Abstract
Objective
Muscle lymphoma (ML) is a relatively uncommon condition. On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ML can manifest with a broad spectrum of radiological features. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the features of DW images of muscle lymphoma (ML).
Materials and methods
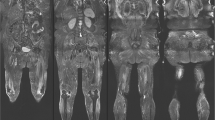
In our database, ten patients (six women and four men) with ML were identified who were investigated by magnetic resonance imaging including acquisition of DW images. DW images were obtained using a multi-shot SE-EPI pulse sequence. Apparent diffusion constant (ADC) maps were also calculated. Furthermore, fusion images were generated manually from DW and HASTE or T2W images.
Results
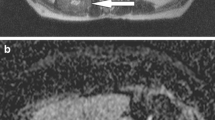
On T2W images, all recognized lesions were hyperintense in comparison to unaffected musculature and on T1W images they were homogeneously hypointense. All lesions demonstrated low signal intensity on ADC images. The calculated ADC values ranged from 0.60 to 0.90 mm2s−1 (mean value 0.76 ± 0.10; median value 0.78). On fusion images, all lesions showed high signal intensity.
Conclusions
ML demonstrated low ADC values and high signal intensity on fusion images suggesting high cellularity of the lesions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zucca E, Roggero E, Bertoni F, et al. Primary extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Part 2: head and neck, central nervous system and other less common sites. Ann Oncol. 1999;10:1023–33.
Surov A, Holzhausen HJ, Arnold D, et al. Intramuscular manifestation of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and myeloma: prevalence, clinical signs, and computed tomography features. Acta Radiol. 2010;51:47–51.
Suresh S, Saifuddin A, O’Donnell P. Lymphoma presenting as a musculoskeletal soft tissue mass: MRI findings in 24 cases. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1628–34.
Eustace S, Winalski CS, McGowen A, Dorfman D. Skeletal muscle lymphoma. Observation at MR imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 1996;25:425–30.
Einarsdóttir H, Karlsson M, Wejde J, Bauer HC. Diffusion-weighted MRI of soft tissue tumours. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:959–63.
van Rijswijk CSP, Kunz P, Hogendoorn PC, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of soft-tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15:302–7.
Surov A, Fiedler E, Voigt W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of intramuscular metastases. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:439–46.
Schnapauff D, Zeile M, Niederhagen MB, et al. Diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of tumor cellularity in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29:1355–9.
Khoo MM, Tyler PA, Saifuddin A, Padhani AR. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in musculoskeletal MRI: a critical review. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:665–81.
Harish S, Chiavaras MM, Kotnis N, Rebello R. MR imaging of skeletal soft tissue infection: utility of diffusion-weighted imaging in detecting abscess formation. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:285–94.
Subhawong TK, Durand DJ, Thawait GK, Jacobs MA, Fayad LM. Characterization of soft tissue masses: can quantitative diffusion-weighted imaging reliably distinguish cysts from solid masses? Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:1583–92.
Oka K, Yakushiji T, Sato H, et al. The value of diffusion-weighted imaging for monitoring the chemotherapeutic response of osteosarcoma: a comparison between average apparent diffusion coefficient and minimum apparent diffusion coefficient. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39:141–6.
Dudeck O, Zeile M, Pink D, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging allows monitoring of anticancer treatment effects in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;27:1109–13.
Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, et al. Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 2001;220:621–30.
Chen Y, Zhong J, Wu H, Chen N. The clinical application of whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging in the early assessment of chemotherapeutic effects in lymphoma: the initial experience. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30(2):165–70.
Holzapfel K, Duetsch S, Fauser C, et al. Value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymph nodes. Eur J Radiol. 2009;72:381–7.
Calli C, Kitis O, Yunten N, Yurtseven T, Islekel S, Akalin T. Perfusion and diffusion MR imaging in enhancing malignant cerebral tumors. Eur J Radiol. 2006;58:394–403.
Rosenkrantz AB, Spieler B, Seuss CR, Stifelman MD, Kim S. Utility of MRI features for differentiation of retroperitoneal fibrosis and lymphoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199:118–26.
Fujii S, Matsusue E, Kanasaki Y, et al. Detection of peritoneal dissemination in gynecological malignancy: evaluation by diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:18–23.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surov, A., Behrmann, C. Diffusion-weighted imaging of skeletal muscle lymphoma. Skeletal Radiol 43, 899–903 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-1850-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-1850-5