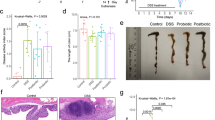
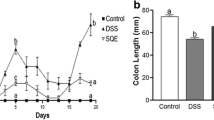
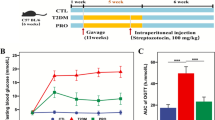
Abstract
Compound prebiotics (CP) have been explored in modulation of intestinal microbiota and remission of inflammatory responses in the acute colitis (AC). Yet, research on the roles of simultaneous prophylactic and therapeutic CP intervention in relation to AC remains lacking. Here, CP were pre-fed to examine preventive effects. CP, CP combined with mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) (CPM), and mesalazine were used to evaluate therapeutic effects on the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)–induced AC. Results showed that prophylactic CP and therapeutic CPM alleviated AC, evidenced by variations of body weight, colon length, spleen index, disease activity index score, histological score, and intestinal mucosa. Ruminococcus and Bifidobacterium were detected in significant abundance in the prophylactic CP and therapeutic CPM groups, respectively. Phylogenetic ecological network analysis revealed that therapeutic CPM probably had the strongest coupling between microbes in changing intestinal microbiota to influence treatment. However, changes in short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) seemed to have no persuasive results, probably due to reduced SCFA level in feces and variability in transit, absorption, and utilization. Furthermore, therapeutic CP exerted higher value in terms of observed species and Shannon diversity, as well as a more concentrated distribution by principal coordinates analysis. Together, the favorable roles of CP in colitis provide directions for prebiotics in designing effective prophylactic functional diets and treatment strategies.
Key points
• Prebiotics as prophylactic intervention effectively inhibited acute colitis.
• Prebiotics as prophylactic and therapeutic interventions had distinct effects on gut microbiota.
• Prebiotics combined with drug intervention had higher efficacy in treating acute colitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The fecal microbial 16S rRNA sequences were deposited to the sequence read archive. The Bioproject accession for the 16S sequencing data is PRJNA764077 (https://dataview.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/object/PRJNA764077).
References
Alexander JL, Wilson ID, Teare J, Marchesi JR, Nicholson JK, Kinross JM (2017) Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(6):356–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.20
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Celiberto LS, Graef FA, Healey GR, Bosman ES, Jacobson K, Sly LM, Vallance BA (2018) Inflammatory bowel disease and immunonutrition: novel therapeutic approaches through modulation of diet and the gut microbiome. Immunology 155(1):36–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12939
Chassaing B, Van de Wiele T, De Bodt J, Marzorati M, Gewirtz AT (2017) Dietary emulsifiers directly alter human microbiota composition and gene expression ex vivo potentiating intestinal inflammation. Gut 66(8):1414–1427. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313099
Cong J, Zhang Y, Xue Y, Zhang C, Xu M, Liu D, Zhang R, Zhu H (2020) A pilot study: changes of intestinal microbiota of patients with non-small cell lung cancer in response to osimertinib therapy. Front Microbiol 11(2901):583535. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.583525
Cong J, Zhou P, Zhang R (2022) Intestinal microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids in host health and disease. Nutrients 14(9):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091977
De Cassan C, Fiorino G, Danese S (2012) Second-generation corticosteroids for the treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis: more effective and less side effects? Dig Dis 30(4):368–375. https://doi.org/10.1159/000338128
den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud DJ, Bakker BM (2013) The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res 54(9):2325–2340. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R036012
Deng Y, Jiang YH, Yang Y, He Z, Luo F, Zhou J (2012) Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 13:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-113
Dominguez-Bello MG, Godoy-Vitorino F, Knight R, Blaser MJ (2019) Role of the microbiome in human development. Gut 68(6):1108–1114. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317503
Dulai PS, Singh S, Casteele NV, Boland BS, Sandborn WJ (2016) How will evolving future therapies and strategies change how we position the use of biologics in moderate to severely active inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 22(4):998–1009. https://doi.org/10.1097/mib.0000000000000661
Evangelista AG, Danielski GM, Corrêa JAF, Cavalari CMA, Souza IR, Luciano FB, Macedo REF (2022) Carnobacterium as a bioprotective and potential probiotic culture to improve food quality, food safety, and human health - a scoping review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2038079
Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, Scott K, Stanton C, Swanson KS, Cani PD, Verbeke K, Reid G (2017) Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(8):491–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75
Glassner KL, Abraham BP, Quigley EMM (2020) The microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 145(1):16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.003
Gu Z, Zhu Y, Jiang S, Xia G, Li C, Zhang X, Zhang J, Shen X (2020) Tilapia head glycolipids reduce inflammation by regulating the gut microbiota in dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis mice. Food Funct 11(4):3245–3255. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo00116c
Hall AB, Yassour M, Sauk J, Garner A, Jiang X, Arthur T, Lagoudas GK, Vatanen T, Fornelos N, Wilson R, Bertha M, Cohen M, Garber J, Khalili H, Gevers D, Ananthakrishnan AN, Kugathasan S, Lander ES, Blainey P, Vlamakis H, Xavier RJ, Huttenhower C (2017) A novel Ruminococcus gnavus clade enriched in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Genome Med 9(1):103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-017-0490-5
