Abstract
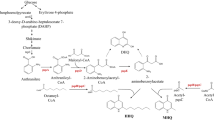
The quorum sensing signalling molecules 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone, termed the “Pseudomonas quinolone signal” (PQS), and 2-heptyl-4(1H)-quinolone (HHQ) play an important role in the control of virulence gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. To construct a bioreporter for the specific and sensitive detection of these compounds, a plasmid with the pqsR gene encoding the PQS- and HHQ-responsive transcriptional regulator PqsR, and with the PqsR-controlled pqsA promoter fused to the lacZ gene, was established in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. The bioreporter responds to HHQ and PQS at concentrations in the range of 0.1–10 and 0.01–5 μM, respectively, with EC50 values of 1.50 ± 0.25 μM for HHQ and 0.15 ± 0.02 μM for PQS. 2,4-Dihydroxyquinoline, a metabolite produced abundantly by P. aeruginosa, did not elicit an increase in reporter enzyme activity. To test whether the bioreporter can be used for the detection of enzymes active on AQ signalling molecules, the hodC gene coding for 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone 2,4-dioxygenase was expressed in the reporter strain. This dioxygenase catalyses the cleavage of PQS, albeit with very low activity. The response of the bioreporter to PQS was significantly quenched by co-expression of the hodC gene, and HPLC analysis of culture extracts verified that the PQS levels decreased during cultivation. The bioreporter can be applied to screen for AQ-converting enzymes, which will be useful tools to interfere with quorum sensing and thus virulence in P. aeruginosa.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bredenbruch F, Geffers R, Nimtz M, Buer J, Häussler S (2006) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal (PQS) has iron-chelating activity. Environ Microbiol 8:1318–1329
Cao H, Krishnan G, Goumnerov B, Tsongalis J, Tompkins R, Rahme LG (2001) A quorum sensing-associated virulence gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a LysR-like transcription regulator with a unique self-regulatory mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14613–14618
Coleman JP, Hudson LL, McKnight SL, Farrow JM III, Calfee MW, Lindsey CA, Pesci EC (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PqsA is an anthranilate-coenzyme A ligase. J Bacteriol 190:1247–1255
Collier DN, Anderson L, McKnight SL, Noah TL, Knowles M, Boucher R, Schwab U, Gilligan P, Pesci EC (2002) A bacterial cell to cell signal in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. FEMS Microbiol Lett 215:41–46
Cugini C, Calfee MW, Farrow JM III, Morales DK, Pesci EC, Hogan DA (2007) Farnesol, a common sesquiterpene, inhibits PQS production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 65:896–906
Davis RW, Botstein D, Roth JR (1980) Advanced bacterial genetics: a manual for genetic engineering. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Déziel E, Lépine F, Milot S, He J, Mindrinos MN, Tompkins RG, Rahme LG (2004) Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1339–1344
Déziel E, Gopalan S, Tampakaki AP, Lépine F, Padfield KE, Saucier M, Xiao G, Rahme LG (2005) The contribution of MvfR to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis and quorum sensing circuitry regulation: multiple quorum sensing-regulated genes are modulated without affecting lasRI, rhlRI or the production of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones. Mol Microbiol 55:998–1014
Diggle SP, Winzer K, Chhabra SR, Worrall KE, Cámara M, Williams P (2003) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl-dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol Microbiol 50:29–43
Diggle SP, Lumjiaktase P, Dipilato F, Winzer K, Kunakorn M, Barrett DA, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Williams P (2006) Functional genetic analysis reveals a 2-alkyl-4-quinolone signaling system in the human pathogen Burkholderia pseudomallei and related bacteria. Chem Biol 13:701–710
Diggle SP, Matthijs S, Wright VJ, Fletcher MP, Chhabra SR, Lamont IL, Kong X, Hider RC, Cornelis P, Cámara M, Williams P (2007) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-quinolone signal molecules HHQ and PQS play multifunctional roles in quorum sensing and iron entrapment. Chem Biol 14:87–96
