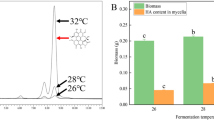
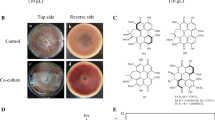
Abstract
Hypocrellins (HYPs), a kind of natural perylenequinones (PQs) with an oxidized pentacyclic core, are important natural compounds initially extracted from the stromata of Hypocrella bambusae and Shiraia bambusicola. They have been widely concerned for their use as anti-microbial, anti-cancers, and anti-viral photodynamic therapy agents in recent years. Considering the restrictions of natural stromal resources, submerged fermentation with Shiraia spp. has been viewed as a promising alternative biotechnology for HYP production, and great efforts have been made to improve HYP production over the past decade. This article reviews recent publications about the mycelium fermentation production of HYPs, and their bioactivities and potential applications, and especially summarizes the progresses toward manipulation of fermentation conditions. Also, their chemical structure and analytic methods are outlined. Herein, it is worth mentioning that the gene arrangement in HYP gene cluster is revised; previous unknown genes in HYP and CTB gene clusters with correct function annotation are deciphered; the homologous sequences of HYP, CTB, and elc are systematically aligned, and especially the biosynthetic pathway of HYPs is full-scale proposed.
Key points
• The mycelial fermentation process and metabolic regulation of hypocrellins are reviewed.
• The bioactivities and potential applications of hypocrellins are summarized.
• The biosynthesis pathway and regulatory mechanisms of hypocrellins are outlined.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Al Subeh ZY, Raja HA, Monro S, Flores-Bocanegra L, El-Elimat T, Pearce CJ, McFarland SA, Oberlies NH (2020) Enhanced production and anticancer properties of photoactivated perylenequinones. J Nat Prod 83(8):2490–2500. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00492
Bu GM, Yang HL (2020) Optimization of fermentation medium for hypocrellin production by Shiraia bambusicola CGMCC 2201 (in Chinese). Chin J Antibiot 45(7):6. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2020.07.005
Cai Y, Liang X, Liao X, Ding Y, Sun J, Li X (2010) High-yield hypocrellin A production in solid-state fermentation by Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168. Appl Biochem. Biotech 160(8):2275–2286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8728-3
Chen CT, Nakanishi K, Natori S (1966) Biosynthesis of elsinochrome A, the perylenequinone from Elsinoë spp. I Chem Pharm Bull 14(12):1434–1437
Chen H, Lee MH, Daub ME, Chung KR (2007) Molecular analysis of the cercosporin biosynthetic gene cluster in Cercospora nicotianae. Mol Microbiol 64(3):755–770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05689.x
Chen YN, Xu CL, Yang HL, Liu ZY, Zhang ZB, Yan RM, Zhu D (2022) L-Arginine enhanced perylenequinone production in the endophytic fungus Shiraia sp. Slf14(w) via NO signaling pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106(7):2619–2636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11877-3
Chooi YH, Zhang G, Hu J, Muria-Gonzalez MJ, Tran PN, Pettitt A, Maier AG, Barrow RA, Solomon PS (2017) Functional genomics-guided discovery of a light-activated phytotoxin in the wheat pathogen Parastagonospora nodorum via pathway activation. Environ Microbiol 19(5):1975–1986. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13711
Choquer M, Lee MH, Bau HJ, Chung KR (2007) Deletion of a MFS transporter-like gene in Cercospora nicotianae reduces cercosporin toxin accumulation and fungal virulence. FEBS Lett 581(3):489–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.011
Daub ME, Herrero S, Chung KR (2013) Reactive oxygen species in plant pathogenesis:the role of perylenequinone photosensitizers. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(9):970–989. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5080
De Jonge R, Ebert MK, Huitt-Roehl CR, Pal P, Suttle JC, Spanner RE, Neubauer JD, Jurick WM 2nd, Stott KA, Secor GA, Thomma B, Van de Peer Y, Townsend CA, Bolton MD (2018) Gene cluster conservation provides insight into cercosporin biosynthesis and extends production to the genus Colletotrichum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(24):E5459–E5466. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1712798115
