Abstract
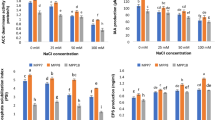
New strategies to improve crop yield include the incorporation of plant growth-promoting bacteria in agricultural practices. The non-pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas putida KT2440 is an excellent root colonizer of crops of agronomical importance and has been shown to activate the induced systemic resistance of plants in response to certain foliar pathogens. In this work, we have analyzed additional plant growth promotion features of this strain. We show it can tolerate high NaCl concentrations and determine how salinity influences traits such as the production of indole compounds, siderophore synthesis, and phosphate solubilization. Inoculation with P. putida KT2440 significantly improved seed germination and root and stem length of soybean and corn plants under saline conditions compared to uninoculated plants, whereas the effects were minor under non-saline conditions. Also, random transposon mutagenesis was used for preliminary identification of KT2440 genes involved in bacterial tolerance to saline stress. One of the obtained mutants was analyzed in detail. The disrupted gene encodes a predicted phosphoethanolamine-lipid A transferase (EptA), an enzyme described to be involved in the modification of lipid A during lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biosynthesis. This mutant showed changes in exopolysaccharide (EPS) production, low salinity tolerance, and reduced competitive fitness in the rhizosphere.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahemad M, Kibret M (2014) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: current perspective. J King Saud Univ Sci 26:1–20
Anandan A, Evans GL, Condic-Jurkic K, O’Mara ML, John CM, Phillips NJ, Jarvis GA, Wills SS, Stubbs KA, Moraes I, Kahler CM, Vrielink A (2017) Structure of a lipid A phosphoethanolamine transferase suggests how conformational changes govern substrate binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(9):2218–2223
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chang WS, Van De Mortel M, Nielsen L, De Guzman GN, Li X, Halverson LJ (2007) Alginate production by Pseudomonas putida creates a hydrated microenvironment and contributes to biofilm architecture and stress tolerance under water-limiting conditions. J Bacteriol 189(22):8290–8299
Chaundhary T, Shukla P (2019) Bioinoculants for bioremediation applications and disease resistance: innovative perspectives. Indian J Microbiol 59(2):129–136
Chen C, Beattie GA (2007) Characterization of the osmoprotectant transporter OpuC from Pseudomonas syringae and demonstration that cystathionine-B-synthase domains are required for its osmoregulatory function. J Bacteriol 189(19):6901–6912
Chen J, Lee SM, Mao Y (2004) Protective effect of exopolysaccharide colanic acid of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to osmotic and oxidative stress. Int J Food Microbiol 93:281–286
Cheng Z, Park E, Glick BR (2007) 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Pseudomonas putida UW4 facilitates the growth of canola in the presence of salt. Can J Microbiol 53:912–918
Compant S, Clément C, Sessitsch A (2010) Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo- and endosphere of plants: their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization. Soil Biol Biochem 42(5):669–678
Cox AD, Wright JC, Li J, Hood DW, Moxon ER, Richards JC (2003) Phosphorylation of the lipid A region of meningococcal lipopolysaccharide: identification of a family of transferases that add phosphoethanolamine to lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol 185(11):3270–3277
de Lorenzo V, Herrero M, Jakubzik U, Timmis KN (1990) Mini-Tn5 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis, promoter probing, and chromosomal insertion of cloned DNA in gram-negative eubacteria. J Bacteriol 172(11):6568–6572
Espinosa-Urgel M, Salido A, Ramos JL (2000) Genetic analysis of functions involved in adhesion of Pseudomonas putida to seeds. J Bacteriol 182(9):2363–2369
Espinosa-Urgel M, Kolter R, Ramos JL (2002) Root colonization by Pseudomonas putida: love at first sight. Microbiology 148:341–344
Fernández-Piñar R, Espinosa-Urgel M, Dubern JF, Heeb S, Ramos JL, Cámara M (2012) Fatty acid-mediated signalling between two Pseudomonas species. Environ Microbiol Rep 4:417–423
Friedman L, Kolter R (2004) Two genetic loci produce distinct carbohydrate-rich structural components of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix. J Bacteriol 186(14):4457–4465
Glick BR (2014) Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol Res 169:30–39
