Abstract
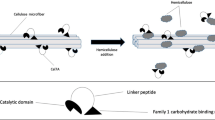
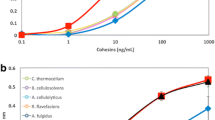
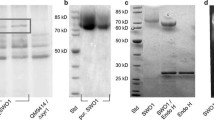
BsEXLX1 from Bacillus subtilis is the first discovered bacterial expansin as a structural homolog of a plant expansin, and it exhibited synergism with cellulase on the cellulose hydrolysis in a previous study. In this study, binding characteristics of BsEXLX1 were investigated using pretreated and untreated Miscanthus x giganteus in comparison with those of CtCBD3, a cellulose-binding domain from Clostridium thermocellum. The amounts of BsEXLX1 bound to cellulose-rich substrates were significantly lower than those of CtCBD3. However, the amounts of BsEXLX1 bound to lignin-rich substrates were much higher than those of CtCBD3. A binding competition assay between BsEXLX1 and CtCBD3 revealed that binding of BsEXLX1 to alkali lignin was not affected by the presence of CtCBD3. This preferential binding of BsEXLX1 to lignin could be related to root colonization in plants by bacteria, and the bacterial expansin could be used as a lignin blocker in the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bak JS, Ko JK, Han YH, Lee BC, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2009) Improved enzymatic hydrolysis yield of rice straw using electron beam irradiation pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 100:1285–1290
Berlin A, Gilkes N, Kurabi A, Bura R, Tu M, Kilburn D, Saddler J (2005) Weak lignin-binding enzymes—a novel approach to improve activity of cellulases for hydrolysis of lignocellulosics. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 121:163–170
Boraston AB, Bolam DN, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ (2004) Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem J 382:769–781
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cosgrove DJ (2000a) Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 407:321–326
Cosgrove DJ (2000b) New genes and new biological roles for expansins. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:73–78
Cosgrove DJ (2001) Enhancement of accessibility of cellulose by expansins. US Patent 6326470
Cosgrove DJ, Takeda T (2007) Use of GR2 proteins to modify cellulosic materials and to enhance enzymatic and chemical modification of cellulose. US Patent 20070166805
Georgelis N, Tabuchi A, Nikolaidis N, Cosgrove DJ (2011) Structure–function analysis of the bacterial expansin EXLX1. J Biol Chem 286:16814–16823
Graham JE, Clark ME, Nadler DC, Huffer S, Chokhawala HA, Rowland SE, Blanch HW, Clark DS, Robb FT (2011) Identification and characterization of a multidomain hyperthermophilic cellulase from an archaeal enrichment. Nat Commun 2:375
Harris PV, Welner D, McFarland KC, Re E, Navarro Poulsen JC, Brown K, Salbo R, Ding H, Vlasenko E, Merino S, Xu F, Cherry J, Larsen S, Lo Leggio L (2010) Stimulation of lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis by proteins of glycoside hydrolase family 61: structure and function of a large, enigmatic family. Biochemistry 49:3305–3316
Helle SS, Duff SJB, Cooper DG (1993) Effect of surfactants on cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:611–617
Henshaw JL, Bolam DN, Pires VMR, Czjzek M, Henrissat B, Ferreira LMA, Fontes CMGA, Gilbert HJ (2004) The family 6 carbohydrate binding module CmCBM6-2 contains two ligand-binding sites with distinct specificities. J Biol Chem 279:21552–21559
Kende H, Bradford KJ, Brummell DA, Cho H-T, Cosgrove DJ, Fleming AJ, Gehring C, Lee Y, McQueen-Mason S, Rose JKC, Voesenek LACJ (2004) Nomenclature for members of the expansin superfamily of genes and proteins. Plant Mol Biol 55:311–314
Kerff F, Amoros A, Herman R, Sauvage E, Petrella S, Filée P, Charlier P, Joris B, Tabuchi A, Nikolaidis N, Cosgrove DJ (2008) Crystal structure and activity of Bacillus subtilis YoaJ (EXLX1), a bacterial expansin that promotes root colonization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16876–16881
Kim ES, Lee HJ, Bang W-G, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2008) A novel cellulase activity enhancing protein from bacillus subtilis, a functional homolog of a plant expansin. J Biotechnol 136S:S426
Kim ES, Lee HJ, Bang W-G, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2009) Functional characterization of a bacterial expansin from Bacillus subtilis for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1342–1353
Kim IJ, Ko H-J, Kim T-W, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2012) Characteristics of the binding of a bacterial expansin (BsEXLX1) to microcrystalline cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng. doi:10.1002/bit.24719
