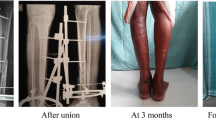
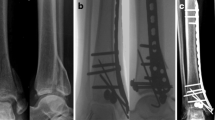
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcome of Ilizarov external fixation (IE) versus dynamic compression plate (PO) in the management of extra-articular distal tibial fractures.
Methods
Between 2010 and 2011, extra-articular distal tibial fractures in 40 consecutive patients met the inclusion criteria. They were classified according to AO classification fracture type A (A1, A2, and A3). In a randomized method, two equal groups were managed using either IE or PO. PO was performed using open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) and DCP through anterolateral approach. IE was done using Ilizarov frame. For the PO group, non-weight bearing ambulation was permitted on the second postoperative day but partial weight bearing was permitted according to the progression in union criteria clinically and radiologically. For the IE group, weight bearing started as tolerated from the first postoperative day. Physiotherapy and pin-site care was performed by the patient themselves.
Results
Modified Mazur ankle score was applied to IE (excellent 10, good 10) and in PO (excellent 2, good 8, poor 6). Data were statically analysed using (Mann–Whitney test). The rate of healing in the IE group (average 130) was higher than the PO (average 196.5); plus, there were no cases of delayed union or nonunion in the IE group (p value 0.003).
Conclusion
It was found that IE compared with PO provides provision of immediate weight bearing as tolerated following postoperative recovery, irrespective of radiological or clinical healing with no infection, deformity or non-union.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newman SD, Mauffrey CP, Krikler S (2011) Distal metadiaphyseal tibial fractures. Injury 42(10):975–984
Coles CP, Gross M (2000) Closed tibial shaft fractures: management and treatment complications. A review of the prospective literature. Can J Surg 43:256–262
Oh CW, Kyung HS, Park IH et al (2003) Distal tibia metaphyseal fractures treated by percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 408:286–291
Hoenig M, Gao F, Kinder J et al (2010) Extra-articular distal tibia fractures: a mechanical evaluation of 4 different treatment methods. J Orthop Trauma 24(1):30–35
Shisha T (2010) Parameters for defining efficacy in fracture healing. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 7(1):15–16
Teeny SM, Wiss DA (1993) Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures variables contributing to poor results and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res 292:108–117
Janssen KW, Biert J, Kampen A (2007) Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail. Int Orthop 31(5):709–714
Lee YS, Lo TY, Huang HL (2008) Intramedullary fixation of tibial shaft fractures: a comparison of the unlocked and interlocked nail. Int Orthop 32:69–74
Mahmood A, Kumar G (2014) Review of the treatment of distal tibia metaphyseal fractures; plating versus intramedullary nailing: a systematic review of recent evidence. Foot Ankle Surg 20(2):151
Court-Brown CM, Gustilo T, Shaw AD (1997) Knee pain after intramedullary nailing: its incidence, etiology, and outcome. J Orthop Trauma 11:103–105
Keating JF, Orfaly R, O’Brien PJ (1997) Knee pain after tibial nailing. J Orthop Trauma 11:10–13
Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis PV (2006) Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 88:576–580
Bedi A, Le TT, Karunakar MA (2006) Surgical treatment of nonarticular distal tibia fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(7):406–416
Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A (2008) Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma 22(5):307–311
BACH AW, Hansen ST Jr (1989) Plates versus external fixation in severe open tibial shaft fractures: a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat 241:89–94
Ristiniemi J, Luukinen P, Ohtonen P (2011) Surgical treatment of extra-articular or simple intra-articular distal tibial fractures: external fixation versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma 25(2):101–105
Richard RD, Kubiak E, Horwitz DS (2014) Techniques for the surgical treatment of distal tibia fractures. Orthop Clin North Am 45(3):295–312
Schurz M, Binder H, Platzer P et al (2010) Physeal injuries of the distal tibia: long-term results in 376 patients. Int Orthop 34(4):547–552
Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV et al (2007) Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma 21(2):83–91
Hosny G, Fadel M (2003) Ilizarov external fixator for open fractures of the tibial shaft. Int Orthop 27(5):303–306
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the LRS.PD program. Professional Diploma in Limb Reconstructive Surgery and Correction of Deformity (LRS.PD) is organized by the Arab Institute for continuing professional development (AICPD) in association with the Pan Arab Orthopaedic Association (PAOA) and scientific support of the International Orthopedic Association (SICOT).
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fadel, M., Ahmed, M.A., Al-Dars, A.M. et al. Ilizarov external fixation versus plate osteosynthesis in the management of extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 513–519 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2607-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2607-4