Deng H, Gao R, Chen J, Liao X, Cai Y (2016a) An efficient polyethylene glycol-mediated transformation system of lentiviral vector in Shiraia bambusicola. Process Biochem 51(10):1357–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.07.013
Deng H, Gao R, Liao X, Cai Y (2017) Genome editing in Shiraia bambusicola using CRISPR-Cas9 system. J Biotechnol 259:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.06.1204
Deng H, Gao R, Liao X, Cai Y (2018) Characterisation of a monooxygenase in Shiraia bambusicola. Microbiology-SGM 164(9):1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000694
Deng H, Liang X, Liu J, Zheng X, Fan TP, Cai Y (2022) Advances and perspectives on perylenequinone biosynthesis. Front Microbiol 13:1070110. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1070110
Deng HX, Chen JJ, Gao RJ, Liao XR, Cai YJ (2016b) Adaptive responses to oxidative stress in the filamentous fungal Shiraia bambusicola. Molecules 21(9):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091118
Deng HX, Liang WY, Fan TP, Zheng XH, Cai YJ (2020) Modular engineering of Shiraia bambusicola for hypocrellin production through an efficient CRISPR system. Int J Biol Macromol 165:796–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.208
Diwu Z, Lown JW (1990) Hypocrellins and their use in photosensitization. Photochem Photobiol 52(3):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1990.tb01807.x
Dong J, Zang K, Zhao Z, Liu W, Li Q (2001) Nematicidal activity of perylenequinones photosensitive compounds (in Chinese). Mycosystema 20(4):515–519
Dong T, Pan W, Zhao Y, Lei X, Chen K, Wang J (2012) Screening of higher hypocrellin A with strains of Shiraia bambusicola by genome-shuffling (in Chinese). Chin J Bioproc Eng 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2012.01.005
Du W, Sun C, Wang B, Wang Y, Dong B, Liu J, Xia J, Xie W, Wang J, Sun J, Liu X, Wang H (2019) Response mechanism of hypocrellin colorants biosynthesis by Shiraia bambusicola to elicitor PB90. AMB Express 9(1):146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0867-5
Du W, Sun CL, Liang ZQ, Han YF, Yu JP (2012) Antibacterial activity of hypocrellin A against Staphylococcus aureus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28(11):3151–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1125-z
Du W, Tian WY, Zeng Q, Wang P, Yu J, Wang W, Han Y, Han J, Gao X, Liang Z (2014) Effect of polysaccharides from bamboo endophytes on hypocrellin production by Shiraia bambusicol (in Chinese). Acta Edulis Fungi 21(4). https://doi.org/10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2014.04.003
Du W, Wang B (2019) High efficiency hypocrellin production by a novel mutant isolated from Shiraia bambusicola. Asian Agric Res 11:94–99. https://doi.org/10.19601/j.cnki.issn.1943-9903.2019.2.017
Fan YD, Zhao X, Wu CF, Wang BX, Wang SY, Shen J, Gui P, Yuan J, Lin HP (2019) Key factors in the antifungal activity of hypocrellin A against Botrytis cinerea (in chinese). Chin J Pestic Sci 21(1):59–65. https://doi.org/10.16801/j.issn.1008-7303.2019.0008
Gao R, Deng H, Guan Z, Liao X, Cai Y (2018a) Enhanced hypocrellin production via coexpression of alpha-amylase and hemoglobin genes in Shiraia bambusicola. AMB Express 8(1):71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0597-0
Gao R, Xu Z, Deng H, Guan Z, Liao X, Zhao Y, Zheng X, Cai Y (2018b) Influences of light on growth, reproduction and hypocrellin production by Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168. Arch Microbiol 200(8):1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1529-8
Gao RJ, Xu ZC, Deng HX, Guan ZB, Liao XR, Zhao Y, Zheng XH, Cai YJ (2018c) Enhanced hypocrellin production of Shiraia sp SUPER-H168 by overexpression of alpha-amylase gene. PLoS One 13(5):e0196519. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196519
Han Q, Shen J, Cai Y, Liao X, Luo J, Zhang D (2013) Effect of vitamins on perylenequinones production of Shiraia bambusicola (in Chinese). J Food Sci Biotechnol 32(2):119–123
Hassan L, Lin LC, Sorek H, Sperl LE, Goudoulas T, Hagn F, Germann N, Tian C, Benz JP (2019) Crosstalk of cellulose and mannan perception pathways leads to inhibition of cellulase production in several filamentous fungi. Mbio 10(4):e00277–e00219. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00277-19
