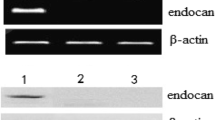
Abstract
The variable domain of immunoglobulin heavy chain (Ig HV) is well-characterized tumor associated antigen expressed in B-cell malignancies, which may function as a T-cell target. However, T-cell epitopes derived from shared framework regions (FRs) of each IgHV subfamily capable of inducing cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) against the B-cell malignancy, have not been identified. Using the specific PCR primers of seven IgHV gene subfamilies, we amplified the IgHV gene rearrangement for 108 cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) patients. The IgHV gene rearrangement fragments of B-ALL patients were directly sequenced then classified into seven different subfamilies. The T-cell epitopes encoded by the IgHV gene in the B-ALL patients were predicted by SYFPEITHI and BIMAS programs and compared with those from 56 representative germline IgHV sequences in the genebank. For the HLA-A*0201 locus, we found 1 or 2 top score shared epitopes from each subfamily and got 12 epitopes altogether. Results showed that ten of them were in the FRs. Using an antigen-specific T-cell expansion system, we generated the peptide-special CTLs in vitro, which were capable of killing B lymphoma cell lines that belonged to the same IgHV subfamily in a peptide-specific and HLA-restricted manner. Furthermore, we proved that the cytotoxicity of CTLs was IgHV subfamily-specific. These data indicate possible immunotherapy approaches for B-cell malignances patients based on IgHV gene subfamilies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- IgHV:
-
Variable domain of immunoglobulin heavy chain
- CDRs:
-
Hypervariable complementary determining regions
- Id:
-
Idiotype
- FRs:
-
Framework regions
- HLA:
-
Human-leukocyte-antigen
- CTLs:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- TCR:
-
T-cell receptor
- B-ALL:
-
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PBMCs:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- APCs:
-
Antigen presenting cells
References
Janeway CA Jr, Sakato N, Eisen HN (1975) Recognition of immunoglobulin idiotypes by thymus-derived lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72(6):2357–2360
Bogen B, Malissen B, Haas W (1986) Idiotope-specific T cell clones that recognize syngeneic immunoglobulin fragments in the context of class II molecules. Eur J Immunol 16(11):1373–1378
Campbell MJ, Carroll W, Kon S, Thielemans K, Rothbard JB, Levy S, Levy R (1987) Idiotype vaccination against murine B cell lymphoma. Humoral and cellular responses elicited by tumor-derived immunoglobulin M and its molecular subunits. J Immunol 15 139(8):2825–2833
Miller RA, Maloney DG, Warnke R, Levy R (1982) Treatment of B-cell malignancies with monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody. N Engl J Med 4 306(9):517–522
Campbell MJ, Esserman L, Byars NE, Allison AC, Levy R (1990) Idiotype vaccination against murine B cell lymphoma. Humoral and cellular requirements for the full expression of antitumor immunity. J Immunol 145(3):1029–1036
Maloney DG, Brown S, Czerwinski DK, Liles TM, Hart SM, Miller RA, Levy R (1992) Monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody therapy of B-cell malignancies: the addition of a short course of chemotherapy does not interfere with the antitumor effect nor prevent the emergence of idiotype-negative variant cells. Blood 80(6):1502–1510
Chen TT, Tao MH, Levy R (1994) Idiotype-cytokine fusion proteins as cancer vaccines. Relative efficacy of IL-2, IL-4, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol 153(10):4775–4787
Barrios Y, Cabrera R, Yanez R, Briz M, Plaza A, Fores R (2002) Anti-idiotypic vaccination in the treatment of low-grade B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 87(4):400–407
Ruffini PA, Neelapu SS, Kwak LW, Biragyn A (2002) Idiotypic vaccination for B-cell malignancies as a model for therapeutic cancer vaccines: from prototype protein to second generation vaccines. Haematologica 87(9):989–1001
Wen YJ, Lim SH. (1997) T cells recognize the VH complementarity-determining region 3 of the idiotypic protein of B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur J Immunol 27(4):1043–1047
Fagerberg J, Yi Q, Gigliotti D, Harmenberg U, Ruden U, Persson B, Osterborg A, Mellstedt H (1999) T-cell-epitope mapping of the idiotypic monoclonal IgG heavy and light chains in multiple myeloma. Int J Cancer 80(5):671–680
Wen YJ, Lim SH (1999) Different properties of T-cell epitopes within complementarity-determining regions 1 and 2 of idiotypic VH in B-lymphoma. Scand J Immunol 50(3):296–301
Rezvany MR, Jeddi-Tehrani M, Rabbani H, Ruden U, Hammarstrom L, Osterborg A, Wigzell H, Mellstedt H (2000) Autologous T lymphocytes recognize the tumour-derived immunoglobulin VH-CDR3 region in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 111(1):230–238
Hansson L, Rabbani H, Fagerberg J, Osterborg A, Mellstedt H (2003) T-cell epitopes within the complementarity-determining and framework regions of the tumor-derived immunoglobulin heavy chain in multiple myeloma. Blood 101(12):4930–4936
