Abstract
Aim
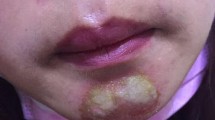
In this clinical study, 16 female patients with vascular compression and occlusion-related ischemia and skin necrosis after hyaluronic acid filling injection were analyzed retrospectively. Dose, timing, and efficacy of hyaluronidase use in skin necrosis are discussed.
Patients and Methods
In a total of 841 cases, aged between 18 and 60 years, hyaluronic acid filling injections were performed. All patients were followed up for 3–24 months. Filling injected areas include nasolabial (391 cases), lip (225 cases), glabella–forehead (90 cases), infraorbital (46 cases), malar region (25 cases), chin (24 cases), and nose (40 cases). Skin complications occurred in four cases during the application and in 12 cases 6–24 h after the procedure. Only palliative treatment was performed in six cases, while hyaluronidase was used in 10 cases in addition to palliative treatment. Hyaluronidase injection was performed 30 s after filling injection in four cases and 6–24 h after the injection in the remaining six cases. A total of 1500 units of hyaluronidase was applied to each case in average.
Results
Recovery period of the patients who received palliative treatment only lasted 40–60 days. The area of necrosis was limited in these patients who did heal well only with some change of pigmentation and no obvious scar. In the patient group who received hyaluronidase in addition to palliative treatment, a large necrosis area was observed at the same time in four patients. Despite the hyaluronidase treatment in this group, recovery period was 20–90 days. The affected and necrosis areas were large. The cause of ischemia depended both on occlusion and on compression. While four patients healed with a scar, the remaining 12 patients healed without any significant scar.
Conclusions
Hyaluronidase injection provides earlier recovery of limited skin necrosis. Immediate hyaluronidase injection allows small damage to heal in a short time; however, it does not completely eliminate large necrosis, although it limits the necrotic area.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narins RS, Jewell M, Rubin M, Cohen J, Strobos J (2006) Clinical conference: management of rare events following dermal fillers-focal necrosis and angry red bumps. Dermatol Surg 32(3):426–434
Hirsh RJ, Cohen JL, Carruthers JD (2007) Successful management of an unusual presentation of impending necrosis following a hyaluronic acid injection embolus and a proposed algorithm for management with hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg 33(3):357–360
King M, Convery C, Davies E (2018) This month’s guideline: the use of hyaluronidase in aesthetic practice (v2.4). J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 11(6):E61–E68
Sito G, Manzoni V, Sommariva R (2019) Vascular complications after facial filler injection: a literature review and meta-analysis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 12(6):E65–E72
Beleznay K, Carruthers JDA, Humphrey S, Carruthers A, Jones D (2019) Update on avoiding and treating blindness from fillers: a recent review of the world literature. Aesthet Surg J 39(6):662–674
Thanasarnaksorn W, Cotofana S, Rudolph C, Kraisak P, Chanasumon N, Suwanchinda A (2018) Severe vision loss caused by cosmetic filler augmentation: case series with review of cause and therapy. J Cosmet Dermatol 17(5):712–718
Loh KTD, Phoon YS, Phua V, Kapoor KM (2018) Successfully managing impending skin necrosis following hyaluronic acid filler injection, using high-dose pulsed hyaluronidase. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(2):e1639
Zhang L, Feng X, Shi H, Wu WTL, Wu S (2019) Blindness after facial filler injections: the role of extravascular hyaluronidase on intravascular hyaluronic acid embolism in the rabbit experimental model. Aesthet Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz280
Han SW, Park MJ, Lee SH (2019) Hyaluronic acid-induced diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: unknown complication induced by a well-known injectable agent. Ann Transl Med 7(1):13