Hirayama J, Ikebuchi K, Abe H, Kwon KW, Ohnishi Y, Horiuchi M, Shinagawa M, Ikuta K, Kamo N, Sekiguchi S (1997) Photoinactivation of virus infectivity by hypocrellin A. Photochem Photobiol 66(5):697–700. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1997.tb03209.x
Hu JY, Sarrami F, Li H, Zhang GZ, Stubbs KA, Lacey E, Stewart SG, Karton A, Piggott AM, Chooi YH (2019) Heterologous biosynthesis of elsinochrome A sheds light on the formation of the photosensitive perylenequinone system. Chem Sci 10(5):1457–1465. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8sc02870b
Hu M, Cai Y, Liao X, Hao Z, Liu J (2012) Development of an HPLC method to analyze and prepare elsinochrome C and hypocrellin A in the submerged fermentation broth of Shiria sp. SUPER-H168. Biomed Chromatogr 26(6):737–742. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.1722
Hudson JB, Zhou J, Chen J, Harris L, Yip L, Towers GH (1994) Hypocrellin, from Hypocrella bambuase, is phototoxic to human immunodeficiency virus. Photochem Photobiol 60(3):253–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1994.tb05100.x
Jan A, Liu C, Deng H, Li J, Ma W, Zeng X, Ji Y (2019) In vitro photodynamic inactivation effects of hypocrellin B on azole-sensitive and resistant Candida albicans. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 27(9):419–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.07.014
Jiang Y, Leung AW, Wang XN, Zhang HW, Xu CS (2013) Inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus by photodynamic action of hypocrellin B. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 10(4):600–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2013.06.004
Khiralla A, Mohammed AO, Yagi S (2022) Fungal perylenequinones. Mycol Prog 21(3):38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-022-01790-4
Kurobane I, Vining LC, Mvinnes AG, Smith DG, Walte JA (1981) Biosynthesis of elsinochromes C and D. pattern of acetate incorporation determined by 13C and 2H nmr. Can J Chem 59:422
Lei XY, Zhang MY, Ma YJ, Wang JW (2017) Transcriptomic responses involved in enhanced production of hypocrellin A by addition of Triton X-100 in submerged cultures of Shiraia bambusicola. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(10):1415–1429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1965-5
Leung AW, Ip M, Xu CS, Wang XN, Yung PT, Hua HY (2017) Sonodynamic bactericidal efficacy of hypocrellin A and B against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Hong Kong Med J 23(Suppl 5):S36–S37
Li D, Zhao N, Guo BJ, Lin X, Chen SL, Yan SZ (2019a) Gentic overexpression increases production of hypocrellin A in Shiraia bambusicola S4201. J Microbiol 57(2):154–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-019-8259-8
Li PX, Ma JY, Wang Y, Wang WJ (2021a) Enhanced hypocrellin production in mycelium Shiraia culture by sodium nitroprusside. Planta Med 87(15):1284–1285. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1736894
Li T, Hou C, Shen X (2019b) Efficient agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Shiraia bambusicola and activation of a specific transcription factor for hypocrellin production. Biotechnol Biotech Eq 33(1):1365–1371. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2019.1667874
Li XP, Ji HY, Wang WJ, Shen WH, Wang JW (2022) Effects of blue light on hypocrellin A production in Shiraia mycelium cultures. Photochem Photobiol 98(6):1343–1354. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.13640
Li XP, Wang Y, Ma YJ, Wang JW, Zheng LP (2020) Nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide signaling in extractive Shiraia fermentation by triton X-100 for hypocrellin A production. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030882
Li XP, Zhou LL, Guo YH, Wang JW (2021b) The signaling role of extracellular ATP in co-culture of Shiraia sp. S9 and Pseudomonas fulva SB1 for enhancing hypocrellin A production. Microb Cell Factories 20(1):144. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01637-9
Li XX, Li XM, Hou CL (2010) Screening of hypocrellin A-producing strains. J Anhui Agric Univ (in chinese) 2(6):218–223
Li YT, Yang C, Wu Y, Lv J, Feng X, Tian X, Zhou Z, Pan X, Liu S, Tian L (2021c) Axial chiral binaphthoquinone and perylenequinones from the stromata of Hypocrella bambusae are SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors. J Nat Prod 84(2):436–443. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01136
