Plast Reconstr Surg 111, 547 (2003)
Panin, G., Strumia, R., Ursini, F.: Topical alpha-tocopherol acetate in the bulk phase: Eight years of experience in skin treatment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1031, 443 (2004)
Patino, O., Novick, C., Merlo, A., Benaim, F.: Massage in hypertrophic scars. J Burn Care Rehabil 20, 268 (1999)
Patterson, R.P., Fisher, S.V.: The accuracy of electrical transducers for the measurement of pressure applied to the skin. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 26, 450 (1979)
Peacock, E.E., Madden, J.W., Trier, W.C.: Biologic basis for treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scar. South Med J 63, 755 (1970)
Pekins, K., Davey, R.B., Wallis, K.A.: Silicone gel: A new treatment for burn scars and contractures. Burns 9, 201 (1982)
Phan, T.T., Lim, I.J., Chan, S.Y., Tan, E.K., et al.: Signaling in keloid-derived fibroblasts by quercetin/smad signaling in keloidderived fibroblasts by quercetin: Implications for the treatment of excessive scars. J Trauma 57, 1032 (2004)
Poveda A, Campech M, Gavroy JP, Ster F (1998) Le massage «en brûlure»: Formes topographiques et chronologiques. 18 Congrés de la Société Française d'Etude et de Traitement de la Brûlure, SFETB, Saint Gervais
Puzey, G.: The use of pressure garments on hypertrophic scars. J Tissue Viability 12, 11 (2002)
Quinn, K.J., Evans, J.H., Courtney, J.M., Gaylor, J.D., Reid, W.H.: Nonpressure treatment of hypertrophic scars. Burns Incl Therm Inj 12, 102 (1985)
Rawlins, J.M., Lam, W.L., Karoo, R.O., Naylor, I.L., Sharpe, D.T.: Pentoxifylline inhibits mature burn scar fibroblasts in culture. Burns 32, 42 (2006)
Rayner, K.: The use of pressure therapy to treat hypertrophic scarring. J Wound Care 9, 151 (2000)
Reid, W.H., Evans, J.H., Naismith, R.S., Tully, A.E., Sherwin, S.: Hypertrophic scarring and pressure therapy. Burns 13, S29 (1987)
Reno, F., Sabbatini, M., Stella, M., Magliacani, G., Cannas, M.: Effect of in vitro mechanical compression on Epilysin (matrix metalloproteinase-28) expression in hypertrophic scars. Wound Repair Regen 13, 255 (2005)
Reiken, S.R., Wolfort, S.F., Berthiaume, F., Compton, C., et al.: Control of hypertrophic scar growth using selective photothermolysis. Lasers Surg Med 21, 7 (1997)
Reiffel, R.S.: Prevention of hypertrophic scars by long-term paper tape application. Plast Reconstr Surg 96, 1715 (1995)
Remlinger, K.A.: Cutaneous reactions to chemotherapy drugs: The art of consultation. Arch Dermatol 139, 77 (2003)
Reno, F., Grazianetti, P., Cannas, M.: Effects of mechanical compression on hypertrophic scars: Prostaglandin E2 release. Burns 27, 215 (2001)
Reno, F., Sabbatini, M., Lombardi, F., Stella, M., et al.: In vitro mechanical compression induces apoptosis and regulates cytokines release in hypertrophic scars. Wound Rep Reg 11, 331 (2003)
Ricketts, C.H., Martin, L., Faria, D.T., Saed, G.M., Fivenson, D.P.: Cytokine mRNA changes during the treatment of hypertrophic scars with silicone and nonsilicone gel dressings. Dermatol Surg 22, 955 (1996)
Rockwell, W.B., Cohen, I.K., Ehrlich, H.P.: Keloids and hypertrophic scars: A comprehensive review. Plast Reconstr Surg 84, 827 (1989)
Roques, C.: Massage applied to scars. Wound Repair Regen 10, 126 (2002)
Rose, M.P., Deitch, E.A.: The clinical use of a tubular compression bandage, Tubigrip, for burn-scar therapy: A critical analysis. Burns 12, 58 (1985)
