Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to describe the technique and usefulness of ultrasound-guided intrasynovial injection of triamcinolone and bupivacaine in treatment of de Quervain′s disease.
Materials and methods
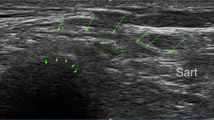
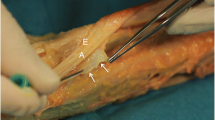
A total of 17 patients with symptomatic De Quervain′s disease were included in this study. The procedure involved confirmation of diagnosis with ultrasound followed by guided injection of a mixture of 20 mg of triamcinolone (40 mg/ml) and 1 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine. Ultrasound guidance with a high resolution 15-Mhz footprint probe was used for injection into the first dorsal extensor compartment tendon sheath (E1). The response to ultrasound-guided injection was ascertained at the post procedure outpatient clinic appointment according to the follow-up clinic notes.
Results
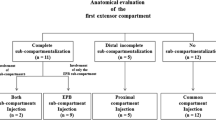
There were 14 female and 3 male patients aged 29 to 74 years. Mean duration of symptoms was 8.9 months. One patient had an atypical septum in the first extensor compartment and the extensor pollicis brevis alone was involved. The mean post-injection follow-up was at 6.75 weeks. One patient was lost to follow-up. Fifteen out of 16 patients had significant symptomatic relief (93.75%). There were no immediate or delayed complications. Recurrence of symptoms was seen in 3 (20%) patients.
Conclusion
Ultrasound-guided injection of triamcinolone and bupivacaine is safe and useful in controlling symptoms of De Quervain′s disease. Correct needle placement with ultrasound guidance avoids intratendinous injection as well as local complications like fat atrophy and depigmentation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piligian G, Herbert R, Hearns M, Dropkin J, Landsbergis P, Cherniack M. Evaluation and management of chronic work-related musculoskeletal disorders of the distal upper extremity. Am J Ind Med. 2000;37(1):75–93.
Sawaizumi T, Nanno M, Ito H. De Quervain’s disease: efficacy of intra-sheath triamcinolone injection. Int Orthop. 2007;31(2):265–8.
Mahakkanukrauh P, Mahakkanukrauh C. Incidence of a septum in the first dorsal compartment and its effects on therapy of de Quervain's disease. Clin Anat. 2000;13(3):195–8.
Hart DA, Frank CB, Bray RC. Inflammatory processes in repetitive motion and overuse syndromes: potential role of neurogenic mechanisms in tendons and ligaments. In: Gordon SL, Blair SJ, Fine LJ, editors. Repetitive motion disorders of the upper extremity. Rosemont, IL: AAOS; 1995. p. 247–62.
Trentanni C, Galli A, Melucci G, Stasi G. Ultrasonic diagnosis of De Quervain's stenosing tenosynovitis. Radiol Med. 1997;93(3):194–8.
Nishijo K, Kotani H, Miki T, Senzoku F, Ueo T. Unusual course of the extensor pollicis longus tendon associated with tenosynovitis, presenting as de Quervain disease—a case report. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71(4):426–8.
Zingas C, Failla JM, Van Holsbeeck M. Injection accuracy and relief of De Quervain’s tendinitis. J Hand Surg [Am]. 1998;23(1):89–96.
Yuasa K, Kiyoshige Y. Limited surgical treatment of de Quervain's disease: decompression of only the extensor pollicis brevis subcompartment. J Hand Surg [Am]. 1998;23(5):840–3.
Bakhach J, Sentucq-Rigal J, Mouton P, Boileau R, Panconi B, Guimberteau JC. The Omega “Omega” pulley plasty: a new technique for the surgical management of the De Quervain′s disease. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2006;51(1):67–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeyapalan, K., Choudhary, S. Ultrasound-guided injection of triamcinolone and bupivacaine in the management of de Quervain′s disease. Skeletal Radiol 38, 1099–1103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-009-0721-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-009-0721-y