Liang XH, Cai YJ, Liao XR, Wu K, Wang L, Zhang D-B, Meng Q (2009) Isolation and identification of a new hypocrellin A-producing strain Shiraia sp. SUPER-H168. Microbiol Res 164(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2008.08.004
Liu B, Bao JY, Zhang ZB, Yan RM, Wang Y, Yang HL, Zhu D (2018) Enhanced production of perylenequinones in the endophytic fungus Shiraia sp Slf14 by calcium/calmodulin signal transduction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(1):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8602-0
Liu XY, Fan L, Gao J, Shen XY, Hou CL (2020a) Global identification of alternative splicing in Shiraia bambusicola and analysis of its regulation in hypocrellin biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(1):211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10189-3
Liu XY, Shen XY, Fan L, Gao J, Hou CL (2016) High-efficiency biosynthesis of hypocrellin A in Shiraia sp. using gamma-ray mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(11):4875–4883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7222-9
Liu ZY, Bao JY, Yang HL, Zhang ZB, Yan RM, Zhu D (2020b) Transcriptome analysis on fructose as the sole carbon source enhancing perylenequinones production of endophytic fungus Shiraia sp. Slf14. 3 Biotech 10(5):190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02181-w
Lu CS, Ma YJ, Wang JW (2019) Lanthanum elicitation on hypocrellin A production in mycelium cultures of Shiraia bambusicola is mediated by ROS generation. J Rare Earths 37(8):895–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.10.010
Lv T, Ding Y, Liao X, Cai Y (2013) Optimization on solid sermentation media of hypocrellin (in Chinese). J Food Sci Biotech 32(8):832–837
Ma GY, Khan SI, Jacob MR, Tekwani BL, Li ZQ, Pasco DS, Walker LA, Khan LA (2004) Antimicrobial and antileishmanial activities of hypocrellins A and B. Antimicrob Agents Ch 48(11):4450–4452. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.48.11.4450-4452.2004
Ma YJ, Li XP, Wang Y, Wang JW (2021) Nitric oxide donor sodium nitroprusside-induced transcriptional changes and hypocrellin biosynthesis of Shiraia sp. S9. Microb Cell Factories 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01581-8
Ma YJ, Lu CS, Wang JW (2018) Effects of 5-Azacytidine on growth and hypocrellin production of Shiraia bambusicola. Front Microbiol 9:2508. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02508
Ma YJ, Sun CX, Wang JW (2019a) Enhanced production of hypocrellin A in submerged cultures of Shiraia bambusicola by red light. Photochem Photobiol 95(3):812–822. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.13038
Ma YJ, Zheng LP, Wang JW (2019b) Bacteria associated with Shiraia fruiting bodies influence fungal production of hypocrellin A. Front Microbiol 10:2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02023
Ma YJ, Zheng LP, Wang JW (2019c) Inducing perylenequinone production from a bambusicolous fungus Shiraia sp. S9 through co-culture with a fruiting body-associated bacterium Pseudomonas fulva SB1. Microb Cell Factories 18(1):121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1170-5
Muller M, Obermaier S, Thiele W, Furtges L (2019) Enantioselective phenol coupling by laccases in the biosynthesis of fungal dimeric naphthopyrones. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 58(27):9125–9128. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201903759
Mulrooey CA, O'Brien EM, Morgan BJ (2012) Kozlowski MC (2012) Perylenequinones: isolation, synthesis, and biological activity. Eur J Org Chem 21:3887–3904. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201200184
Newman AG, Townsend CA (2016) Molecular characterization of the cercosporin biosynthetic pathway in the fungal plant pathogen Cercospora nicotianae. J Am Chem Soc 138(12):4219–4228. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b00633
Niu T, Tian Y, Wang G, Guo G, Tong Y, Shi Y (2020) Inhibition of ROS-NF-κB-dependent autophagy enhances Hypocrellin A united LED red light-induced apoptosis in squamous carcinoma A431 cells. Cell Signal 69:109550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109550
Okuno A, Yamazaki S, Fuwa K (1975) Biosynthesis of cercosporin. Agric Biol Chem 39(5):1173–1175