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the Salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(2):793–796
Goswami D, Janki N, Pinakin C (2016) Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): a review. Cogent Food Agric 2:1127500
Haas D, Défago G (2005) Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:307–319
Hamamoto S, Horie T, Hauser F, Deinlein U, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2015) HKT transporters mediate salt stress resistance in plants: from structure and function to the field. Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:113–120
Hardoim PR, Van Overbeek LS, Berg G, Pirttilä AM, Compant S, Campisano A, Döring M, Sessitsch A (2015) The hidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 79(3):293–320
Honma M, Shimomura T (1978) Metabolism of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid. Agric Biol Chem 42:1825–1831
Huang TP, Somers EB, Wong ACL (2006) Differential biofilm formation and motility associated with lipopolysaccharide/exopolysaccharide-coupled biosynthetic genes in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Bacteriol 188(8):3116–3120
Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B, Van Montagu M, Kellenberger E (1994) Root colonization and systemic spreading of Azoarcus sp. strain BH72 in grasses. J Bacteriol 176(7):1913–1923
Jiang H, Dong H, Yu B, Liu X, Li Y, Ji S, Zhang CL (2007) Microbial response to salinity change in Lake Chaka, a hypersaline lake on Tibetan plateau. Environ Microbiol 9(10):2603–2621
Kan G, Zhang W, Yang W, Ma D, Zhang D, Hao D, Hu Z, Yu D (2015) Association mapping of soybean seed germination under salt stress. Mol Gen Genomics 290:2147–2162
Kang SM, Khan AL, Waqas M, You YH, Kim JH, Kim J-G, Hamayun M, Lee IJ (2014) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria reduce adverse effects of salinity and osmotic stress by regulating phytohormones and antioxidants in Cucumis sativus. J Plant Interact 9(1):673–682
Kao CC, Sequiera L (1991) A gene cluster required for coordinated biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide and extracellular polysaccharide also affects virulence of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol 173(24):7841–7847
Kingsley MT, Gabriel DW, Marlow GC, Roberts PD (1993) The opsX locus of Xanthomonas campestris affects host range and biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide and extracellular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol 175(18):5839–5850
Kloepper JW, Schroth M (1978) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on radishes. Proc 4th Int Conf Plant Pathog Bact 2:879–882
Lee Y, Oh S, Park W (2009) Inactivation of the Pseudomonas putida KT2440 dsbA gene promotes extracellular matrix production and biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 297:38–48
Lerner A, Castro-Sowinski S, Valverde A, Lerner H, Dror R, Okon Y, Burdman S (2009a) The Azospirillum brasilense Sp7 noeJ and noeL genes are involved in extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis. Microbiology 155:4058–4068
Lerner A, Okon Y, Burdman S (2009b) The wzm gene located on the pRhico plasmid of Azospirillum brasilense Sp7 is involved in lipopolysaccharide synthesis. Microbiology 155:791–804
Liebens V, Defraine V, Fauvart M (2016) A whole-cell-based high-throughput screening method to identify molecules targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa persister cells. Methods Mol Biol 1333:113–120
Lloret J, Bolaños L, Lucas MM, Peart JM, Brewin NJ, Bonilla I, Rivilla R (1995) Ionic stress and osmotic pressure induce different alterations in the lipopolysaccharide of a Rhizobium meliloti strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(10):3701–3704
Lynch JM, de Leij F (2012) Rhizosphere. eLS
Mao Y, Doyle MP, Chen J (2001) Insertion mutagenesis of wca reduces acid and heat tolerance of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7. J Bacteriol 183(12):3811–3815
Martínez-Gil M, Yousef-Coronado F, Espinosa-Urgel M (2010) LapF, the second largest Pseudomonas putida protein, contributes to plant root colonization and determines biofilm architecture. Mol Microbiol 77(3):549–561
Martínez-Gil M, Quesada JM, Ramos-González MI, Soriano MI, de Cristóbal RE, Espinosa-Urgel M (2013) Interplay between extracellular matrix components of Pseudomonas putida biofilms. Res Microbiol 164:382–389
Matilla MA, Ramos JL, Bakker PAHM, Doornbos R, Badri DV, Vivanco JM, Ramos-González MI (2009) Pseudomonas putida KT2440 causes induced systemic resistance and changes in Arabidopsis root exudation. Environ Microbiol Rep 2(3):381–388
