Abstract
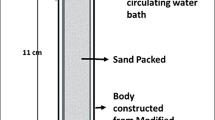
Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) depends on the in situ microbial activity to release trapped oil in reservoirs. In practice, undesired consumption is a universal phenomenon but cannot be observed effectively in small-scale physical simulations due to the scale effect. The present paper investigates the dynamics of oil recovery, biomass and nutrient consumption in a series of flooding experiments in a dedicated large-scale sand-pack column. First, control experiments of nutrient transportation with and without microbial consumption were conducted, which characterized the nutrient loss during transportation. Then, a standard microbial flooding experiment was performed recovering additional oil (4.9 % Original Oil in Place, OOIP), during which microbial activity mostly occurred upstream, where oil saturation declined earlier and steeper than downstream in the column. Subsequently, more oil remained downstream due to nutrient shortage. Finally, further research was conducted to enhance the ultimate recovery by optimizing the injection strategy. An extra 3.5 % OOIP was recovered when the nutrients were injected in the middle of the column, and another additional 11.9 % OOIP were recovered by altering the timing of nutrient injection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afrapoli MS, Alipour S, Torsaeter O (2012) Analysis of microscopic displacement mechanisms of a mior process in porous media with different wettability. Transp Porous Media 93(3):705–719. doi:10.1007/s11242-012-9978-z
AI-Sulaimani H, AI-Wahaibi Y, AI-Bahry S, Elshafie A, AI-Bemani A, Joshi S (2012) Residual-oil recovery through injection of biosurfactan, chemical surfactant, and mixtures of both under reservoir temperatures: induced-wettability and interfacial-tension effects. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 15(2):210–216. doi:10.2118/158022-PA
AI-Wahaibia Y, Joshib S, Al-Bahryb S, Elshafieb A, Al-Bemania A, Shibulal B (2014) Biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis B30 and its application in enhancing oil recovery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 114(1):324–333. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb. 2013.09.022
Armstrong RT, Wildenschild D (2012) Microbial enhanced oil recovery in fractional-wet systems: a pore-scale investigation. Transp Porous Media 92(3):819–835. doi:10.1007/s11242-011-9934-3
Banat IM (1995) Biosurfactants production and possible uses in microbial enhanced oil recovery and oil pollution remediation: a review. Bioresour Technol 51:1–12. doi:10.1016/0960-8524(94)00101-6
Bryant RS, Burchfield TE (1989) Review of microbial technology for improving oil recovery. SPE Reserv Eval Eng 4:151–154. doi:10.2118/16646-PA
Cao G, Liu T, Ba Y, Xu D, Wang T, Zhao F, Shu Q (2013) Microbial flooding after polymer flooding pilot test in Ng3 of Zhong1 area, Gudao oil⁃field. Petrol Geol Recover Effic 20(6):94–96. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603. 2013.06.023
Cao G, Ba Y, Liu T, Bi A, Yao H (2014) Field pilot test of indigenous microbial flooding in block Zhan-3. Spec Oil Gas Reserv 21(1):145–147. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2014.01.037
Chang MM, Bryant RS, Chung TH, Gao HW (1991) Modeling and laboratory Investigations of microbial transport phenomena in porous media. SPE 22845. doi:10.2118/22845-MS
Dastgheib SMM, Amoozegar MA, Elahi E, Asad S, Banat IM (2008) Bioemulsifier production by a halothermophilic Bacillus strain with potential applications in microbial enhanced oil recovery. Biotechnol Lett 30:263–270. doi:10.1007/ s10529-007-9530-3
Gang HZ, Liu MT, Mu BZ (2008) Modeling of microorganisms transport in a cylindrical pore. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35(6):495–500. doi:10.1007/s10295 -008-0307-z
Gao CH, Zekri A (2011) Applications of microbial-enhanced oil recovery technology in the past decade. Energy Sources A Recover Util Environ Eff 33:972–989. doi:10.1080/15567030903330793
Gao P, Li G, Dai X, Dai L, Wang H, Zhao L, Chen Y, Ma T (2013) Nutrients and oxygen alter reservoir biochemical characters and enhance oil recovery during biostimulation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(11):2045–2054. doi:10.1007/ s11274-013-1367-4
Ghojavand H, Vahabzadeh F, Shahraki AK (2012) Enhanced oil recovery from low permeability dolomite cores using biosurfactant produced by a Bacillus mojavensis (PTCC 1696) isolated from Masjed-I Soleyman field. J Pet Sci Eng 81:24–30. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2011.12.002
Gray ND, Sherry A, Larter SR, Erdmann M, Leyris J, Liengen T, Beeder J, Head IM (2009) Biogenic methane production in formation waters from a large gas field in the North Sea. Extremophiles 13(3):511–519. doi:10.1007/s00792-009-0237-3
Halim A, Shapiro A, Lantz AE, Nielsen SM (2014) Experimental study of bacterial penetration into chalk rock: mechanisms and effect on permeability. Transp Porous Media 101(1):1–15. doi:10.1007/s11242-013-0227-x