Pan W, Ji Y, Yang Z, Wang J (2012) Screening of high-yield hypocrellin A producing mutants from Shiraia sp. S8 by protoplast mutagenesis and ultraviolet irradiation(in Chinese). Chinese J Bioproc Eng 10(6). https://doi.org/10.3639/j.issn.1672-3678.2012.06.004
Qi SS, Guo LY, Yan SZ, Lee RJ, Yu SQ, Chen SL (2019) Hypocrellin A-based photodynamic action induces apoptosis in A549 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial signaling pathway. Acta Pharm Sin B 9(2):279–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2018.12.004
Qiu YR, Zhao AL, Sun PD (2011) Preparation of hypocrellin liposome and determination of its extent of encapsulation (in Chinese). China Surfact Det Cosmet 41(6):422–425
Shen WH, Cong RP, Li XP, Huang QY, Zheng LP, Wang JW (2023) Effects of branched-chain amino acids on Shiraia perylenequinone production in mycelium cultures. Microb Cell Factories 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-023-02066-6
Shen XY, Hu YJ, Song L, Hou CL (2016) Improvement of hypocrellin production by a new fungal source and optimization of cultivation conditions. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 30(4):819–826. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2016.1178077
Shim WB, Dunkle LD (2003) CZK3, a MAP kinase kinase kinase homolog in Cercospora zeae-maydis, regulates cercosporin biosynthesis, fungal development, and pathogenesis. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16(9):760–768. https://doi.org/10.1094/mpmi.2003.16.9.760
Silva CAD, Oka ML, Fonseca GG (2019) Physiology of yeast strains isolated from Brazilian biomes in a minimal medium using fructose as the sole carbon source reveals potential biotechnological applications. 3 Biotech 9(5):191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1721-9
Silva D, Pozza EA, Monteiro FP, Rodrigues CV, Lima VD (2016) Effect of light and temperature on Cercospora coffeicola and Coffea arabica pathosystem. Coffee Sci 11(2):148–160 http://www.sbicafe.ufv.br:80/handle/123456789/8061
Song S, Sun X, Meng L, Wu Q, Wang K, Deng Y (2021) Antifungal activity of hypocrellin compounds and their synergistic effects with antimicrobial agents against Candida albicans. Microb Biotechnol 14(2):430–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13601
Su Y, Rao S, Cai Y, Yang Y (2010) Preparation and characterization of the inclusion complex of hypocrellin A with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Eur Food Res Technol 231(5):781–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-010-1322-7
Su YJ, Si SH, Qiao LW, Cai YJ, Xu ZM, Yang YJ (2011) The effect of a hypocrellin A enriched diet on egg yolk quality and hypocrellin A distributions in the meat of laying hens. Eur Food Res Technol 232(6):935–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1461-5
Su YJ, Yin XY, Rao SQ, Cai YJ, Reuhs B, Yang YJ (2009) Natural colourant from Shiraia bambusicola: stability and antimicrobial activity of hypocrellin extract. Int J Food Sci Technol 44(12):2531–2537. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2009.02080.x
Sun CX, Ma YJ, Wang JW (2017) Enhanced production of hypocrellin A by ultrasound stimulation in submerged cultures of Shiraia bambusicola. Ultrason Sonochem 38:214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.03.020
Sun CX, Ma YJ, Wang JW (2018) Improved hypocrellin A production in Shiraia bambusicola by light-dark shift. J Photochem Photobiol B 182:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.004
Tang L, Bao J, Yan R, Wang Y, Yang H, Zhang Z, Zhu D (2019) The effects of different carbon sources on production of perylenequinones in endophytic fungus Shiraia sp.Slfl4 (in Chinese). J Jiangxi Norm Univ (Nat Sci) 43(5):6
Tantry MA, Idris AS, Williamson JS, Shafi T, Dar JS, Malik TA, Ganai BA, Shawl AS (2018) Perylenequinones from an endophytic Alternaria sp. of Pinus ponderosa. Heliyon 4(12). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e01046
Tong Z, Mao L, Liang H, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Yan R, Zhu D (2017) Simultaneous determination of six perylenequinones in Shiraia sp. Slf14 by HPLC. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 40(10):536–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2017.1331172
