Abstract
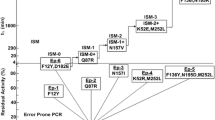
Enantioselective hydrolysis of epoxides by epoxide hydrolase (EH) is one of the most attractive approaches for the synthesis of chiral epoxides. So far, attempts to develop an efficient epoxide hydrolase -mediated biotransformation have been limited by either the low activity or insufficient enantioselectivity of epoxide hydrolase. In this study, iterative saturation mutagenesis (ISM) of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 (ArEH) was performed for efficient production of (R)-epichlorohydrin. Six amino acid residues, I108, A110, D131, I133, T247, and G245, were selected for site saturation mutagenesis, and a sequential combination of positive mutants using ISM was constructed. Targeted mutagenesis generated five mutants (T247K, I108L, D131S, T247K/I108L, and T247K/I108L/D131S) with improved activity and enantioselectivity. Kinetics analysis showed that the best mutant, T247K/I108L/D131S, exhibited a 4.5-fold higher catalytic efficiency (k cat/K m) value and a 2.1-fold higher enantioselectivity (E value) towards epichlorohydrin than the wild-type (WT) enzyme. Molecular docking computations support the source of notably improved enantioselectivity. In addition, the triple mutant also displayed a significantly enhanced thermostability, with > 8-fold longer half-life at 50 °C than WT. A gram-scale kinetic resolution of (R,S)-epichlorohydrin was performed using T247K/I108L/D131S mutant as biocatalyst, affording a (R)-epichlorohydrin yield of 40.2% (> 99.9% enantiomeric excess) and an average productivity of 1410 g L−1 d−1. The engineered T247K/I108L/D131S variant is a promising biocatalyst for the enzymatic synthesis of (R)-epichlorohydrin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ba L, Li P, Zhang H, Duan Y, Lin Z (2013) Semi-rational engineering of cytochrome P450sca-2 in a hybrid system for enhanced catalytic activity: insights into the important role of electron transfer. Biotechnol Bioeng 110(11):2815–2825. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24960
Choi WJ (2009) Biotechnological production of enantiopure epoxides by enzymatic kinetic resolution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84(2):239–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2110-9
Choi YH, Kim JH, Park BS, Kim BG (2016) Solubilization and iterative saturation mutagenesis of alpha 1,3-fucosyltransferase from Helicobacter pylori to enhance its catalytic efficiency. Biotechnol Bioeng 113(8):1666–1675. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25944
De Vries EJ, Janssen DB (2003) Biocatalytic conversion of epoxides. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14(4):414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(03)00102-2
Goldberg K, Schroer K, Lutz S, Liese A (2007) Biocatalytic ketone reduction—a powerful tool for the production of chiral alcohols—part II: whole-cell reductions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(2):249–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1005-x
Gong Y, GC X, Chen Q, Yin JG, Li CX, JH X (2016) Iterative multitarget evolution dramatically enhances the enantioselectivity and catalytic efficiency of Bacillus subtilis esterase towards bulky benzoate esters of DL-menthol. Catal Sci Technol 6(7):2370–2376. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CY01723H
Han R, Liu L, H-d S, Chen RR, Li J, Du G, Chen J (2013) Iterative saturation mutagenesis of -6 subsite residues in cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Paenibacillus macerans to improve maltodextrin specificity for 2-O-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(24):7562–7568. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02918-13
Jacobsen EN (2000) Asymmetric catalysis of epoxide ring opening reactions. Accounts Chem Res 33(6):421–431. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar960061v
Jin HX, ZC H, Zheng YG (2012) Enantioselective hydrolysis of epichlorohydrin using whole Aspergillus niger ZJB-09173 cells in organic solvents. J Biosci 37(4):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-012-9243-1
Jin HX, Liu ZQ, ZC H, Zheng YG (2013) Biosynthesis of (R)-epichlorohydrin at high substrate concentration by kinetic resolution of racemic epichlorohydrin with a recombinant epoxide hydrolase. Eng Life Sci 13(4):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201200179
Jin HX, Ouyang XK, ZC H (2017) Enhancement of epoxide hydrolase production by 60Co gamma and UV irradiation mutagenesis of Aspergillus niger ZJB-09103. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 64(3):392–399. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1502
Jung SH, Linh PT, Lim HK, Kim HJ, Kim KH, Kang JS (2000) Enantioselective preparation of metoprolol and its major metabolites. Arch Pharm Res 23(3):226–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976449
