Abstract
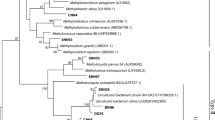
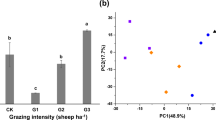
Knowledge about methanotrophs and their activities is important to understand the microbial mediation of the greenhouse gas CH4 under climate change and human activities in terrestrial ecosystems. The effects of simulated warming and sheep grazing on methanotrophic abundance, community composition, and activity were studied in an alpine meadow soil on the Tibetan Plateau. There was high abundance of methanotrophs (1.2–3.4 × 108 pmoA gene copies per gram of dry weight soil) assessed by real-time PCR, and warming significantly increased the abundance regardless of grazing. A total of 64 methanotrophic operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were obtained from 1,439 clone sequences, of these OTUs; 63 OTUs (98.4%) belonged to type I methanotrophs, and only one OTU was Methylocystis of type II methanotrophs. The methanotroph community composition and diversity were not apparently affected by the treatments. Warming and grazing significantly enhanced the potential CH4 oxidation activity. There were significantly negative correlations between methanotrophic abundance and soil moisture and between methanotrophic abundance and NH4–N content. The study suggests that type I methanotrophs, as the dominance, may play a key role in CH4 oxidation, and the alpine meadow has great potential to consume more CH4 under future warmer and grazing conditions on the Tibetan Plateau.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell GCJ, Stralis-Pavese N, Sessitsch A, Bodrossy L (2009) Grazing affects methanotroph activity and diversity in an alpine meadow soil. Environ Microbiol Rep 1:457–465
Bodelier PLE, Roslev P, Henckel T, Frenzel P (2000) Stimulation by ammonium-based fertilizers of methane oxidation in soil around rice roots. Nature 403:421–424
Börjesson G, Sundh I, Tunlid A, Frostegard A, Svensson BH (1998) Microbial oxidation of CH4 at high partial pressures in an organic landfill cover soil under different moisture regimes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:207–217
Börjesson G, Sundh I, Svensson B (2004) Microbial oxidation of CH4 at different temperatures in landfill cover soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:305–312
Bremner JM (1996) Nitrogen—total. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis: Part 3—chemical methods, Vol. 37. Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1085–1121
Cao GM, Xu XL, Long RJ, Wang QL, Wang CT, Du YG, Zhao XQ (2008) Methane emissions by alpine plant communities in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biol Lett 4:681–684
Chen Y, Dumont MG, Cebron A, Murrell JC (2007) Identification of active methanotrophs in a landfill cover soil through detection of expression of 16S rRNA and functional genes. Environ Microbiol 9:2855–2869
Costello AM, Lidstrom ME (1999) Molecular characterization of functional and phylogenetic genes from natural populations of methanotrophs in lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5066–5074
Degelmann DM, Borken W, Drake HL, Kolb S (2010) Different atmospheric methane-oxidizing communities in European beech and Norway spruce soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3228–3235
Dunfield PF, Yuryev A, Senin P, Smirnova AV, Stott MB, Hou SB, Ly B, Saw JH, Zhou ZM, Ren Y, Wang JM, Mountain BW, Crowe MA, Weatherby TM, Bodelier PLE, Liesack W, Feng L, Wang L, Alam M (2007) Methane oxidation by an extremely acidophilic bacterium of the phylum Verrucomicrobia. Nature 450:879–882
Einola JKM, Kettunen RH, Rintala JA (2007) Responses of methane oxidation to temperature and water content in cover soil of a boreal landfill. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1156–1164
Hanson RS, Hanson TE (1996) Methanotrophic bacteria. Microbiol Rev 60:439–471
Holmes AJ, Roslev P, McDonald IR, Iversen N, Henriksen K, Murrell JC (1999) Characterization of methanotrophic bacterial populations in soils showing atmospheric methane uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3312–3318
Horz HP, Rich V, Avrahami S, Bohannan BJM (2005) Methane-oxidizing bacteria in a California upland grassland soil: diversity and response to simulated global change. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2642–2652
Houghton JT, Ding Y, Griggs DJ, Noguer M, van der Linden PJ, Dai X, Maskell K, Johnson CA (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Third IPCC Report. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hu YG, Chang XF, Lin XW, Wang YF, Wang SP, Duan JC, Zhang ZH, Yang XX, Luo CY, Xu GP, Zhao XQ (2010) Effects of warming and grazing on N2O fluxes in an alpine meadow ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau. Soil Biol Biochem 42:944–952