Wan XX, Xu Y, Li YL, Liao QM, Tao H, Wang HL (2022) Photodynamic inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus in the system of titanium dioxide nanoparticles sensitized by hypocrellin B and its application in food preservation. Food Res Int 156:111141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111141
Wang LY, Bau HJ, Liao HL, Chung KR (2009) Factors affecting the production of elsinochrome phytotoxin by the citrus scab pathogen, Elsinoë fawcettii. Open Mycol J 3:1–8. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874437000903010001
Wang L, Wang J, Cao YY, Li WJ, Wang Y, Xu JL, Xu GL (2019) Molecular evidence for better efficacy of hypocrellin A and oleanolic acid combination in suppression of HCC growth. Eur J Pharmacol 842:281–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.10.042
Wang WJ, Huang QY, Wang Y, Li XP, Wang JW, Zheng LP (2022) Melatonin-induced inhibition of Shiraia hypocrellin A biosynthesiso is mediated by hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide. J Fungi 8(8):836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080836
Wang XN, Ip M, Leung AW, Wang P, Zhang HW, Hua HY, Xu CS (2016) Sonodynamic action of hypocrellin B on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ultrasonics 65:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2015.10.008
Weiss U, Merlini L, Nasini G (1987) Naturally occurring perylenequinones. In: Achenbach H, Bhattacharyya P, Chakraborty DP, Goto T, Merlini L, Nasini G, Weiss U (eds) Fortschritte der chemie organischer naturstoffe/progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products. Springer Vienna, Vienna, pp 1–71
Wen Y, Liao B, Yan X, Wu Z, Tian X (2022) Temperature-responsive regulation of the fermentation of hypocrellin A by Shiraia bambusicola (GDMCC 60438). Microb Cell Factories 21(1):135. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01862-w
Wu HM, Lao XF, Wang QW, Lu RR (1989) The shiraiachromes: novel fungal perylenequinone pigments from Shiraia Bambusicola. J Nat Prod 52(5):948–951. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50065a006
Wu T, Weng M, Chen S, Wang L, Bi Z, Li T, Zhang M, Shen T (1998) Photovoltaic and electrical properties of Langmuir–Blodgett films incorporating hypocrellins derivatives. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 118(3):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(98)00351-7
Xia G, Ma H (2012) Screening and molecular identification of hypocrellin-producing Shiraia bambusicola (in Chinese). J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Agric Sci) 30(6):1–5, 21. https://doi.org/10.3969/J.ISSN.1671-9964.2012.06.001
Xiang X (2010) Optimization of Shiraia bambusicola P. Henn. under liquid fermentation (in Chinese). Biotechnol 20(4):73–75. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-311X.2010.04.135
Xu C, Lin W, Chen Y, Gao B, Zhang Z, Zhu D (2023) Heat stress enhanced perylenequinones biosynthesis of Shiraia sp. Slf14(w) through nitric oxide formation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107(11):3745–3761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12554-9
Xu R, Li XP, Zhang X, Shen WH, Min CY, Wang JW (2022) Contrasting regulation of live Bacillus cereus No.1 and its volatiles on Shiraia perylenequinone production. Microb Cell Factories 21(1):172. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01897-z
Xu S, Chen S, Zhang M, Shen T, Zhang X, Wang Z (2003) Synthesis and characterization of three novel amphiphilic aminated hypocrellins as photodynamic therapeutic agents. Photochem Photobiol 78:411–415. https://doi.org/10.1562/0031-8655
Xue Z, Li P, Zhu X, Zhang P, Shuang Z, Jiang D, Lou J, Lin H (2015) Inhibitory effect of hypocrellin A against Botrytis cinerea (in Chinese). Chin J Pestic Sci 17(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-7303.2015.02.05
Yan X, Wen Y, Hu M, Wu Z, Tian X (2021) Promotion of the hypocrellin yield by a co-culture of Shiraia bambusicola (GDMCC 60438) with Arthrinium sp. AF-5 fungus. Fermentation 7(4):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040316
Yang H, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Yan R, Zhu D (2014) Whole-genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Shiraia sp. strain Slf14, a novel endophytic fungus producing huperzine A and hypocrellin A. Genome Announc 2(1):e00011–e00014. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00011-14