He XX, Li YH, Yan PG, Meng XC, Chen CY, Li KM, Li JN (2021) Relationship between clinical features and intestinal microbiota in Chinese patients with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 27(28):4722–4737. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4722
Hong Y, Sheng L, Zhong J, Tao X, Zhu W, Ma J, Yan J, Zhao A, Zheng X, Wu G, Li B, Han B, Ding K, Zheng N, Jia W, Li H (2021) Desulfovibrio vulgaris, a potent acetic acid-producing bacterium, attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut Microbes 13(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1930874
Humbel F, Rieder JH, Franc Y, Juillerat P, Scharl M, Misselwitz B, Schreiner P, Begré S, Rogler G, von Känel R, Yilmaz B, Biedermann L (2020) Association of alterations in intestinal microbiota with impaired psychological function in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases in remission. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(9):2019-2029.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.022
Imhann F, Vich Vila A, Bonder MJ, Fu J, Gevers D, Visschedijk MC, Spekhorst LM, Alberts R, Franke L, van Dullemen HM, Ter Steege RWF, Huttenhower C, Dijkstra G, Xavier RJ, Festen EAM, Wijmenga C, Zhernakova A, Weersma RK (2018) Interplay of host genetics and gut microbiota underlying the onset and clinical presentation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 67(1):108–119. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312135
Jiang W, Ling Z, Lin X, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yu J, Xiang C, Chen H (2014) Pyrosequencing analysis of oral microbiota shifting in various caries states in childhood. Microb Ecol 67(4):962–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-014-0372-y
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Bäckhed F (2016) From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 165(6):1332–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041
Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Jamieson C, Johnson IT, Colquhoun IJ, Kemsley EK, Narbad A (2011) Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res 10(9):4208–4218. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr2003598
Liu C, Huang S, Wu Z, Li T, Li N, Zhang B, Han D, Wang S, Zhao J, Wang J (2021) Cohousing-mediated microbiota transfer from milk bioactive components-dosed mice ameliorate colitis by remodeling colonic mucus barrier and lamina propria macrophages. Gut Microbes 13(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1903826
Liu S, Zhao W, Lan P, Mou X (2021) The microbiome in inflammatory bowel diseases: from pathogenesis to therapy. Protein Cell 12(5):331–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-020-00745-3
Maloy KJ, Powrie F (2011) Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 474(7351):298–306. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10208
Mao B, Li D, Zhao J, Liu X, Gu Z, Chen YQ, Zhang H, Chen W (2015) Metagenomic insights into the effects of fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on the composition of fecal microbiota in mice. J Agric Food Chem 63(3):856–863. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf505156h
Mazmanian SK, Round JL, Kasper DL (2008) A microbial symbiosis factor prevents intestinal inflammatory disease. Nature 453(7195):620–625. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07008
McDonald D, Price MN, Goodrich J, Nawrocki EP, DeSantis TZ, Probst A, Andersen GL, Knight R, Hugenholtz P (2012) An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J 6(3):610–618. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.139
Mukherjee A, Lordan C, Ross RP, Cotter PD (2020) Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 12(1):1802866. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2020.1802866
Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG (2017) Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 390(10114):2769–2778. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32448-0
Nguyen NH, Singh S, Sandborn WJ (2020) Positioning therapies in the management of Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(6):1268–1279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.035
Ni J, Wu GD, Albenberg L, Tomov VT (2017) Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(10):573–584. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.88
Pascal V, Pozuelo M, Borruel N, Casellas F, Campos D, Santiago A, Martinez X, Varela E, Sarrabayrouse G, Machiels K, Vermeire S, Sokol H, Guarner F, Manichanh C (2017) A microbial signature for Crohn’s disease. Gut 66(5):813–822. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313235
Qi Q, Liu YN, Lv SY, Wu HG, Zhang LS, Cao Z, Liu HR, Wang XM, Wu LY (2022) Gut microbiome alterations in colitis rats after moxibustion at bilateral Tianshu acupoints. BMC Gastroenterol 22(1):62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-022-02115-1
Radhakrishnan ST, Alexander JL, Mullish BH, Gallagher KI, Powell N, Hicks LC, Hart AL, Li JV, Marchesi JR, Williams HRT (2022) Systematic review: the association between the gut microbiota and medical therapies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 55(1):26–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.16656
Rooks MG, Garrett WS (2016) Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 16(6):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.42
Ruemmele FM, Veres G, Kolho KL, Griffiths A, Levine A, Escher JC, Amil Dias J, Barabino A, Braegger CP, Bronsky J, Buderus S, Martín-de-Carpi J, De Ridder L, Fagerberg UL, Hugot JP, Kierkus J, Kolacek S, Koletzko S, Lionetti P, Miele E, NavasLópez VM, Paerregaard A, Russell RK, Serban DE, Shaoul R, Van Rheenen P, Veereman G, Weiss B, Wilson D, Dignass A, Eliakim A, Winter H, Turner D (2014) Consensus guidelines of ECCO/ESPGHAN on the medical management of pediatric Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 8(10):1179–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2014.04.005
