Abstract
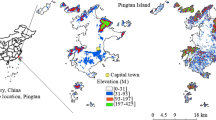
Although rapid land-use change has taken place in many arid and semi-arid regions of northwestern China, relatively less attention has been paid to studying the characteristics of land use change, as well as the ecological responses of land use change in these regions, especially in fragile agro-pastoral regions. This paper analyzes the land use change and its ecological responses during 1985–2005 based on the landscape metrics change and transition matrix of land use types by the combined use of satellite remote sensing and geographical information systems in Shandan County, a typical agro-pastoral region in the middle and upper reaches of Heihe River, northwest China. The results indicate significant changes in land use have occurred and the landscape has become more continuous, clumped and more homogeneous within the examined area. Land use change was mainly characterized by remarkable expansion of barred land and water area, slight increase of cropland and urbanized land, and evident shrinkage of grassland and woodland. The study also demonstrates that the land cover suffered severe degeneration and the ecological environment tended to deteriorate over the study period, mainly as follows: grassland degradation, land desertification and ecosystem services decline.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown DG (2003) Land use and forest cover on private parcels in the upper midwest USA, 1970 to 1990. Landsc Ecol 18:777–790
Chavez PS, MacKinnon DJ (1994) Automatic detection of vegetation changes in the Southwestern United States using remotely sensed images. Photogrammetric Eng Remote Sens 60(5):571–583
Chen X (2002) Using remote sensing and GIS to analyze land cover change and its impacts on regional sustainable development. Int J Remote Sens 23:107–124
Dunn RR (2004) Recovery of faunal communities during tropical forest regeneration. Conserv Biol 18(2):302–309
Hunt A, Ditzer T (2001) Long-term impacts of logging in a tropical rain forest–a simulation study. For Ecol Manage 142:33–51
Kreuter UP, Harris HG, Matlock MD, Lacey RE (2001) Change in ecosystem service values in the San Antonio area, Texas. Ecol Econ 39:33–46
Liu J, Liu M, Zhuang D et al (2003) Study on spatial pattern of land-use change in China during 1995–2000. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 46(4):373–384
Longley PA (2002) Geography: will development in urban remote sensing and GIS lead to better urban geography? Prog Hum Geogr 26(2):231–239
Luo F, Qi S, Xiao H (2005) Landscape change and sandy desertification in arid areas: a case study in the Zhangye Region of Gansu Province, China. Environ Geol 49:90–97
McGarigal K, Cushman SA, Neel MC, Ene E (2002) FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps. Computer
McGarigal K, Marks B (1994) FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure. Reference manual. Forest Science Department, Oregon State University, Corvallis Oregon
Qi S, Li X, Duan H (2007) Oasis land-use change and its environmental impact in Jinta Oasis, arid northwestern China. Environ Monit Assess 134:313–320
Qi S, Luo F (2006) Land-use change and its environmental impact in the Heihe River Basin, arid northwestern China. Environ Geol 50:535–540
Software Program Produced by the authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Available at the following web site: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html
Su Y, Li Y, Cui J, Zhao W (2005) Influences of continuous grazing and livestock exclusion on soil properties in a degraded sandy grassland, inner Mongolia, northern China. Catena 59:267–278
Sun Z, Ma R, Wang Y (2008) Using Landsat data to determine land use changes in Datong basin, China. Environ Geol. doi 10.1007/s00254-008-1470-2
Veldkamp A, Lambin EF (2001) Predicting land-use change. Agric Ecosyst Environ 85:1–6
Veldkamp A, Verburg PH (2004) Modeling land use change and environmental impact. J Environ Manage 72:1–3
Wang G, Ding Y, Lai Y (2003) Environmental degradation in the Hexi Corridor region of China over the last 50 years and comprehensive mitigation and rehabilitation strategies. Environ Geol 44:68–77
Wang J (2004) Modeling dynamic assessment on ecosystem services based on remote sensing technology-case study on Gansu grassland ecosystem. Graduate University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing
Wang X, Zhang Zh (2004) Effect of land-use change on ecosystem services value in Heihe river basin. Ecol Environ 13(4):608–611
Wang Y, Zhou G, Jia B (2008) Modeling SOC and NPP responses of meadow steppe to different grazing intensities in Northeast China. Ecol Modell 217:72–78
Wang Z, Zhang B, Zhang S, Li X (2006) Changes of land use and of ecosystem service values in Sanjiang Plain, northeast China. Environ Monit Assess 112:69–91
Zhang Zh, Xu Z, Wang J et al (2001) Value of the ecosystem services in the Heihe River Basin. J Glaciol Geocryol 23(4):360–367
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Action Plan for West Development Project “Watershed Airborne Telemetry Experimental Research (WATER)” (grant no. KZCX2-XB2-09), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 863 Program-2002AA133062), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 40671040). Special thanks are extended to editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Z., Shen, Y., Wang, J. et al. Land-use change and its ecological responses: a pilot study of typical agro-pastoral region in the Heihe River, northwest China. Environ Geol 58, 1549–1556 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1656-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1656-7