Abstract
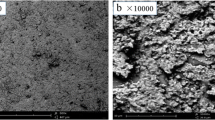
Laboratory simulation of clogging in the Lixi tailings dam (Shaanxi Province, China) is urgently required because clogging is an important factor affecting the dam stability. This work firstly presents the results of ferrous iron oxidation experiments using buffer solution. The results indicate that the ferrous iron oxidation follows first order kinetics, and the oxidation process is strongly dependent on pH, a higher pH resulting in a higher oxidation rate. Furthermore, when the pH exceeds 7.0, the oxidation rate constant increases significantly. Secondly, a column experiment was carried out under the conditions of the pH ranging from 6.8 to 7.5 and the natural oxygen supply. Ferrous iron oxidation and precipitation were found to reach equilibrium under these conditions. After 23 days, the column experiment was stopped when the clogging materials blocked the column outlet. The clogging materials were found to be a mixture of ferric hydroxide and its converted products, and these existed in amorphous form with a loose cluster microstructure according to the results of XRD and SEM.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM D2434-68 (2000) Standard test method for permeability of granular soils (constant head). American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
Das T, Panchanadikar VV, Chaudhury GR (1998) Short communication: bio-oxidation of iron using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:297–298
Fleming IR, Rowe RK, Cullimore DR (1999) Field observations of clogging in a landfill leachate collection system. Can Geotech J 36(4):685–707
Hauck S, Benz M, Brune A, Schink B (2001) Ferrous iron oxidation by denitrifying bacteria in profundal sediments of a deep lake (Lake Constance). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37:127–134
Iliuta I, Iliuta MC, Larachi F (2005) Hydrodynamics Modeling of bioclogging in waste gas treating trickle-bed bioreactors. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:5044–5052
Islam J, Singhal N, O’Sullivan M (2001) Modeling biogeochemical processes in leachate-contaminated soils: a review. Trans Porous Media 43:407–440
Islam J, Singhal N (2004) A laboratory study of landfill-leachate transport in soils. Water Res 38:2035–2042
Kildsgaard J, Engesgaard P (2001) Numerical analysis of biological clogging in two-dimensional sand box experiments. J Contam Hydrol 50:261–285
Lin R, Spicer RL, Tungate FL, Davis BH (1996) A study of the oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in slightly basic solution to produce γ-FeOOH. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 113:79–96
Meruane G, Vargas T (2003) Bacterial oxidation of ferrous iron by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in the pH range 2.5–7.0. Hydrometallury 71:149–158
Park B, Dempsey BA (2005) Heterogeneous oxidation of Fe(II) on ferric oxide at neutral pH and a low partial pressure of O2. Environ Sci Technol 39:6494–6500
Rao SR, Finch JA, Kuyucak N (1995) Ferrous-ferric oxidation in acidic mineral process effluents: comparison of methods. Miner Eng 8(8):905–911
Rinck-Pfeiffer S, Ragusa S, Sztajnbok P, Vandevelde T (2000) Interrelationships between biological, chemical, and physical processes as an analog to clogging in aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) wells. Water Res 34(7):2110–2118
Rowe RK, McIsaac R (2005) Clogging of tire shreds and gravel permeated with landfill leachate. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 131(6):682–693
Seki K, Miyazaki T, Nakano M (1998) Effects of microorganisms on hydraulic conductivity decrease in infiltration. Eur J Soil Sci 49:231–236
Tüfekci N, Sarikaya HZ (1996) Catalytic effects of high Fe(III) concentrations on Fe(II) oxidation. Water Sci Technol 34(7–8):389–396
Tufekci N, Sarikaya HZ (1998) Influence of ageing on the catalytic activity of ferric sludge for oxidation of Fe(II). Water Sci Technol 38(6):129–137
VanGulck JF, Rowe RK, Rittmann BE, Cooke AJ (2003) Predicting biogeochemical calcium precipitation in landfill leachate collection systems. Biodegradation 14(5):331–346
VanGulck JF (2003) Biodegradation and clogging in gravel size material. Ph.D. Queen’s University, Kingston
VanGulck JF, Rowe RK (2004) Evolution of clog formation with time in columns permeated with synthetic landfill leachate. J Contam Hydrol 75:115–139
Willey JD, Whitehead RF, Kieber RJ, Hardison DR (2005) Oxidation of Fe(II) in Rainwater. Environ Sci Technol 39:2579–2585
Wu J, Wu Y, Lu J, Lee L (2007) Field investigations and laboratory simulation of clogging in Lixi tailings dam of Jinduicheng, China. Environ Geol (in press)
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the National Foundation of Science of China (No. 10572090). The authors would like to thank Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for making XRD and SEM-EDS facilities available to us. Leonora Lee is thanked for her suggestions to improve this paper. The authors also wish to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Wu, Y. & Lu, J. Laboratory study of the clogging process and factors affecting clogging in a tailings dam. Environ Geol 54, 1067–1074 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0873-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0873-9