Abstract
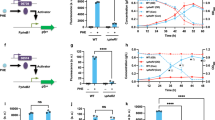
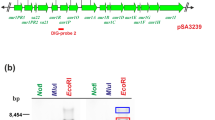
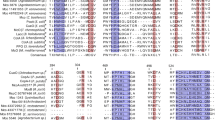
The major utilization pathway for lignin-derived aromatic compounds in microorganisms is the β-ketoadipate pathway. Through this pathway, the aromatic compounds protocatechuate and catechol are converted to acetyl coenzyme A and succinyl coenzyme A. The enzymes of the protocatechuate branch of this pathway are encoded by the pca genes. Here, we describe a gene cluster in Streptomyces coelicolor containing the pca structural genes and a regulatory gene required for the catabolism of protocatechuate. We found that transcription of the structural genes in S. coelicolor is induced by protocatechuate and p-hydroxybenzoate. We also observed inducible transcription of pca structural genes in the ligninolytic strain Streptomyces viridosporus ATCC 39115. Disruption of a gene encoding a putative MarR family transcription factor that is divergently transcribed from the pca structural genes resulted in constitutive transcription of the structural genes. Thus, the transcription factor encoded by this gene is an apparent negative regulator of pca gene transcription in S. coelicolor. Our findings suggest how Streptomyces bacteria could be engineered for and used in biotechnology for the utilization and degradation of lignin and lignin-derived aromatic compounds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler E (1977) Lignin chemistry—past, present, and future. Wood Sci Technol 11:169–218
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeño-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D et al (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor. Nature 417:141–147
Bisaria VS, Ghose TK (1981) Biodegradation of cellulosic materials: substrates, microorganisms, enzymes, and products. Enzyme Microb Technol 3:90–94
Borgmeyer JR, Crawford DL (1985) Production and characterization of polymeric lignin degradation intermediates from two different Streptomyces spp. Appl Env Microbiol 49:273–278
Breznak JA, Brune A (1994) Role of microorganisms in the digestion of lignocellulose by termites. Annu Rev Entomol 39:453–487
Brinkrolf K, Brune I, Tauch A (2006) Transcriptional regulation of catabolic pathways for aromatic compounds in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Genet Mol Res 5:773–789
Chen F, Dixon RA (2007) Lignin modification improves fermentable sugar yields for biofuel production. Nat Biotechnol 25:759–761
Crawford DL (1981) Microbial conversion of lignin into useful chemicals using a lignin degrading Streptomyces. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 11:275–291
Crawford DL, Pometto AL, Crawford RL (1983) Lignin degradation by Streptomyces viridosporous, isolation and characterization of a new polymeric lignin degradation intermediates. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:898–904
Crawford DL, Pettey TM, Thede BM, Deobald LE (1984) Genetic manipulation of lignolytic Streptomyces and generation of improved lignin to chemical bioconversion strains. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 14:241–255
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
Gerischer U (2002) Specific and global regulation of genes associated with the degradation of aromatic compounds in bacteria. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4:111–121
Gerischer U, Jerg B, Fischer R (2008) Spotlight on the Acinetobacteri baylyi β-ketoadipate pathway multiple levels of regulation. In: Acinetobacter molecular microbiology. Horizon Scientific Press, Norwich
Gregory MA, Till R, Smith MCM (2003) Integration site for Streptomyces phage ΦBT1 and development of site-specific integrating vectors. J Bacteriol 185:5320–5323
Grund E, Kutzner HJ (1998) Utilization of quinate and p-hydroxybenzoate by actinomycetes: key enzymes and taxonomic relevance. J Basic Microbiol 4:241–255
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1541–1546
Harwood CS, Parales RE (1996) The β-ketoadipate pathway and the biology of self-identity. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:553–590
Hatakka A (1994) Lignin-modifying enzymes from selected white rot fungi: production and role in lignin degradation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:124–135
Himmel ME, Ding S-Y, Johnson DK, Adney WS, Nimlos MR, Brady JW, Foust TD (2007) Biomass recalcitrance: engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315:804–807
Hopwood DA (2007) Streptomyces in nature and medicine. Oxford University Press
Iwagami SG, Yang K, Davies J (2000) Characterization of the protocatechuic acid catabolic gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. strain 2065. App Environ Microbiol 66:1499–1508