Trojan A, Schultze JL, Witzens M, Vonderheide RH, Ladetto M, Donovan JW, Gribben JG (2000) Immunoglobulin framework-derived peptides function as cytotoxic T-cell epitopes commonly expressed in B-cell malignancies. Nat Med 6(6):667–672
Lou Q, Kelleher RJ Jr, Sette A, Loyall J, Southwood S, Bankert RB, Bernstein SH (2004) Germ line tumor-associated immunoglobulin IgHV region peptides provoke a tumor-specific immune response without altering the response potential of normal B cells. Blood 104(3):752–759
Scaviner D, Barbie V, Ruiz M, Lefranc MP (1999) Protein displays of the human immunoglobulin heavy, kappa and lambda variable and joining regions. Exp Clin Immunogenet 16(4):234–240
Lin NJ, Zhu P, Zhang YP, Shi YJ, Zhang X, Bu DF, Dong YJ (2002) The experimental study on the idiotypic nucleic Acid vaccine constructed from the genomic DNA to lymphoma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 10(2):126–130
Lin N, Zhu P, Zhang X, Dong Y, Ren Y, Wang Y, Li W (2002) Specific humoral immune response against B-cell lymphoma elicited by mixed immunoglobulin fragments. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 82(11):766–770
Liu H, Zhu P, Lin NJ, Zhang Y, Bu DF, Wang YJ, Wang YQ, Yang Y (2004) Development of IgHV family specific nucleic acid vaccine against lymphoma by construction of fusion gene of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region and cytokine. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 84(1):48–53
Zhang Y, Zhu P, Shi Y, Liu J, Pu D, Cao X, Zhu Q, Wang Y, Ma M, Yu J (2002) Experimental study on TCRbeta idiotypic antigenic determinants DNA vaccine to induce anti-lymphoma antibodies. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 23(2):68–72
Liu Y, Zhu P, Hu YM (2004) Characteristics of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes in childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 25(1):8–12
Vonderheide RH, Hahn WC, Schultze JL, Nadler LM (1999) The telomerase catalytic subunit is a widely expressed tumor-associated antigen recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 10:673–679
Valmori D, Dutoit V, Lienard D, Rimoldi D, Pittet MJ, Champagne P, Ellefsen K, Sahin U, Speiser D, Lejeune F, Cerottini JC, Romero P (2000) Naturally occurring human lymphocyte antigen-A2 restricted CD8+ T-cell response to the cancer testis antigen NY-ESO-1 in melanoma patients. Cancer Res 60(16):4499–4506
Clark RE, Dodi IA, Hill SC, Lill JR, Aubert G, Macintyre AR, Seran C (2001) Direct evidence that leukemic cells present HLA-associated immunogenic peptides derived from the BCR-ABL b3a2 fusion protein. Blood 98(10):2887–2893
Heemskerk MH, Hoogeboom M, de Paus RA, Kester MG, van der Hoorn MA (2003) Redirection of antileukemic reactivity of peripheral T lymphocytes using gene transfer of minor histocompatibility antigen HA-2-specific T-cell receptor complexes expressing a conserved alpha joining region. Blood 102(10):3530–3540
Yang YH, Li HF, Zhu P (2003) The T-lymphocyte clonal proliferation in a patient with chronic eosinophilic leukemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 11(4):405–408
Weidmann E, Brieger J, Jahn B, Hoelzer D, Bergmann L, Mitrou PS (1995) Lactate dehydrogenase-release assay: a reliable, nonradioactive technique for analysis of cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated lytic activity against blasts from acute myelocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol 70(3):153–158
Harig S, Witzens M, Krackhardt AM, Trojan A, Barrett P, Broderick R, Zauls AJ, Gribben JG (2001) Induction of cytotoxic T-cell responses against immunoglobulin V region-derived peptides modified at human leukocyte antigen-A2 binding residues. Blood 98(10):2999–3005
Acknowledgements
The thorough reviewing of this manuscript by Dr. Daniel H. Conrad from the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Virginia Commonwealth University, Medical College of Virginia, and Dr Zeng gang from the Division of Urologic Oncology, Department of Urology, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA are greatly appreciated. We thank Dr Dingfang-PU, Yongjin-SHI for their research suggestions and technical assistance. We also thank Jiaxia-YUAN for FCM assay, Dr Weifeng-CHEN for providing the T2 cell line. Dr Mirjam H. M. Heemskerk, (Department of Hematology, Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC), Leiden, the Netherlands) for supplying us with the primer of d TCRBV for RT-PCR. Supported by: National Natural Science Foundation of China (39970313) and grant 2002AA229011 from the ministry of Science and Technology, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaoling, G., Ying, L., Jing, L. et al. Induction of anti B-cell malignance CTL response by subfamily-shared peptides derived from variable domain of immunoglobulin heavy chain. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54, 1106–1114 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0696-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0696-z