Kim KH, Tucker MP, Nguyen QA (2002) Effects of pressing lignocellulosic biomass on sugar yield in two-stage dilute-acid hydrolysis process. Biotechnol Prog 18:489–494
Kim T-W, Chokhawala HA, Hess M, Dana CM, Baer Z, Sczyrba A, Rubin EM, Blanch HW, Clark DS (2011) High-throughput in vitro glycoside hydrolase (HIGH) screening for enzyme discovery. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:11215–11218
Ko JK, Bak JS, Jung MW, Lee HJ, Choi I-G, Kim TH, Kim KH (2009) Ethanol production from rice straw using optimized aqueous-ammonia soaking pretreatment and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation processes. Bioresour Technol 100:4374–4380
Lynd LR, Laser MS, Brandsby D, Dale BE, Davison B, Hamilton R, Himmel M, Keller M, McMillan JD, Sheehan J, Wyman CE (2008) How biotech can transform biofuels. Nat Biotechnol 26:169–172
McQueen-Mason S, Cosgrove DJ (1994) Disruption of hydrogen bonding between plant cell wall polymers by proteins that induce wall extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6574–6578
McQueen-Mason SJ, Cosgrove DJ (1995) Expansin mode of action on cell walls—analysis of wall hydrolysis, stress relaxation, and binding. Plant Physiol 107:87–100
Merino ST, Cherry J (2007) Progress and challenges in enzyme development for biomass utilization. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:95–120
Ooshima H, Sakata M, Harano Y (1986) Enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose by surfactant. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1727–1734
Qin L, Kudla U, Roze EHA, Goverse A, Popeijus H, Nieuwland J, Overmars H, Jones JT, Schots A, Smant G, Bakker J, Helder J (2004) Plant degradation: a nematode expansin acting on plants. Nature 427:30
Quiroz-Castañeda RE, Martínez-Anaya C, Cuervo-Soto LI, Segovia L, Folch-Mallol JL (2011) Loosenin, a novel protein with cellulose-disrupting activity from Bjerkandera adusta. Microb Cell Fact 10:8
Ruiz R, Ehrman T (1996) Laboratory Analytical Procedure-002: determination of carbohydrates in biomass by high performance liquid chromatography. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, USA
Saloheimo M, Paloheimo M, Hakola S, Pere J, Swanson B, Nyyssönen E, Bhatia A, Ward M, Penttilä M (2002) Swollenin, a Trichoderma reesei protein with sequence similarity to the plant expansins, exhibits disruption activity on cellulosic materials. Eur J Biochem 269:4202–4211
Suwannarangsee S, Bunterngsook B, Arnthong J, Paemanee A, Thamchaipenet A, Eurwilaichitr L, Laosiripojana N, Champreda V (2012) Optimisation of synergistic biomass-degrading enzyme systems for efficient rice straw hydrolysis using an experimental mixture design. Bioresour Technol 119:252–261
Tengborg C, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2001) Reduced inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-pretreated softwood. Enzyme Microb Technol 28:835–844
Tormo J, Lamed R, Chirino AJ, Morag E, Bayer EA, Shoham Y, Steitz TA (1996) Crystal structure of a bacterial family-III cellulose-binding domain: a general mechanism for attachment to cellulose. EMBO J 15:5739–5751
Yang B, Wyman CE (2006) BSA treatment to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose in lignin containing substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:611–617
Yennawar NH, Li L-C, Dudzinski DM, Tabuchi A, Cosgrove DJ (2006) Crystal structure and activities of EXPB1 (Zea m 1), a β-expansin and group-1 pollen allergen from maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14664–14671
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Advanced Biomass R&D Center of Korea (2011-0031353) and the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center (No. 2011-0031953) funded by the Korean Government (MEST). K.H.K acknowledges financial support from the Energy Biosciences Institute (EBI), Berkeley, CA, USA and I.J.K. is grateful to the instrumental training and technical support provided by Drs. Mara Bryan and Stefan Bauer at the EBI. Facility support at Korea University Food Safety Hall for the Institute of Biomedical Science and Food Safety is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 52.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, I.J., Ko, HJ., Kim, TW. et al. Binding characteristics of a bacterial expansin (BsEXLX1) for various types of pretreated lignocellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 5381–5388 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4412-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4412-6