Matilla MA, Travieso ML, Ramos JL, Ramos-González MI (2011) Cyclic diguanylate turnover mediated by the sole GGDEF/EAL response regulator in Pseudomonas putida: its role in the rhizosphere and an analysis of its target processes. Environ Microbiol 13(7):1745–1766
McWilliams R, Chapman M, Kowalczuk KM, Hersberger D, Sun J, Kao CC (1995) Complementation and analysis of Pseudomonas solanacearum extracellular polysaccharide mutants and identification of genes responsive of EpsR. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8(6):837–844
Molina-Romero D, Baez A, Quinteros-Hernández V, Castañeda-Lucio M, Fuentes-Ramírez LE, Bustillos-Cristales MR, Rodríguez-Andrade O, Morales-García YE, Munive A, Muñoz-Rojas J (2017a) Compatible bacterial mixture, tolerant to desiccation, improves maize plant growth. PLoS One 12(11):e0187913
Molina-Romero D, Morales-García YE, Hernández-Tenorio AL, Castañeda-Lucio M, Netzahuatl-Muñoz AR, Muñoz-Rojas J (2017b) Pseudomonas putida estimula el crecimiento de maíz en función de la temperatura. Rev Iberoam Cienc 4:80–88
Nakazawa T (2002) Travels of a Pseudomonas, from Japan around the world. Environ Microbiol 4(12):782–786
Nautiyal CS (1999) An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170:265–270
Neal AL, Ton J (2013) Systemic defense priming by Pseudomonas putida KT2440 in maize depends on benzoxazinoid exudation from the roots. Plant Signal Behav 8(1):e22655
Nezarat S, Gholami A (2009) Screening plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for improving seed germination, seedling growth and yield of maize. Pak J Biol Sci 12:26–32
Nielsen L, Li X, Halverson LJ (2011) Cell-cell and cell-surface interactions mediated by cellulose and a novel exopolysaccharide contribute to Pseudomonas putida biofilm formation and fitness under water-limiting conditions. Environ Microbiol 13(5):1342–1356
Nilsson M, Chiang WC, Fazli M, Gjermansen M, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2011) Influence of putative exopolysaccharide genes on Pseudomonas putida KT2440 biofilm stability. Environ Microbiol 13(5):1357–1369
O’Toole GA, Kolter R (1998) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signaling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28(3):449–461
Patil AD (2015) Alleviating salt stress in crop plants through salt tolerant microbes. Int J Sci Res 4(1):1297–1302
Pattanaik B, Schumann R, Karstein U (2007) Effects of ultraviolet radiation on cyanobacteria and their protective mechanisms. In: Seckbach J (ed) Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 31–48
Patten CL, Glick BR (2002) Role of Pseudomonas putida indoleacetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(8):3795–3801
Paul D, Lade H (2014) Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria to improve crop growth in saline soils: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:737–752
Petrocelli S, Tondo ML, Daurelio LD, Orellano EG (2012) Modifications of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri lipopolysaccharide affect the basal response and the virulence process during citrus canker. PLoS One 7(7):e40051
Planchamp C, Glauser G, Mauch-Mani B (2015) Root inoculation with Pseudomonas putida KT2440 induces transcriptional and metabolic changes and systemic resistance in maize plants. Front Plant Sci 5:1
Poole K (2002) Outer membranes and efflux: the path to multidrug resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 3(2):77–98
Regenhardt D, Heuer H, Heim S, Fernandez DU, Strömpl C, Moore ERB, Timmis KN (2002) Pedigree and taxonomic credentials of Pseudomonas putida strain KT2440. Environ Microbiol 4(12):912–915
Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C (2009) Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:305–339
Roberson EB, Firestone MK (1992) Relationship between desiccation and exopolysaccharide production in a soil Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(4):1284–1291
Rodriguez-Herva JJ, Reniero D, Galli E, Ramos JL (1999) Cell envelope mutants of Pseudomonas putida: physiological characterization and analysis of their ability to survive in soil. Environ Microbiol 1(6):479–488
Romic D, Ondrasek G, Romic M, Josip B, Vranjes M, Petosic D (2008) Salinity and irrigation method affect crop yield and soil quality in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.) growing. Irrig Drain 57:463–469
Saghafi D, Delangiz N, Lajayer BA, Ghorbanpour M (2019) An overview on improvement of crop productivity in saline soils by halotolerant and halophilic PGPRs. J Biotechnol 9:261