Karimi M, Mahmoodi M, Niazi A, AI-Wahaibi Y, Ayatollahi S (2012) Investigating wettability alteration during MEOR process, a micro/macro scale analysis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 95:129–136. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.02.035
Kaster KM, Hiorth A, Kjeilen-Eilertsen G, Boccadoro K, Lohne A, Berland H, Stavland A, Brakstad OG (2012) Mechanisms involved in microbially enhanced oil recovery. Transp Porous Media 91(1):59–79. doi:10.1007/s11242-011-9833-7
Nazina TN, Pavlova NK, Ni F, Shestakova NM, Ivoilov VS, Feng Q, Zhao D, Prusakova TS, Belyaev SS, Ivanov MV (2008) Regulation of geochemical activity of microorganisms in a petroleum reservoir by injection of H2O2 or water-air mixture. Microbiology 77(3):324–333. doi:10.1134/S0026261708030120
Nielsen SM, Shapiro AA, Michelsen ML, Stenby EH (2010) 1D simulations for microbial enhanced oil recovery with metabolite partitioning. Transp Porous Media 85(3):785–802. doi:10.1007/s11242-010-9592-x
Nielsen SM, Nesterov I, Shapiro AA (2014) Simulations of microbial-enhanced oil recovery: adsorption and filtration. Transp Porous Media 102(2):227–259. doi:10.1007/s11242-014-0273-z
Qin H, Yang H, Qiao Z, Gao S, Liu Z (2013) Identification and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis strain HB-1 isolated from Yandou, a fermented soybean food in China. Food Control 31(1):22–27. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.10.004
Rabiei A, Sharifinik M, Niazi A, Hashemi A, Ayatollahi S (2013) Core flooding tests to investigate the effects of IFT reduction and wettability alteration on oil recovery during MEOR process in an Iranian oil reservoir. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(13):5979–5991. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-4863-4
Ren HY, Zhang XJ, Song ZY, Rupert W, Gao GJ, Guo SX, Zhao LP (2011) Comparison of microbial community compositions of injection and production well samples in a long-term water-flooded petroleum reservoir. PLoS ONE 6(8), e23258. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023258
She YH, Zhang F, Xia JJ, Kong SQ, Wang ZL, Shu FC, Hu JM (2011) Investigation of biosurfactant-producing indigenous microorganisms that enhance residue oil recovery in an oil reservoir after polymer flooding. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163:223–234. doi:10.1007/s12010-010-9032-y
Simpson DR, Natraj NR, McInerney MJ, Duncan KE (2011) Biosurfactant-producing Bacillus are present in produced brines from Oklahoma oil reservoirs with a wide range of salinities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1083–1093. doi:10.1007/ s00253-011-3326-z
Song ZY, Guo LY, Yuan SW, Hao B, Wu XL (2010) Microbial plugging and community distribution of indigenous thermophilic microbes in high temperature oil reservoirs. Acta Pet Sin 31(6):975–979. doi:10.7623/syxb201006017
Thrasher D, Puckett DA, Davies A, Beattie G, Gordon PG, Boccardo G, Vance I, Jackson S (2010) MEOR from lab to field. SPE: 129701. doi:10.2118/129701-MS
Weidong W, Junzhang L, Xueli G, Jing W, Ximing L, Yan J, Fengmin Z (2014) MEOR field test at block Luo801 of Shengli oil field in China. Pet Sci Technol 32(6):673–679. doi:10.1080/10916466.2011.601507
Xia WJ, Luo ZB, Dong HP, Yu L (2013) Studies of biosurfactant for microbial enhanced oil recovery by using bacteria isolated from the formation water of a petroleum reservoir. Pet Sci Technol 31(21):2311–2317. doi:10.1080/ 10916466.2011.569812
Youssef N, Simpson DR, McInerney MJ, Duncan KE (2013) In-situ lipopeptide biosurfactant production by Bacillus strains correlates with improved oil recovery in two oil wells approaching their economic limit of production. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 81:127–132. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.05.010
Yu DF, Dong HP, Yu L, Cui QF, Xia WJ, Yu DX (2012) Laboratory study of indigenous microorganism activation system in long core. Oilfield Chem 29(2):236–239
Zahner RL, Sheehy A, Govreau BR (2010) MEOR success in southern California. SPE: 129742. doi:10.2118/129742-MS
Zhao LX, Ma T, Gao ML, Gao PK, Cao MN, Zhu XD, Li GQ (2012) Characterization of microbial diversity and community in water flooding oil reservoirs in China. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:3039–3052. doi:10.1007/s11274-012-1114-2
Acknowledgments
The study has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11372033) and Special Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (FRF-MP-B12006B).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Zhu, W., Sun, G. et al. Dynamic investigation of nutrient consumption and injection strategy in microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR) by means of large-scale experiments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 6551–6561 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6586-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6586-1