Dong YH, Wang LH, Zhang LH (2007) Quorum-quenching microbial infections: mechanisms and implications. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 362:1201–1211
Farrow JM III, Sund ZM, Ellison ML, Wade DS, Coleman JP, Pesci EC (2008) PqsE functions independently of PqsR-Pseudomonas quinolone signal and enhances the rhl quorum-sensing system. J Bacteriol 190:7043–7051
Fernández M, Duque E, Pizarro-Tobias P, van Dillewijn P, Wittich RM, Ramos JL (2009) Microbial response to xenobiotic compounds. Identification of genes that allow Pseudomonas putida KT2440 to cope with 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Microb Biotechnol 2:287–294
Fernández-Piñar R, Cámara M, Dubern JF, Ramos JL, Espinosa-Urgel M (2011a) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone quorum sensing signal alters the multicellular behaviour of Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Res Microbiol 162:773–781
Fernández-Piñar R, Cámara M, Soriano MI, Dubern JF, Heeb S, Ramos JL, Espinosa-Urgel M (2011b) PpoR, an orphan LuxR-family protein of Pseudomonas putida KT2440, modulates competitive fitness and surface motility independently of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:79–85
Fletcher MP, Diggle SP, Crusz SA, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Williams P (2007) A dual biosensor for 2-alkyl-4-quinolone quorum-sensing signal molecules. Environ Microbiol 9:2683–2693
Frerichs-Deeken U, Ranguelova K, Kappl R, Hüttermann J, Fetzner S (2004) Dioxygenases without requirement for cofactors, and their chemical model reaction: Compulsory order ternary complex mechanism of 1H-3-hydroxy-4-oxoquinaldine 2,4-dioxygenase involving general base catalysis by histidine 251 and single-electron oxidation of the substrate dianion. Biochemistry 43:14485–14499
Gallagher LA, McKnight SL, Kuznetsova MS, Pesci EC, Manoil C (2002) Functions required for extracellular quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184:6472–6480
Givskov M, de Nys R, Manefield M, Gram L, Maximilien R, Eberl L, Molin S, Steinberg PD, Kjelleberg S (1996) Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J Bacteriol 178:6618–6622
Grant SG, Jessee J, Bloom FR, Hanahan D (1990) Differential plasmid rescue from transgenic mouse DNAs into Escherichia coli methylation-restriction mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4645–4649
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166:557–580
Hays EE, Wells IC, Katzman PA, Cain CK, Jacobs FA, Thayer SA, Doisy EA, Gaby WL, Roberts EC, Muir RD, Carroll CJ, Jones LR, Wade NJ (1945) Antibiotic substances produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 159:725–750
Hazan R, He J, Xiao G, Dekimpe V, Apidianakis Y, Lesic B, Astrakas C, Déziel E, Lépine F, Rahme LG (2010) Homeostatic interplay between bacterial cell–cell signaling and iron in virulence. PLoS Pathog 6(3):e1000810
Heeb S, Blumer C, Haas D (2002) Regulatory RNA as mediator in GacA/RsmA-dependent global control of exoproduct formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. J Bacteriol 184:1046–1056
Heeb S, Fletcher MP, Chhabra SR, Diggle SP, Williams P, Cámara M (2011) Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:247–274
Iwasaki K, Uchiyama H, Yagi O, Kurabayashi T, Ishizuku K, Takamura Y (1994) Transformation of Pseudomonas putida by electroporation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:851–854
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM II, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Lamarche MG, Déziel E (2011) MexEF-OprN efflux pump exports the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) precursor HHQ (4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline). PLoS One 6(9):e24310
Leadbetter JR, Greenberg EP (2000) Metabolism of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus. J Bacteriol 182:6921–6926
Lee SJ, Gralla JD (2001) Sigma38 (rpoS) RNA polymerase promoter engagement via −10 region nucleotides. J Biol Chem 276:30064–30071
Lee J, Attila C, Cirillo SLG, Cirillo JD, Wood TK (2009) Indole and 7-hydroxyindole diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Microb Biotechnol 2:75–90