Ansari ZA, Choi CJ, Rong AJ, Erickson BP, Tse DT (2019) Ocular and cerebral infarction from periocular filler injection. Orbit 38(4):322–324
Chen H, Wang H, Yang Z (2018) A case of hyaluronic acid induced blindness with ophthalmoplegia and ptosis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 34(6):e184–e186
Rivers JK, Mistry BD (2018) Soft-tissue infection caused by streptococcus anginosus after intramucosal hyaluronidase injection: a rare complication related to dermal filler injection. Dermatol Surg 44(Suppl 1):S51–S53
Lee W, Oh W, Oh SM, Yang EJ (2020) Comparative effectiveness of different interventions of perivascular hyaluronidase. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000006639
Lee W, Oh W, Ko HS, Lee SY, Kim KW, Yang EJ (2019) Effectiveness of retrobulbar hyaluronidase injection in an iatrogenic blindness rabbit model using hyaluronic acid filler injection. Plast Reconstr Surg 144(1):137–143
Grunebaum LD, Bogdan Allemann I, Dayan S, Bauman L (2009) The risk of alar necrosis associated with dermal filler injection. Dermatol Surg 35(Supp 2):1635–1640
Ohen JL (2008) Understanding, avoiding, and managing dermal filler complications. Dermatol Surg 34:S92–S99
Vasquez RAS, Park K, Braunlich K, Aguilera SB (2019) Prolonged periorbicular edema after injection of hyaluronic acid for nasojugal groove correction. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 12(9):32–35
Kleydman K, Cohen JL, Marmur E (2012) Nitroglycerin: a review of its use in the treatment of vascular occlusion after soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol Surg 38(12):1889–1897
Yang Q, Qiu L, Yi C, Xue P, Yu Z, Ma X, Su Y, Guo S (2017) Reversible alopecia with localized scalp necrosis after accidental embolization of the parietal artery with hyaluronic acid. Aesthet Plast Surg 41(3):695–699
Coleman SR (2002) Avoidance of arterial occlusion from injection of soft tissue fillers. Aesthet Surg J 22(6):555–557
Woodward J (2016) Review of periorbital and upper face: pertinent anatomy, aging, injection techniques, prevention, and management of complications of facial fillers. J Drugs Dermatol 15(12):1524–1531
Lin CH, Chiang CP, Wu BY, Gao HW (2017) Filler migration to the forehead due to multiple filler injections in a patient addicted to cosmetic fillers. J Cosmet Laser Ther 19(2):124–126
Snozzi P, van Loghem JAJ (2018) Complication management following rejuvenation procedures with hyaluronic acid fillers-an algorithm-based approach. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(12):e2061
Han J, He Y, Liu K, Yang Q (2018) Necrosis of the glabella after injection with hyaluronic acid into the forehead. J Craniofac Surg 29(7):e726–e727
Wang Q, Zhao Y, Li H, Li P, Wang J (2018) Vascular complications after chin augmentation using hyaluronic acid. Aesthet Plast Surg 42(2):553–559
Schanz S, Schippert W, Ulmaer A, Rassner G, Fierlbeck G (2002) Arterial embolization caused by injection of hyaluronic acid (Restylane). Br J Dermatol 146(5):928–929
Wattanakrai P, Jurairattanaporn N, Rojhirunsakool S, Visessiri Y, Suwanchinda A, Thanasarnaksorn W (2018) The study of histological changes of the arterial vascular structure after hyaluronidase exposure. J Cosmet Dermatol 17(4):632–636
Oh B-L, Jung C, Park KH, Hong YJ et al (2014) Therapeutic intra-arterial hyaluronidase infusion for ophthalmic artery occlusion following cosmetic facial filler (hyaluronic acid) injection. Neuro-Ophthalmology 38:39–43
Acknowledgements
The authors declare no financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval of the retrospective clinical study was granted by the research ethics committee.
Informed Consent
Informed consent form was used for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ors, S. The Effect of Hyaluronidase on Depth of Necrosis in Hyaluronic Acid Filling-Related Skin Complications. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 1778–1785 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01759-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01759-2