Russo E, Giudici F, Fiorindi C, Ficari F, Scaringi S, Amedei A (2019) Immunomodulating activity and therapeutic effects of short chain fatty acids and tryptophan post-biotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol 10:2754. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02754
Sartor RB, Wu GD (2017) Roles for intestinal bacteria, viruses, and fungi in pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterology 152(2):327-339.e4. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.012
Shinde T, Perera AP (2019) Synbiotic supplementation containing whole plant sugar cane fibre and probiotic spores potentiates protective synergistic effects in mouse model of IBD. Nutrients 11(4):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040818
Singh SB, Coffman CN, Varga MG, Carroll-Portillo A, Braun CA, Lin HC (2022) Intestinal alkaline phosphatase prevents sulfate reducing bacteria-induced increased tight junction permeability by inhibiting snail pathway. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:882498. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.882498
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly YM, Glickman JN, Garrett WS (2013) The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 341(6145):569–573. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241165
Sonnenburg JL, Bäckhed F (2016) Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 535(7610):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18846
Sun Y, Xie R, Li L, Jin G, Zhou B, Huang H, Li M, Yang Y, Liu X, Cao X, Wang B, Liu W, Jiang K, Cao H (2021) Prenatal maternal stress exacerbates experimental colitis of offspring in adulthood. Front Immunol 12:700995. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.700995
Takaishi H, Matsuki T, Nakazawa A, Takada T, Kado S, Asahara T, Kamada N, Sakuraba A, Yajima T, Higuchi H, Inoue N, Ogata H, Iwao Y, Nomoto K, Tanaka R, Hibi T (2008) Imbalance in intestinal microflora constitution could be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Med Microbiol 298(5–6):463–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2007.07.016
Tomova A, Bukovsky I, Rembert E, Yonas W, Alwarith J, Barnard ND, Kahleova H (2019) The effects of vegetarian and vegan diets on gut microbiota. Front Nutr 6:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00047
Vich Vila A, Imhann F, Collij V, Jankipersadsing SA, Gurry T, Mujagic Z, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ, Jiang X, Tigchelaar EF, Dekens J, Peters V, Voskuil MD, Visschedijk MC, van Dullemen HM, Keszthelyi D, Swertz MA, Franke L, Alberts R, Festen EAM, Dijkstra G, Masclee AAM, Hofker MH, Xavier RJ, Alm EJ, Fu J, Wijmenga C, Jonkers D, Zhernakova A, Weersma RK (2018) Gut microbiota composition and functional changes in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Sci Transl Med 10(472):eaap8914. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aap8914
Wang J, Ji H, Wang S, Liu H, Zhang W, Zhang D, Wang Y (2018) Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum promotes intestinal barrier function by strengthening the epithelium and modulating gut microbiota. Front Microbiol 9:1953. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01953
Wang X, Tsai T, Deng F, Wei X, Chai J, Knapp J, Apple J, Maxwell CV, Lee JA, Li Y, Zhao J (2019) Longitudinal investigation of the swine gut microbiome from birth to market reveals stage and growth performance associated bacteria. Microbiome 7(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0721-7
Weiss S, Xu ZZ, Peddada S, Amir A, Bittinger K, Gonzalez A, Lozupone C, Zaneveld JR, Vázquez-Baeza Y, Birmingham A, Hyde ER, Knight R (2017) Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 5(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-017-0237-y
Wirtz S, Neufert C, Weigmann B, Neurath MF (2007) Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat Protoc 2(3):541–546. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.41
Yan F, Li N, Shi J, Li H, Yue Y, Jiao W, Wang N, Song Y, Huo G, Li B (2019) Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct 10(9):5804–5815. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo01062a
Zhang J, Guo Z, Lim AA, Zheng Y, Koh EY, Ho D, Qiao J, Huo D, Hou Q, Huang W, Wang L, Javzandulam C, Narangerel C, Jirimutu M, Lee YK, Zhang H (2014) Mongolians core gut microbiota and its correlation with seasonal dietary changes. Sci Rep 4:5001. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05001
Zhang SL, Wang SN, Miao CY (2017) Influence of microbiota on intestinal immune system in ulcerative colitis and its intervention. Front Immunol 8:1674. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01674
Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E (2020) Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res 30(6):492–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7
Zhou J, Deng Y, Luo F, He Z, Yang Y (2011) Phylogenetic molecular ecological network of soil microbial communities in response to elevated CO2. mBio 2(4):e00122. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00122-11
Funding
This work was supported by the funding from CNS-ZD Tizhi and Health Fund (CNS-ZD2020-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. C. and P. W. were involved in the conception and design of the study. J. C., P. W., S. Y. Z., Y. Z., and T. Y. Z. were involved in the collection and assembly of data. J. C. was involved in the data analysis and interpretation. G. H. R. was involved in the revision of figures and tables. All authors interpreted the data. J. C. wrote the first draft of manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All the procedures used in this study followed national institutes of health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Qingdao University.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cong, J., Wang, P., Gai, H. et al. Effects of compound prebiotics as prophylactic and therapeutic supplementation in a mouse model of acute colitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 2597–2609 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12453-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12453-z