Lee Y, Yeom J, Kim J, Jung J, Jeon CO, Park W (2010) Phenotypic and physiological alterations by heterologous acylhomoserine lactone synthase expression in Pseudomonas putida. Microbiology 156:3762–3772
Leisinger T, Margraff R (1979) Secondary metabolites of the fluorescent pseudomonads. Microbiol Rev 43:422–442
Lépine F, Déziel E, Milot S, Rahme LG (2003) A stable isotope dilution assay for the quantification of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta 1622:36–41
Lépine F, Dekimpe V, Lesic B, Milot S, Lesimple A, Mamer OA, Rahme LG, Déziel E (2007) PqsA is required for the biosynthesis of 2,4-dihydroxyquinoline (DHQ), a newly identified metabolite produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia thailandensis. Biol Chem 388:839–845
Lu C, Kirsch B, Zimmer C, de Jong JC, Henn C, Maurer CK, Müsken M, Häussler S, Steinbach A, Hartmann RW (2012) Discovery of antagonists of PqsR, a key player in 2-alkyl-4-quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem Biol 19:381–390
Martinez A, Kolvek SJ, Yip CLT, Hopke J, Brown KA, MacNeil IA, Osburne MS (2004) Genetically modified bacterial strains and novel bacterial artificial chromosome shuttle vectors for constructing environmental libraries and detecting heterologous natural products in multiple expression hosts. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2452–2463
McGrath S, Wade DS, Pesci EC (2004) Dueling quorum sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa control the production of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS). FEMS Microbiol Lett 230:27–34
Michael JP (2007) Quinoline, quinazoline and acridone alkaloids. Nat Prod Rep 24:223–246
Michael JP (2008) Quinoline, quinazoline and acridone alkaloids. Nat Prod Rep 25:166–187
Nelson KE, Weinel C, Paulsen IT, Dodson RJ, Hilbert H, Martins dos Santos VA, Fouts DE, Gill SR, Pop M, Holmes M, Brinkac L, Beanan M, DeBoy RT, Daugherty S, Kolonay J, Madupu R, Nelson W, White O, Peterson J, Khouri H, Hance I, Chris Lee P, Holtzapple E, Scanlan D, Tran K, Moazzez A, Utterback T, Rizzo M, Lee K, Kosack D, Moestl D, Wedler H, Lauber J, Stjepandic D, Hoheisel J, Straetz M, Heim S, Kiewitz C, Eisen JA, Timmis KN, Düsterhöft A, Tümmler B, Fraser CM (2002) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the metabolically versatile Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol 4:799–808
Niewerth H, Bergander K, Chhabra SR, Williams P, Fetzner S (2011) Synthesis and biotransformation of 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolones by recombinant Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1399–1408
Ortori CA, Dubern JF, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Hardie K, Williams P, Barrett DA (2011) Simultaneous quantitative profiling of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone and 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolone families of quorum-sensing signaling molecules using LC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:839–850
Parschat K, Overhage J, Strittmatter AW, Henne A, Gottschalk G, Fetzner S (2007) Complete nucleotide sequence of the 113-kilobase linear catabolic plasmid pAL1 of Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus Rü61a and transcriptional analysis of genes involved in quinaldine degradation. J Bacteriol 189:3855–3867
Pesci EC, Milbank JBJ, Pearson JP, McKnight S, Kende AS, Greenberg EP, Iglewski BH (1999) Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11229–11234
Pini C, Godoy P, Bernal P, Ramos JL, Segura A (2011) Regulation of the cyclopropane synthase cfaB gene in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. FEMS Microbiol Lett 321:107–114
Pustelny C, Albers A, Büldt-Karentzopoulos K, Parschat K, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Williams P, Fetzner S (2009) Dioxygenase-mediated quenching of quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem Biol 16:1259–1267
Que YA, Hazan R, Ryan CM, Milot S, Lépine F, Lydon M, Rahme LG (2011) Production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa intercellular small signaling molecules in human burn wounds. J Pathog Article ID 549302. doi:10.4061/2011/549302
