Abstract
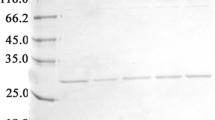
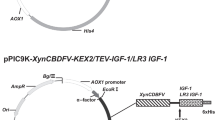
Endostatin, a 20-kDa C-terminal fragment derived from type XVIII collagen, is a potent angiogenesis inhibitor and an antitumor factor. To improve the production of recombinant human endostatin on increasing demand in clinical practice, we constructed an artificial gene encoding its mature peptide sequence in human collagen XVIII. The synthetic gene consisted of 20 codons in preference in methylotropic yeast—Pichia pastoris and was cloned into expression vector pPICZαA; and the recombinant protein was expressed in P. pastoris strain SMD1168 and purified to near homogeneity using heparin affinity chromatography. The amount of expressed recombinant protein in cultural media using described strategy was 80 mg/l in shake flask cultivation and 435 mg/l in high-density bioreactor fermentation. Methylthiazolium assay demonstrated that human endostatin expressed in P. pastoris using artificial synthetic gene of preference in P. pastoris was able to inhibit the acidic fibroblast growth factor-induced proliferation of endothelial cells in vitro.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertolini F, Fusetti L, Mancuso P, Gobbi A, Corsini C, Ferrucci PF, Martinelli G, Pruneri G (2000) Endostatin, an antiangiogenic drug, induces tumor stabilization after chemotherapy or anti-CD20 therapy in a NOD/SCID mouse model of human high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 96:282–287
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’Reilly MS (1997) Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 390:404–407
Cereghino JL, Cregg JM (2000) Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:45–66
Dhanabal M, Ramchandran R, Volk R, Stillman IE, Lombardo M, Iruela-Arispe ML, Simons M, Sukhatme VP (1999a) Endostatin, yeast production, mutants, and antitumor effect in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 59:189–197
Dhanabal M, Volk R, Ramchandran R, Simons M, Sukhatme VP (1999b) Cloning, expression, and in vitro activity of human endostatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258:345–352
Feng W, Cai J, Pierce WM, Song ZH (2002) Expression of CB2 cannabinoid receptor in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 26:496–505
Folkman J (1995) Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 333:1757–1763
Herbst RS, Mullani ZA, Davis DW, Hess KR, McConkey DJ, Charnsangavej C, O’Reilly MS, Kim HW, Baker C, Roach J, Ellis ML, Rashid A, Pluda J, Bucana C, Madden TL, Tran HT, Abbruzzese JL (2003) Development of biologic markers of response and assessment of antiangiogenic activity in a clinical trial of human recombinant endostatin. J Clin Oncol 20:3804–3814
Huang Y, Su Z, Zheng Q (2003) Human TGF-β3 gene synthesis and expression in E. coli. Journal of China Pharmaceutical University 34:264–267
Gellissen G (2000) Heterologous protein production in methylotrophic yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:741–750
Kunes YZ, Sanz MC, Tumanova I, Birr CA, Shi PQ, Bruguera P, Ruiz JA, Sanchez-Martinez D (2002) Expression and characterization of a synthetic protein C activator in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 26:406–415
Mundhenke C, Thomas JP, Wilding G, Lee FT, Kelzc F, Chappell R, Neider R, Sebree LA, Friedl A (2003) Tissue examination to monitor antiangiogenic therapy: a phase I clinical trial with endostatin. Clin Cancer Res 7:3366–3374
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88:277–285
Sinclair G, Choy FY (2002) Synonymous codon usage bias and the expression of human glucocerebrosidase in the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 26:96–105
Thomas JP, Arzoomanian RZ, Alberti D, Marnocha R, Lee F, Friedl A, Tutsch K, Dresen A, Geiger P, Pluda J, Fogler W, Schiller JH, Wilding G (2003) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of recombinant human endostatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 20:223–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Z., Wu, X., Feng, Y. et al. High level expression of human endostatin in Pichia pastoris using a synthetic gene construct. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73, 1355–1362 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0604-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0604-2