Yang H, Xiao C, Ma W, He G (2009) The production of hypocrellin colorants by submerged cultivation of the medicinal fungus Shiraia bambusicola. Dyes Pigments 82(2):142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2008.12.012
Yang X, Yan Z, Jiang L, Wang X, Zheng K, Wang Y, Li Q, Wang J (2013) Synthesis and photocatalysis of Al doped CdS templated by non-surfactant hypocrellins. Procedia Environ Sci 18:572–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2013.04.077
Yang Y, Wang C, Zhuge Y, Zhang J, Xu K, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Chen H, Chu M, Jia C (2019) Photodynamic antifungal activity of hypocrellin A against Candida albicans. Front Microbiol 10:1810. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01810
You BJ, Lee MH, Chung KR (2008) Production of cercosporin toxin by the phytopathogenic Cercospora fungi is affected by diverse environmental signals. Can J Microbiol 54(4):259–269. https://doi.org/10.1139/w08-002
Zhang WL, Wan XY, Wang QF (1989) Determination of hypocrellin B in the alcochol extracts from Hyocrella bambusae and preprations by spectrophotometric method (in Chinese). J Yunnan Univ (Nat Sci) 11:37–39
Zhang YL, Zhang L, Gao J, Bai J, Yan DJ, Zhang YY, Hu YC (2020) Heterologous biosynthesis of main active components of medicinal fungus Bambusa bambusa (in Chinese). Acta Pharm Sin 55(7):1691–1698. https://doi.org/10.16438/j.0513-4870.2020-069
Zhao N, Li D, Guo BJ, Tao X, Lin X, Yan SZ, Chen SL (2020) Genome sequencing and analysis of the hypocrellin-producing fungus Shiraia bambusicola S4201. Front Microbiol 11:643. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00643
Zhao N, Lin X, Qi SS, Luo ZM, Chen SL, Yan SZ (2016) De novo transcriptome assembly in Shiraia bambusicola to investigate putative genes involved in the biosynthesis of hypocrellin A. Int J Mol Sci 17(3):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030311
Zhao N, Yu YY, Yue YX, Dou MZ, Guo BJ, Yan SZ, Chen SL (2021a) Nitric oxide regulates perylenequinones biosynthesis in Shiraia bambusicola S4201 induced by hydrogen peroxide. Sci Rep 11(1):2365. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81990-2
Zhao X, Li PJ, Zhu XW, Zhang PY, Zhang S, Jiang DJ, Lou JY, Lin HP (2015) Inhibitory effect of hypocrellin A on Botrytis cinerea (in Chinese). Chin J Pestic Sci 17(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-7303.2015.02.05
Zhao YX, Yuan WW, Sun MN, Zhang XG, Zheng WF (2021b) Regulatory effects of nitric oxide on reproduction and melanin biosynthesis in onion pathogenic fungus Stemphylium eturmiunum. Fungal Biol 125(7):519–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2021.01.010
Zhong Q, Zhou LG, Yuan MM, Liao YY, Zhou GP (2020) Simultaneous determination of three quinones in Zhuhuang capsules by HPLC (in Chinese). Chin J Pharm Anal 40(1):139–144 https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:YWFX.0.2020-01-019
Zhou LL, Shen WH, Ma YJ, Li XP, Wu JY, Wang JW (2023) Structure characterization of an exopolysaccharide from a Shiraia-associated bacterium and its strong eliciting activity on the fungal hypocrellin production. Int J Biol Macromol 226:423–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.005
Zhu D, Wang J, Zeng Q, Zhang Z, Yan R (2010) A novel endophytic huperzine A–producing fungus, Shiraia sp. Slf14, isolated from Huperzia serrata. J Appl Microbiol 109(4):1469–1478. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04777.x
Zhu Q (2014) Inhibition of hypocrellin A against 18 pathogenic fungi (in Chinese). Acta Phytopathol Sin 44(1):107–109. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0412-0914.2014.01.013
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32260016 and 31460021) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province of China (Grant No. 20181BAB214003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DZ and YX designed the structure of this review. ZB and CX wrote the manuscript. DZ and ZZ revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No human participants or animals were used in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Z., Xie, Y., Xu, C. et al. Biotechnological production and potential applications of hypocrellins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 6421–6438 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12727-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12727-6