Roseborough, I.E., Grevious, M.A., Lee, R.C.: Prevention and treatment of excessive dermal scarring. J Natl Med Assoc 96, 108 (2004)
Rusciani, L., Rossi, G., Bono, R.: Use of cryotherapy in the treatment of keloids. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 19, 529 (1993)
Sanders, K.W., Gage-White, L., Stucker, F.J.: Topical mitomycin C in the prevention of keloid scar recurrence. Arch Facial Plast Surg 7, 172 (2005)
Saray, Y., Gulec, A.T.: Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with dermojet injections of bleomycin: A preliminary study. Int J Dermatol 44, 777 (2005)
Saulis, A., Mogford, J.H., Mustoe, T.A.: Effect of Mederma on hypertrophic scarring in the rabbit ear model. Plast Reconstr Surg 110, 177 (2002)
Sawada, Y., Urushidate, S., Nihei, Y.: Hydration and occlusive treatment of a sutured wound. Ann Plast Surg 41, 508 (1998)
Sawada, Y., Sone, K.: Treatment of scars and keloids with a cream containing silicone oil. Br J Plast Surg 43, 683 (1990)
Sawada, Y., Sone, K.: Hydration and occlusion treatment for hypertrophic scars and keloids. Br J Plast Surg 45, 599 (1992)
Schmidt, A., Gassmueller, J., Hughes-Formella, B., Bielfeldt, S.: Treating hypertrophic scars for 12 or 24 hours with a self-adhesive hydroactive polyurethane dressing. J Wound Care 10, 149 (2001)
Schultze-Mosgau, S., Blaese, M.A., Grabenbauer, G., Wehrhan, F., et al.: Smad-3 and Smad-7 expression following antitransforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFbeta1)-treatment in irradiated rat tissue. Radiother Oncol 70, 249 (2004)
Shakespeare, P.G., van Reeterghem, L.: Some observations on the surface structure of collagen in hypertrophic scars. Burns 11, 175 (1985)
Sheridan, R.L., MacMillan, K., Donelan, M., Choucair, R., et al.: Tunable dye laser neovessel ablation as an adjunct to the management of hypertrophic scarring in burned children: Pilot trial to establish safety. J Burn Care Rehabil 18, 317 (1997)
Sherris, D.A., Larrabee Jr., W.F., Murakami, C.S.: Management of scar contractures, hypertrophic scars, and keloids. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 28, 1057 (1995)
Shmoilov, A.M., Rudenskaya, G.N., Isaev, V.A., Baydakov, A.V., et al.: A comparative study of collagenase complex and new homogeneous collagenase preparations for scar treatment. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 16, 285 (2006)
Silfen, R., Amir, A., Hauben, D.J., Calderon, S.: Effect of facial pressure garments for burn injury in adult patients after orthodontic treatment. Burns 27, 409 (2001)
Slemp, A.E., Kirschner, R.E.: Keloids and scars: A review of keloids and scars, their pathogenesis, risk factors, and management. Curr Opin Pedatr 18, 396 (2006)
Smeets, L., Grandjean, F.-X., Nickers, P., Deleuze, J.-P., et al.: How I treat fibroproliferative scars. Rev Med Liege 61, 11 (2006)
So, K., Umraw, N., Scott, J., Campbell, K., et al.: Effects of enhanced patient education on compliance with silicone gel sheeting and burn scar outcome: A randomized prospective study. J Burn Care Rehabil 24, 411 (2003)
Sproat, J.E., Dalcin, A., Weitauer, N., Roberts, R.S.: Hypertrophic sternal scars: Silicone gel sheeting versus kenalog injection treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 90, 988 (1992)
Staley, M.J., Richard, R.L.: Use of pressure to treat hypertrophic burn scars. Adv Wound Care 10, 44 (1997)
Stewart, R., Bhagwanjee, A.M., Mbakaza, Y., Binase, T.: Pressure garment adherence in adult patients with burn injuries: An analysis of patient and clinician perceptions. Am J Occup Ther 54, 598 (2000)