Katsuki T (2002) Chiral metallosalen complexes: structures and catalyst tuning for asymmetric epoxidation and cyclopropanation. Advan Synth Catal 344(2):131–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/1615-4169(200202)344:2<131::AID-ADSC131>3.0.CO;2-T
Kim HS, Lee JH, Park S, Lee EY (2004) Biocatalytic preparation of chiral epichlorohydrins using recombinant Pichia pastoris expressing epoxide hydrolase of Rhodotorula glutinis. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 9(1):62–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02949324
Laskowski RA, Macarthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26:28–291
Li Y, Cirino PC (2014) Recent advances in engineering proteins for biocatalysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 111(7):1273–1287. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25240
Liu ZQ, Zhang LP, Cheng F, Ruan LT, ZC H, Zheng YG, Shen YC (2011) Characterization of a newly synthesized epoxide hydrolase and its application in racemic resolution of (R,S)-epichlorohydrin. Catal Commun 16(1):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.09.010
Misawa E, Chion CKCCK, Archer IV, Woodland MP, Zhou NY, Carter SF, Widdowson DA, Leak DJ (1998) Characterisation of a catabolic epoxide hydrolase from a Corynebacterium sp. Eur J Biochem 253(1):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2530173.x
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256
Nardini M, Ridder IS, Rozeboom HJ, Kalk KH, Rink R, Janssen DB, Dijkstra BW (1999) The X-ray structure of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1—an enzyme to detoxify harmful epoxides. J Biol Chem 274(21):14579–14586. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.21.14579
Nardini M, Rick RB, Janssen DB, Dijkstra BW (2001) Structure and mechanism of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1. J Mol Catal B Enzym 11(4–6):1035–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1177(00)00049-7
Nestl BM, Hammer SC, Nebel BA, Hauer B (2014) New generation of biocatalysts for organic synthesis. Angew Chem Int Edit 53(12):3070–3095. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201302195
Niu CT, Zhu LJ, Xu X, Li Q (2017) Rational design of thermostability in bacterial 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanases through spatial compartmentalization of mutational hotspots. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(3):1085–1097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7826-8
Reetz MT (2011) Laboratory evolution of stereoselective enzymes: a prolific source of catalysts for asymmetric reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(1):138–174. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000826
Reetz MT, D Carballeira J, Vogel A (2006) Iterative saturation mutagenesis on the basis of B factors as a strategy for increasing protein thermostability. Angew Chem Int Ed 45(46):7745–7751. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602795
Reetz MT, Bocola M, Wang LW et al (2009) Directed evolution of an enantioselective epoxide hydrolase: uncovering the source of enantioselectivity at each evolutionary stage. J Am Chem Soc 131(21):7334–7343
Reetz MT, Prasad S, Carballeira JD, Gumulya Y, Bocola M (2010a) Iterative saturation mutagenesis accelerates laboratory evolution of enzyme stereoselectivity: rigorous comparison with traditional methods. J Am Chem Soc 132(26):9144–9152. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1030479
Reetz MT, Soni P, Fernandez L, Gumulya Y, Carballeira JD (2010b) Increasing the stability of an enzyme toward hostile organic solvents by directed evolution based on iterative saturation mutagenesis using the B-FIT method. Chem Commun 46(45):8657–8658. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc02657c
Rink R, Fennema M, Smids M, Dehmel U, Janssen DB (1997) Primary structure and catalytic mechanism of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1. J Biol Chem 272(23):14650–14657. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.23.14650
Rink R, Spelberg JHL, Pieters RJ, Kingma J, Nardini M, Kellogg RM, Dijkstra BW, Janssen DB (1999) Mutation of tyrosine residues involved in the alkylation half reaction of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 results in improved enantioselectivity. J Am Chem Soc 121(32):7417–7418. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja990501o
Rink R, Kingma J, Spelberg JHL, Janssen DB (2000) Tyrosine residues serve as proton donor in the catalytic mechanism of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter. Biochemistry 39(18):5600–5613. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9922392