Salazar J, Alarcón M, Huerta J, Navarro B, Aguayo D (2017) Phosphoethanolamine addition to the heptose I of the lipopolysaccharide modifies the inner core structure and has an impact on the binding of polymyxin B to the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys 620:28–34
Sandhya V, Ali SZK (2015) The production of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas putida GAP-P45 under various abiotic stress conditions and its role in soil aggregation. Microbiology 84(4):512–519
Sandhya V, Ali SKZ, Grover M, Reddy G, Venkateswarlu B (2009) Alleviation of drought stress effects in sunflower seedlings by the exopolysaccharides producing Pseudomonas putida strain GAP-p45. Biol Fertil Soils 46:17–26
Schippers B, Bakker AW, Bakker PAHM (1987) Interactions of deleterious and beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms and the effect of cropping practices. Annu Rev Phytopathol 25:339–358
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Soussi M, Santamaría M, Ocaña A, Lluch C (2001) Effects of salinity on protein and lipopolysaccharide pattern in a salt-tolerant strain of Mesorhizobium ciceri. J Appl Microbiol 90:476–481
Sun L, Vella P, Schnell R, Polyakova A, Bourenkov G, Li F, Cimdins A, Schneider TR, Lindqvist Y, Galperin MY, Schneider G, Römling U (2018) Structural and functional characterization of the BcsG subunit of the cellulose synthase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol 430:3170–3189
Tewari S, Arora NK (2014) Talc based exopolysaccharides formulation enhancing growth and production of Hellianthus annuus under saline conditions. Cell Mol Biol 60:73–81
Trombley MP, Post DMB, Rinker SD, Reinders LM, Fortney KR, Zwickl BW, Janowicz DM, Baye FM, Katz BP, Spinola SM, Bauer ME (2015) Phosphoethanolamine transferase EptA in Haemophilus ducreyi modifies lipid a and contributes to human defensin resistance in vitro. PLoS One 10(4):e0124373
Upadhyay SK, Singh JS, Singh DP (2011) Exopolysaccharide-producing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under salinity condition. Pedosphere 21:214–222
Vaishnav A, Ajit V, Narendra T, Devendra K (2017) PGPR-mediated amelioration of crops under salt stress. Springer, Singapore
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–37
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W296–W303
Wei W, Jiang J, Li X, Wang L, Yang SS (2004) Isolation of salt-sensitive mutants from Sinorhizobium meliloti and characterization of genes involved in salt tolerance. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:278–283
Whatmore AM, Chudek JA, Reed RH (1990) The effects of osmotic upshock on the intracellular solute pools of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol 136:2527–2535
Wu X, Monchy S, Taghavi S, Zhu W, Ramos J, van der Lelie D (2011) Comparative genomics and functional analysis of niche-specific adaptation in Pseudomonas putida. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:299–323
Yan K, Shao H, Shao C, Chen P, Zhao S, Brestic M, Chen X (2013) Physiological adaptive mechanisms of plants grown in saline soil and implications for sustainable saline agriculture in coastal zone. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2867–2878
Yang J, Kloepper JW, Ryu CM (2009) Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci 14:1–4
Yao L, Wu Z, Zheng Y, Kaleem I, Li C (2010) Growth promotion and protection against salt stress by Pseudomonas putida Rs-198 on cotton. Eur J Soil Biol 46:49–54
Yousef-Coronado F, Travieso ML, Espinosa-Urgel M (2008) Different, overlapping mechanisms for colonization of abiotic and plant surfaces by Pseudomonas putida. FEMS Microbiol Lett 288:118–124
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. Priscilla R. de Gregorio for help with the statistical analysis and useful suggestions to the manuscript.
Disclaimer
The funders had no role in the experimental design, data collection, interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT; grant PICT 2222) and Consejo de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET; grant PIP 908/15) and partly supported by EMHE-CSIC (grant MHE200019) and Plan Estatal de I + D + I (MINECO and EFRD funds, grant BFU2016–80122-P).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 450 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa-Gutierrez, S.B., Lami, M.J., Santo, M.C.CD. et al. Plant growth promotion by Pseudomonas putida KT2440 under saline stress: role of eptA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 4577–4592 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10516-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10516-z