Su, C.W., Alizadeh, K., Boddie, A., Lee, R.C.: The problem scar. Clin Plast Surg 25, 451 (1998)
Suetak, T., Sasai, S., Zhen, Y.X., Tagami, H.: Effects of silicone gel sheet on the stratum corneum hydration. Br J Plast Surg 53, 503 (2000)
Sumitra, M., Manikandau, P., Suguna, L.: Efficacy of Butea monosperma on dermal wounds in rats. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37, 566 (2005)
Tredget, E.E., Nedelec, B., Scott, P.G., Ghahary, A.: Hypertrophic scars, keloids, and contractures: The cellular and molecular basis for therapy. Surg Clin North Am 77, 701 (1997)
Tredget, E.E., Shankowsky, H.A., Pannu, R., Nedelec, B., et al.: Transforming growth factor-beta in thermally injured patients with hypertrophic scars: Effects of interferon alpha-2b. Plast Reconstr Surg 102, 1317 (1998)
Tredget, E.E., Wang, R., Shen, Q., Scott, P.G., Ghahary, A.: Transforming growth factor-beta mRNA and protein in hypertrophic scar tissues and fibroblasts: Antagonism by IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma in vitro and in vivo. J Interferon Cytokine Res 20, 143 (2000)
Tsubota, A., Chayama, K., Ikeda, K., Yasuji, A., et al.: Factors predictive of response to interferon-alpha therapy in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 19, 1080 (1994)
Tuan, T., Nichter, L.S.: The molecular basis of keloid and hypertrophic scar formation. Mol Med Today 1, 19 (1998)
Urioste, S.S., Arndt, K.A., Dover, J.S.: Keloids and hypertrophic scars: Review and treatment strategies. Semin Cutan Med Surg 18, 159 (1999)
Van den Kerckhove, E., Stappaerts, K., Boeckx, W., Van den Hof, B., et al.: Silicones in the rehabilitation of burns: A review and overview. Burns 27, 205 (2001)
Van den Kerckhove, E., Stappaerts, K., Fieuws, S., Laperre, J., et al.: The assessment of erythema and thickness on burn related scars during pressure garment therapy as a preventive measure for hypertrophic scarring. Burns 31, 696 (2005)
Ward, R.S.: Pressure therapy for the control of hypertrophic scar formation after burn injury: A history and review. J Burn Care Rehabil 12, 257 (1991)
Widgerow, A.D., Chait, L.A., Stals, R., Stals, P.J.: New innovations in scar management. Aesth Plast Surg 24, 227 (2000)
Wu, J.-X., Liu, Q.-S., Zhou, X.-L., Qin, W., et al.: Primary observation of therapeutic effect of collagenase on hypertrophic scar. Chin J Clin Rehab 38, 168 (2005)
Yamamoto, T.: Bleomycin and the skin. Br J Dermatol 155, 869 (2006)
Yii, N.W., Frame, J.D.: Evaluation of cynthaskin and topical steroid in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Eur J Plast Surg 19, 162 (1996)
Yosipovitch, G., Widijanti Sugeng, M., Goon, A.: A comparison of the combined effect of cryotherapy and corticosteroid injections versus corticosteroids and cryotherapy on keloids: A controlled study. J Dermatol Treat 12, 87 (2001)
Ziegler, U.E.: International clinical recommendations on scar management. Zentralbl. Chir 129, 296 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is being reprinted for ISAPS 50th Anniversary Special Issue.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atiyeh, B.S. Nonsurgical Management of Hypertrophic Scars: Evidence-Based Therapies, Standard Practices, and Emerging Methods. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 1320–1344 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01820-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01820-0