IPCC (2007) Summary for policymakers. Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 539–543
Islam T, Jensen S, Reigstad LJ, Larsen Ø, Birkeland NK (2008) Methane oxidation at 55°C and pH 2 by a thermoacidophilic bacterium belonging to the Verrucomicrobia phylum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:300–304
Kimball BA, Conley MM, Wang SP, Lin XW, Luo CY, Morgan J, Smith D (2008) Infrared heater arrays for warming ecosystem field plots. Glob Change Biol 14:309–320
King GM (1997) Responses of atmospheric methane consumption by soils to global climate change. Glob Change Biol 3:351–362
Klein JA, Harte J, Zhao XQ (2005) Dynamic and complex microclimate responses to warming and grazing manipulations. Glob Change Biol 11:1440–1451
Knief C, Lipski A, Dunfield PF (2003) Diversity and activity of methanotrophic bacteria in different upland soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6703–6714
Knoblauch C, Zimmermann U, Blumenberg M, Michaelis W, Pfeiffer EM (2008) Methane turnover and temperature response of methane-oxidizing bacteria in permafrost-affected soils of northeast Siberia. Soil Biol Biochem 40:3004–3013
Kolb S (2009) The quest for atmospheric methane oxidizers in forest soils. Environ Microbiol Rep 1:336–346
Le Mer J, Roger P (2001) Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: a review. Eur J Soil Biol 37:25–50
Le Roux X, Poly F, Currey P, Commeaux C, Hai B, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schloter M, Attard E, Klumpp K (2008) Effects of aboveground grazing on coupling among nitrifier activity, abundance and community structure. ISME J 2:221–232
Liebner S, Wagner D (2007) Abundance, distribution and potential activity of methane oxidizing bacteria in permafrost soils from the Lena Delta, Siberia. Environ Microbiol 9:107–117
Luesken FA, Zhu BL, van Alen TA, Butler MK, Diaz MR, Song B, Op den Camp HJM, Jetten MSM, Ettwig KF (2011) pmoA primers for detection of anaerobic methanotrophs. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3877–3880
Luo CY, Xu GP, Wang YF, Wang SP, Lin XW, Hu YG, Zhang ZH, Chang XF, Duan JC, Su AL, Zhao XQ (2009) Effects of grazing and experimental warming on DOC concentrations in the soil solution on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2493–2500
Luo CY, Xu GP, Chao ZG, Wang SP, Lin XW, Hu YG, Zhang ZH, Duan JC, Chang XF, Su AL, Li YN, Zhao XQ, Du MY, Tang YH, Kimball B (2010) Effect of warming and grazing on litter mass loss and temperature sensitivity of litter and dung mass loss on the Tibetan plateau. Glob Change Biol 16:1606–1617
Magurran AE (1988) Ecological diversity and its measurement. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Martineau C, Whyte LG, Greer CW (2010) Stable isotope probing analysis of the diversity and activity of methanotrophic bacteria in soils from the Canadian high Arctic. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5773–5784
McDonald IR, Bodrossy L, Chen Y, Murrell JC (2008) Molecular ecology techniques for the study of aerobic methanotrophs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1305–1315
Menyailo OV, Hungate BA, Abraham WR, Conrad R (2008) Changing land use reduces soil CH4 uptake by altering biomass and activity but not composition of high-affinity methanotrophs. Glob Change Biol 14:2405–2419
Mohanty SR, Bodelier PLE, Conrad R (2007) Effect of temperature on composition of the methanotrophic community in rice field and forest soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:24–31
Op den Camp HJM, Islam T, Stott MB, Harhangi HR, Hynes A, Schouten S, Jetten MSM, Birkeland NK, Pol A, Dunfield PF (2009) Environmental, genomic and taxonomic perspectives on methanotrophic Verrucomicrobia. Environ Microbiol Rep 1:293–306
Pol A, Heijmans K, Harhangi HR, Tedesco D, Jetten MSM, Op den Camp HJM (2007) Methanotrophy below pH 1 by a new Verrucomicrobia species. Nature 450:874–878
R Development Core Team (2009) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available at http://www.R-project.org
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Semrau JD (2011) Current knowledge of microbial community structures in landfills and its cover soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:961–969
Semrau JD, DiSpirito AA, Yoon S (2010) Methanotrophs and copper. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:496–531
Singh BK, Bardgett RD, Smith P, Reay DS (2010) Microorganisms and climate change: terrestrial feedbacks and mitigation options. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:779–790
Singleton DR, Furlong MA, Rathbun SL, Whitman WB (2001) Quantitative comparisons of 16S rRNA gene sequence libraries from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4374–4376
