Abstract
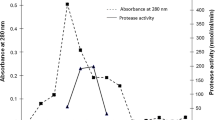
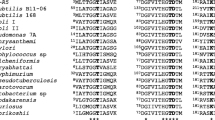
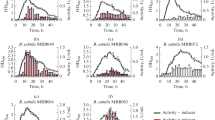
Screening cultures of nonpathogenic microorganisms led us to a glutamic-acid-specific endopeptidase from Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051, which we purified and named BSase. The nucleotide sequence encoding BSase, with a molecular mass of 23 894 Da, completely agreed with that of the mpr gene, which had been reported by Rufo Jr. and Sloma et al. to encode a metalloprotease [J Bacteriol (1990) 172:1019–1023 and 1024–1029 respectively]. However, enzymatic characterization revealed it to have the catalytic triad of a serine protease and not the consensus sequence of a metalloprotease, and it was inhibited by diisopropylfluorophosphate. We therefore consider BSase (mpr) to be a serine protease. In the alignment of the acidic-amino-acid-specific proteases, the proteases from bacilli have a highly conserved histidine residue, which is most important in the histidine triad in the proteases from streptomycetes. Furthermore, Ca2+ was necessary for its activity and stability. BSase cleaved the C-terminal glutamic acid with high specificity and was very stable over a wide pH range. On the basis of these properties, we tried to retrieve a bioactive peptide from a fusion protein by sequence-specific digestion, and succeeded in obtaining the bioactive peptide. BSase was found to be very useful as a tool for selective cleavage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 December 1996 / Received revision: 3 February 1997 / Accepted: 22 February 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, H., Fujiwara, T., Nakamura, E. et al. Purification and characterization of a glutamic-acid-specific endopeptidase from Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051; application to the recovery of bioactive peptides from fusion proteins by sequence-specific digestion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48, 27–33 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051010
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051010