Abstract
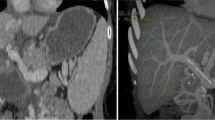
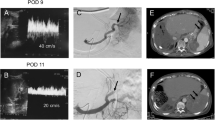
We describe a case of living donor liver transplantation with hepatofugal portal flow caused by acute cellular rejection. The reversed portal flow was corrected by splenectomy and ligation of the residual collateral veins. Hepatofugal flow causes ischemic damage to the graft, which does not normalize spontaneously. In this particular case, meticulous Doppler ultrasound examination and prompt response to reversed portal flow salvaged the graft.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
T Takayama M Makuuchi K Kubota et al. (2000) ArticleTitleLiving-related transplantation of left liver plus caudate lobe J Am Coll Surg 190 635–638 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00255-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3lvV2ksw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10801033
K Urata S Kawasaki H Matsunami et al. (1995) ArticleTitleCalculation of child and adult standard liver volume for liver transplantation Hepatology 21 1317–1321 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0270-9139(95)90053-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB2MrotVU%3D Occurrence Handle7737637
Y Sugawara M Makuuchi J Kaneko et al. (2002) ArticleTitleCorrelation between optimal tacrolimus doses and the graft weight in living donor liver transplantation Clin Transpl 16 102–106 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1399-0012.2002.1o106.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD383mt1ahtw%3D%3D
A Handengue D Lebrec R Moreau et al. (1993) ArticleTitlePersistence of systemic and splanchnic hyperkinetic circulation in liver transplantation patients Hepatology 17 175–178 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0270-9139(93)90072-U Occurrence Handle8428714
L DeCarlis E Favero ParticleDel G Rondinara et al. (1992) ArticleTitleThe role of spontaneous portosystemic shunts in the course of orthotopic liver transplantation Transpl Int 5 9–14 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00337182 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2B2MrotFE%3D Occurrence Handle1580990
H Sugimoto T Kaneko Y Marui et al. (2001) ArticleTitleReversal of portal flow after acute rejection in living-donor liver transplantation J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 8 573–576 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s005340100028 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD383hslGhtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11956911
M Cescon Y Sugawara T Takayama et al. (2001) ArticleTitleRole of splenectomy in living donor transplantation for adults Hepatogastroenterology 49 721–723
M Cescon Y Sugawara J Kaneko et al. (2001) ArticleTitleRestoration of portal vein flow by splenorenal shunt ligation and splenectomy after living-related liver transplantation Hepatogastroenterology 48 1453–1454 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrntFanug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11677985
R Reding J Gras E Sokal et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSteroid-free liver transplantation in children Lancet 362 2068–2070 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15104-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvFylsLY%3D Occurrence Handle14697809
MM Aw RM Taylor A Verma et al. (2003) ArticleTitleBasiliximab for the treatment of steroid-resistant rejection in pediatric liver transplanted recipients: a preliminary experience Transplantation 75 796–799 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.TP.0000054682.53834.EA Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitlyrsLY%3D Occurrence Handle12660504
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and Grants-in-aid for Research on HIV/AIDS and Research on Measures for Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyoden, Y., Sugawara, Y., Matsui, Y. et al. Hepatofugal portal flow due to acute cellular rejection. Abdom Imaging 30, 303–305 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-004-0269-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-004-0269-1