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Theisen AR, Ali MH, Radajewski S, Dumont MG, Dunfield PF, McDonald IR, Dedysh SN, Miguez CB, Murrell JC (2005) Regulation of methane oxidation in the facultative methanotroph Methylocella silvestris BL2. Mol Microbiol 58:682–692
Thompson LG, Yao T, Mosley-Thompson E, Davis ME, Henderson KA, Lin PN (2000) A high-resolution millennial record of the South Asian monsoon from Himalayan ice cores. Science 289:1916–1919
Urmann K, Lazzaro A, Gandolfi I, Schroth MH, Zeyer J (2009) Response of methanotrophic activity and community structure to temperature changes in a diffusive CH4/O2 counter gradient in an unsaturated porous medium. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:202–212
Vorob’ev AV, Baani M, Doronina NV, Brady AL, Liesack W, Dunfield PF, Dedysh SN (2011) Methyloferula stellata gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidophilic, obligately methanotrophic bacterium possessing only a soluble methane monooxygenase. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.028118-0
Wang ZP, Ineson P (2003) Methane oxidation in a temperate coniferous forest soil: effects of inorganic N. Soil Biol Biochem 35:427–433
Wang GX, Wang YB, Li YS, Cheng HY (2007) Influences of alpine ecosystem responses to climatic change on soil properties on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Catena 70:506–514
Wang YL, Wu WX, Ding Y, Liu W, Perera A, Chen YX, Devare M (2008) Methane oxidation activity and bacterial community composition in a simulated landfill cover soil is influenced by the growth of Chenopodium album L. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2452–2459
Wang SP, Yang XX, Lin XW, Hu YG, Luo CY, Xu GP, Zhang ZH, Su AL, Chang XF, Chao ZG, Duan JC (2009) Methane emission by plant communities in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: a new experimental study of alpine meadows and oat pasture. Biol Lett 5:535–538
Wu J, Joergensen RG, Pommerening B, Chaussod R, Brookes PC (1990) Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation extraction—an automated procedure. Soil Biol Biochem 22:1167–1169
Wu YB, Tan HC, Deng YC, Wu J, Xu XL, Wang YF, Tang YH, Higashi T, Cui XY (2010) Partitioning pattern of carbon flux in a Kobresia grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau revealed by field 13C pulse-labeling. Glob Change Biol 16:2322–2333
Yamulki S, Jarvis SC, Owen P (1998) Nitrous oxide emissions from excreta applied in a simulated grazing pattern. Soil Biol Biochem 30:491–500
Yrjälä KIM, Tuomivirta T, Juottonen H, Putkinen A, Lappi K, Tuittila E, Penttilä T, Minkkinen K, Laine J, Peltoniemi K, Fritze H (2011) CH4 production and oxidation processes in a boreal fen ecosystem after long-term water table drawdown. Glob Change Biol 17:1311–1320
Zhang F, She YH, Zheng Y, Zhou ZF, Kong SQ, Hou DJ (2010) Molecular biologic techniques applied to the microbial prospecting of oil and gas in the Ban 876 gas and oil field in China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1183–1194
Zhao XQ, Zhou XM (1999) Ecological basis of alpine meadow ecosystem management in Tibet: Haibei alpine meadow ecosystem research station. Ambio 28:642–647
Zhao L, Li YN, Xu SX, Zhou HK, Gu S, Yu GR, Zhao XQ (2006) Diurnal, seasonal and annual variation in net ecosystem CO2 exchange of an alpine shrubland on Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Glob Change Biol 12:1940–1953
Zheng Y, Zhang LM, Zheng YM, Di HJ, He JZ (2008) Abundance and community composition of methanotrophs in a Chinese paddy soil under long-term fertilization practices. J Soils Sediments 8:406–414
Zheng Y, Liu XZ, Zhang LM, Zhou ZF, He JZ (2010) Do land utilization patterns affect methanotrophic communities in a Chinese upland red soil? J Environ Sci 22:1936–1943
Zhou HK, Zhao XQ, Tang YH, Gu S, Zhao L (2005) Alpine grassland degradation and its control in the source region of Yangtze and Yellow rivers, China. Grassland Sci 51:191–203
Zhou XQ, Wang YF, Huang XZ, Tian JQ, Hao YB (2008) Effect of grazing intensities on the activity and community structure of methane-oxidizing bacteria of grassland soil in Inner Mongolia. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 80:145–152
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant of the Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (no. KSCX2-YW-Z-1020), the Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 41001149), and the National Basic Research Program (2010CB833502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Yang, W., Sun, X. et al. Methanotrophic community structure and activity under warming and grazing of alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 2193–2203 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3535-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3535-5