Rampioni G, Pustelny C, Fletcher MP, Wright VJ, Bruce M, Rumbaugh KP, Heeb S, Cámara M, Williams P (2010) Transcriptomic analysis reveals a global alkyl-quinolone-independent regulatory role for PqsE in facilitating the environmental adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to plant and animal hosts. Environ Microbiol 12:1659–1673
Roca A, Rodriguez-Herva JJ, Duque E, Ramos JL (2008) Physiological responses of Pseudomonas putida to formaldehyde during detoxification. Microb Biotechnol 1:158–169
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Santos PM, Di Bartolo I, Blatny JM, Zennaro E, Valla S (2001) New broad-host-range promoter probe vectors based on the plasmid RK2 replicon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 195:91–96
Schertzer JW, Boulette ML, Whiteley M (2009) More than a signal: non-signaling properties of quorum sensing molecules. Trends Microbiol 17:189–195
Schertzer JW, Brown SA, Whiteley M (2010) Oxygen levels rapidly modulate Pseudomonas aeruginosa social behaviours via substrate limitation of PqsH. Mol Microbiol 77:1527–1538
Steiner RA, Janßen HJ, Roversi P, Oakley AJ, Fetzner S (2010) Structural basis for cofactor-independent dioxygenation of N-heteroaromatic compounds at the α/β hydrolase fold. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:657–662
Tashiro Y, Toyofuku M, Nakajima-Kambe T, Uchiyama H, Nomura N (2010) Bicyclic compounds repress membrane vesicle production and Pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 301:123–130
Wade DS, Calfee MW, Rocha ER, Ling EA, Engstrom E, Coleman JP, Pesci EC (2005) Regulation of Pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 187:4372–4380
Wells IC (1952) Antibiotic substances produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Syntheses of Pyo Ib, Pyo Ic, and Pyo III. J Biol Chem 196:331–340
Xiao G, Déziel E, He J, Lépine F, Lesic B, Castonguay MH, Milot S, Tampakaki AP, Stachel SE, Rahme LG (2006a) MvfR, a key Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity LTTR-class regulatory protein, has dual ligands. Mol Microbiol 62:1689–1699
Xiao G, He J, Rahme LG (2006b) Mutation analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa mvfR and pqsABCDE gene promoters demonstrates complex quorum-sensing circuitry. Microbiology 152:1679–1686
Yu S, Jensen V, Seeliger J, Feldmann I, Weber S, Schleicher E, Häussler S, Blankenfeldt W (2009) Structure elucidation and preliminary assessment of hydrolase activity of PqsE, the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) response protein. Biochemistry 48:10298–10307
Zhang XG, Bremer H (1995) Control of the Escherichia coli rrnB P1 promoter strength by ppGpp. J Biol Chem 270:11181–11189
Zhang LH, Dong YH (2004) Quorum sensing and signal interference: diverse implications. Mol Microbiol 53:1563–1571
Zhang YM, Frank MW, Zhu K, Mayasundari A, Rock CO (2008) PqsD is responsible for the synthesis of 2,4-dihydroxyquinoline, an extracellular metabolite produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 283:28788–28794
Zor T, Selinger Z (1996) Linearization of the Bradford protein assay increases its sensitivity: theoretical and experimental studies. Anal Biochem 236:302–308
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Dr. Paul Williams and Dr. Stephan Heeb, University of Nottingham, UK, for providing the pME6032 vector, and Prof. Dr. Svein Valla, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, for the gift of plasmid pPR9TT. We also thank Olha Schneider (Münster) for help in β-galactosidase experiments, Sven Thierbach (Münster) for help in determination of kinetic parameters of HodC and data analysis, and Heiko Niewerth (Münster) for devising the HPLC protocol and for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported, in part, by the German Research Foundation (DFG, grant FE 383/16-1 to S.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, C., Fetzner, S. A Pseudomonas putida bioreporter for the detection of enzymes active on 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolone signalling molecules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 751–760 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4236-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4236-4