Rui LY, Cao L, Chen W, Reardon KF, Wood TK (2004) Active site engineering of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 to enhance aerobic mineralization of cis-1,2-dichloroethylene in cells expressing an evolved toluene ortho-monooxygenase. J Biol Chem 279(45):46810–46817. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M407466200
Rui LY, Cao L, Chen W, Reardon KF, Wood TK (2005) Protein engineering of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 for enhanced activity and enantioselective production of (R)-1-phenylethane-1,2-diol. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(7):3995–4003. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.7.3995-4003.2005
Saini P, Sareen D (2017) An overview on the enhancement of enantioselectivity and stability of microbial epoxide hydrolases. Mol Biotechnol 59(2–3):98–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-9996-8
Shivange AV, Roccatano D, Schwaneberg U (2016) Iterative key-residues interrogation of a phytase with thermostability increasing substitutions identified in directed evolution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(1):227–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6959-5
Spelberg JHL, Rink R, Archelas A, Furstoss R, Janssen DB (2002) Biocatalytic potential of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 and a mutant with enhanced enantioselectivity. Adv Syn Catal 344(9):980–985. https://doi.org/10.1002/1615-4169(200210)344:9<980::AID-ADSC980>3.0.CO;2-A
Stepankova V, Bidmanova S, Koudelakova T, Prokop Z, Chaloupkova R, Damborsky J (2013) Strategies for stabilization of enzymes in organic solvents. ACS Catal 3(12):2823–2836. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400684x
van Loo B, Spelberg JHL, Kingma J, Sonke T, Wubbolts MG, Janssen DB (2004) Directed evolution of epoxide hydrolase from A-radiobacter toward higher enantioselectivity by error-prone PCR and DNA shuffling. Chem Biol 11(7):981–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.04.019
Widersten M, Gurell A, Lindberg D (2010) Structure-function relationships of epoxide hydrolases and their potential use in biocatalysis. BBA-Gen Subjects 1800(3):316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.11.014
Woo JH, Kang JH, Kang S, Hwang YO, Kim SJ (2009) Cloning and characterization of an epoxide hydrolase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82(5):873–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1791-9
Woo JH, Hwang YO, Kang JH, Lee HS, Kim SJ, Kang SG (2010) Enantioselective hydrolysis of racemic epichlorohydrin using an epoxide hydrolase from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans. J Biosci Bioeng 110(3):295–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.02.014
Xue F, Liu ZQ, Zou SP, Wan NW, Zhu WY, Zhu Q, Zheng YG (2014) A novel enantioselective epoxide hydrolase from Agromyces mediolanus ZJB120203: cloning, characterization and application. Process Biochem 49(3):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.003
Yang Y, Liu J, Li Z (2014) Engineering of P450pyr hydroxylase for the highly regio- and enantioselective subterminal hydroxylation of alkanes. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(12):3120–3124. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201311091
Yildirim D, Tukel SS, Alptekin O, Alagoz D (2013) Immobilized Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolases: cost-effective biocatalysts for the prepation of enantiopure styrene oxide, propylene oxide and epichlorohydrin. J Mol Catal B Enzym 88:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2012.11.015
Zeine C (2013) Metal impurities in pharmaceutical products. Pharm Ind 75(4):595–601
Zhu QQ, He WH, Kong XD, Fan LQ, Zhao J, Li SX, JH X (2014) Heterologous overexpression of Vigna radiata epoxide hydrolase in Escherichia coli and its catalytic performance in enantioconvergent hydrolysis of p-nitrostyrene oxide into (R)-p-nitrophenyl glycol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(1):207–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4845-6
Zou SP, Yan HW, ZC H, Zheng YG (2013) Enzymatic resolution of epichlorohydrin catalyzed by whole cells in an organic solvent/buffer biphasic system. Chinese J Catal 34(7):1339–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60576-2
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 21406205) and Natural Sciences Fund of Zhejiang Province (grant number Y17C050005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 212 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, SP., Zheng, YG., Wu, Q. et al. Enhanced catalytic efficiency and enantioselectivity of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 by iterative saturation mutagenesis for (R)-epichlorohydrin synthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 733–742 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8634-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8634-5