Abstract
Background
The most common complication experienced by patients who have undergone mammary implant surgery is capsular contracture. This matter concerns physicians and patients, but to date, there is no effective way to avoid this complication. Surgical intervention usually is required. In 2002, the use of zafirlukast, a leukotriene inhibitor (a drug used for asthma treatment), was reported for the treatment of capsular contracture, with good results.
Methods
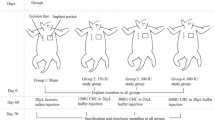
For this study, 30 female Wistar rats were used. These animals received two silicone implants each: one with a smooth surface and one with a textured surface. All the animals received daily intraperitoneal injections for 90 days and were divided as follows: control group (C) receiving only saline solution, experimental group 1 (E-I) receiving 1.25 mg/kg/day of zafirlukast, and experimental group 2 (E-II) receiving 5 mg/kg/day of zafirlukast. Histologic analysis used hematoxilin and eosin to verify vessels, capsule thickness, and inflammatory cells. Immunoistochemical analysis with smooth muscle anti-actin antibody was used for myofibroblast verification. Picro-Sirius under polarized light was used for collagen analysis.
Results
Textured implant experimental groups presented smaller numbers of vessels, thinner capsules, lower collagen density, and smaller numbers of mastocytes and eosinophils than the control group. No significant differences were found in smooth surface implants, as compared with the control group.
Conclusion
Zafirlukast reduced the occurrence of factors directly and indirectly connected with capsular contracture.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker JL Jr, Chandler ML, LeVier RR: Occurrence and activity of myofibroblasts in human capsular tissue surrounding mammary implants. Plast Reconstr Surg 68(6):905–912, 1981
Bastos EM, Sabino MN, Ferreira LM, Garcia EB, Liebano RE, Han YA: Experimental model of capsular contracture in silicone implants. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira 18:22–28, 2003
Bucky LP, Ehrlich HP, Sohoni S, May JW Jr: The capsule quality of saline-filled smooth silicone, textured silicone, and polyurethane implants in rabbits: A long-term study. Plast Reconstr Surg 93:1123–1231, discussion 1132–1133, 1994
Cairns JA, Walls AF: Mast cell tryptase stimulates the synthesis of type I collagen in human lung fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 99:1313–1321, 1997
Camirand A, Doucet J: Breast augmentation: Teaching our patients how compression can help prevent capsular contracture. Aesth Plast Surg 24:221–226, 2000
Clugston PA, Perry LC, Hammond DC, Maxwell GP: A rat model for capsular contracture: The effects of surface texturing. Ann Plast Surg 33:595–599, 1994
Frangou J, Kanellaki M: The effect of local application of mitomycin-C on the development of capsule around silicone implants in the breast: An experimental study in mice. Aesth Plast Surg 25:118–128, 2001
Gruber BL: Mast cells in the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 5:147–153, 2003
Gryskiewicz JM. What doctors aren’t being told: Using the freedom of information act. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:743–745
Hackshaw KV, Voelkel NF, Thomas RB, Westcott JY: Urine leukotriene E4 levels are elevated in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 19:252–258, 1992
Horn BR, Robin ED, Theodore J, Van Kessel A: Total eosinophil counts in the management of bronchial asthma. N Engl J Med 292:1152–1155, 1975
Hu ZQ, Yamazaki T, Cai Z, Yoshida T, Shimamura T: Mast cells display natural suppressor activity partially by releasing transforming growth factor-beta. Immunology 82:482–486, 1994
Ihara T, Uchiide I, Sugamata M: Light and electron microscopic evaluation of antileukotriene therapy for experimental rat endometriosis. Fertil Steril 81(Suppl 1):819–823, 2004
Imber G, Schwager RG, Guthrie RH Jr: Gray GF: Fibrous capsule formation after subcutaneous implantation of synthetic materials in experimental animals. Plast Reconstr Surg 54:183–186, 1974
Jain NK, Kulkarni SK, Singh A: Role of cysteinyl leukotrienes in nociceptive and inflammatory conditions in experimental animals. Eur J Pharmacol 423:85–92, 2001
Katzin WE, Feng L-J, Abbuhl M, Klein MA: Phenotype of lymphocytes associated with the inflammatory reaction to silicone gel breast implants. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 3:156–161, 1996
Ksander GA: Effects of diffused soluble steroid on capsules around experimental breast prostheses in rats. Plast Reconstr Surg 63:708–716, 1979
Ksander GA, Vistnes LM, Kosek J: Effect of implant location on compressibility and capsule formation around miniprostheses in rats, and experimental capsule contracture. Ann Plast Surg 6:182–193, 1981
Lin CC, Chang CF, Liaw SF, Lin CY: Maximal forced expiratory maneuver to measure airway obstruction in allergen challenged mice. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 130:79–87, 2002
Peters CR, Shaw TE, Raju DR: The influence of vitamin E on capsule formation and contracture around silicone implants. Ann Plast Surg 5:347–352, 1980
Qu Z, Liebler JM, Powers MR, Galey T, Ahmadi P, Huang XN, et al.: Mast cells are a major source of basic fibroblast growth factor in chronic inflammation and cutaneous haemangioma. Am J Pathol 147:564–173, 1995
Rennekampff HO, Exner K, Lemperle G, Nemsmann B: Reduction of capsular formation around silicone breast implants by D-penicillamine in rats. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 26:253–255, 1992
Rohrich RJ, Kenkel JM, Adams WP: Preventing capsular contracture in breast augmentation: In search of the Holy Grail. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1759–1760, 1999
Rubino C, Mazzarello V, Farace F, D’Andrea F, Montella A, Fenu G, Campus GV: Ultrastructural anatomy of contracted capsules around textured implants in augmented breasts. Ann Plast Surg 46:95–102, 2001
Sanders JE, Goldstein BS, Leotta DF, Richards KA: Image processing techniques for quantitative analysis of skin structures. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 59:167–180, 1999
Schlesinger SL, Ellenbogen R, Desvigne MN, Svehlak S, Heck R: Zafirlukast (Accolate): A new treatment of a difficult problem. Aesth Surg J 22:329–336, 2002
Siggelkow W, Faridi A, Spiritus K, Klinge U, Rath W, Klosterhalfen B: Histological analysis of silicone breast implant capsules and correlation with capsular contracture. Biomaterials 24:1101–1109, 2003
Solomon G: Clinical and serologic features of 639 symptomatic women with silicone gel implants: Evidence for novel disease siliconosis. Arthritis Rheum 37:S423, 1994
Vistnes LM, Ksander GA, Kosek J: Study of encapsulation of silicone rubber implants in animals: A foreign-body reaction. Plast Reconstr Surg 62:580–588, 1978
Weitz J, Kienle P, Böhrer H, Hofmann W, Theilmann L, Otto G: Fatal hepatic necrosis after isoflurane anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 52:892–895, 1997
Acknowledgments.
We thank Silimed for the implant donation and partial financial support for the development of this project. We also thank Astra Zeneca for providing the compound zafirlukast.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bastos, E.M., Neto, M.S., Alves, M.T.S. et al. Histologic Analysis of Zafirlukast’s Effect on Capsule Formation Around Silicone Implants. Aesth Plast Surg 31, 559–565 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0257-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0257-7