Jones GH, Paget MSB, Chamberlin L, Buttner MJ (1997) Sigma-E is required for the production of the antibiotic actinomycin in Streptomyces antibioticus. Mol Microbiol 23:169–178
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Ljungdahl LG, Eriksson KE (1985) Ecology of microbial cellulose degradation. Adv Microb Ecol 8:237–299
MacLean AM, MacPherson G, Aneja P, Finan TM (2006) Characterization of the β-ketoadipate pathway on Sinorhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5403–5413
Martinez D et al (2004) Genome sequence of the lignocellulose degrading fungus Phanaerochaete chrysosporium strain RP78. Nat Biotechnol 22:695–700
Masai E, Katayama Y, Fukuda M (2007) Genetic and biochemical investigations on bacterial catabolic pathways for lignin-derived aromatic compounds. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1–15
McCarthy AJ (1987) Lignocellulose-degrading actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 46:145–163
Omura S, Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Takahashi C, Shinose M et al (2001) Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12215–12220
Ottow JCG, Zolg W (1974) Improved procedure and colorimetric test for the detection of ortho- and meta-cleavage of protocatechuate by Pseudomonas isolates. Can J Microbiol 20:1059–1061
Park H-J, Kim E-S (2003) An inducible Streptomyces gene cluster involved in aromatic compound metabolism. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:151–157
Parke D (1995) Supraoperonic clustering of pca genes for catabolism of the phenolic compound protocatechuate in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 177:3808–3817
Pometto AL, Sutherland JB, Crawford DL (1981) Streptomyces setonii: catabolism of vanillic acid via guaicol and catechol. Can J Microbiol 27:636–638
Pometto AL, Crawford DL (1986) Catabolic fate of Streptomyces viridosporous T7A produced acid precipitable polymeric lignins upon incubation with lignolytic Streptomyces species and Phanerchaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:171–179
Ragauskas AJ, Williams CK, Davison BH, Britovsek G, Cairney J, Eckert CA, Frederick WJ, Hallett JP, Leak DJ, Liotta CL, Mienlenz JR, Murphy R, Templer R, Tschaplinski T (2006) The path forward for the biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311:484–489
Ramachandra M, Crawford DL, Pometto AL (1987) Extracellular enzyme activities during lignocellulose degradation by Streptomyces spp.: a comparative study of wild-type and genetically manipulated strains. Appl Env Microbiol 53:2754–2760
Ramachandra M, Crawford DL, Hertel G (1988) Characterization of an extracellular lignin peroxidase of the lignocellulolytic actinomycete Streptomyces viridosporous. Appl Environ Microbiol 54: 3057–3063
Rubin EM (2008) Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature 454:841–845
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Siehler SY, Dal S, Fischer R, Patz P, Gerischer U (2007) Multiple-level regulation of genes for protocatechuate degradation in Acinetobacter baylyi includes cross-regulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:232–242
Stanier RY, Palleroni NJ, Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol 43:159–271
Sutherland JB, Crawford DL, Pometto AJ (1983) Metabolism of cinnamic, p-coumaric, and ferulic acids by Streptomyces setonii. Can J Microbiol 29:1253–1257
Tropel D, van der Meer JR (2004) Bacterial transcriptional regulators for degradation pathways. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:474–500
Van Wyk JP (2001) Biotechnology and the utilization of biowaste as a resource for bioproduct development. Trends Biotechnol 19:1172–1177
Zimmerman W (1990) Degradation of lignin by bacteria. J Biotechnol 13:119–130
Acknowledgments
This work was generously supported by a National Science Foundation research grant (MCB-09020713) to J.K.S. Financial support was also provided by Brown University, including a Frontiers in Chemistry Research Grant from the Department of Chemistry and a Salomon Award from the Office of the Vice President for Research to J.K.S. J.R.D. is a graduate student in the Graduate Program in Molecular Pharmacology and Physiology. J.R.D. was the recipient of a Pharmacia graduate fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, J.R., Sello, J.K. Regulation of genes in Streptomyces bacteria required for catabolism of lignin-derived aromatic compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 921–929 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2358-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2358-0