Abstract
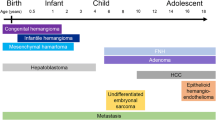
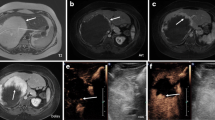
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is commonly used to characterize focal liver masses in the pediatric population. MRI is the preferred modality because of its superior contrast resolution and utility for obtaining functional sequences such as diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). MR exams performed with a hepatocyte-specific gadolinium-based contrast agent can characterize focal liver lesions, which helps in differentiating a common benign entity such as focal nodular hyperplasia from other liver pathology when the background liver is normal. The most common benign focal lesion is a hemangioma, and metastases followed by hepatoblastoma are the most common malignant lesions. This article can help radiologists become familiar with the pre- and post-contrast imaging features of common pediatric liver masses.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakshi P, Srinivasan R, Rao KL et al (2006) Fine needle aspiration biopsy in pediatric space occupying lesions of liver: a retrospective study evaluating its role and diagnostic efficacy. J Pediatr Surg 41:1903–1908
Meyers RL (2007) Tumors of the liver in children. Surg Oncol 16:195–203
Adeyiga AO, Lee EY, Eisenberg RL (2012) Focal hepatic masses in pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:W422–W440
Shelmerdine SC, Roebuck DJ, Towbin AJ et al (2016) MRI of paediatric liver tumours: how we review and report. Cancer Imaging 16:21
von Schweinitz D (2006) Management of liver tumors in childhood. Semin Pediatr Surg 15:17–24
Chavhan GB, Shelmerdine S, Jhaveri K et al (2016) Liver MR imaging in children: current concepts and technique. Radiographics 36:1517–1532
Mitchell CL, Vasanawala SS (2011) An approach to pediatric liver MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:W519–W526
Meyers AB, Towbin AJ, Serai S et al (2011) Characterization of pediatric liver lesions with gadoxetate disodium. Pediatr Radiol 41:1183–1197
Basaran C, Karcaaltincaba M, Akata D et al (2005) Fat-containing lesions of the liver: cross sectional imaging findings with emphasis on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:1103–1110
Kochin IN, Miloh TA, Arnon R et al (2011) Benign liver masses and lesions in children: 53 cases over 12 years. Isr Med Assoc J 13:542–547
Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Temple M et al (2013) Diagnosis of postoperative bile leak and accurate localization of the site of leak by gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR cholangiography in a child. Pediatr Radiol 43:763–766
Chung EM, Cube R, Lewis RB et al (2010) From the archives of the AFIP: pediatric liver masses: radiologic-pathologic correlation part 1. Benign tumors Radiographics 30:801–826
Donnelly LF, Adams DM, Bisset GS 3rd (2000) Vascular malformations and hemangiomas: a practical approach in a multidisciplinary clinic. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:597–608
Kollipara R, Dinneen L, Rentas KE et al (2013) Current classification and terminology of pediatric vascular anomalies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201:1124–1135
Masand P (2014) Radiographic findings associated with vascular anomalies. Semin Plast Surg 28:69–78
Dickie B, Dasgupta R, Nair R et al (2009) Spectrum of hepatic hemangiomas: management and outcome. J Pediatr Surg 44:125–133
Christison-Lagay ER, Burrows PE, Alomari A et al (2007) Hepatic hemangiomas: subtype classification and development of a clinical practice algorithm and registry. J Pediatr Surg 42:62–67
Kassarjian A, Zurakowski D, Dubois J et al (2004) Infantile hepatic hemangiomas: clinical and imaging findings and their correlation with therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:785–795
Moore M, Anupindi SA, Mattei P et al (2009) Mesenchymal cystic hamartoma of the liver: MR imaging with pathologic correlation. J Radiol Case Rep 3:22–26
Jha P, Chawla SC, Tavri S et al (2009) Pediatric liver tumors — a pictorial review. Eur Radiol 19:209–219
Bahador A, Geramizadeh B, Rezazadehkermani M et al (2014) Mesenchymal hamartoma mimicking hepatoblastoma. Int J Organ Transplant Med 5:78–80
Towbin AJ, Luo GG, Yin H, Mo JQ (2011) Focal nodular hyperplasia in children, adolescents, and young adults. Pediatr Radiol 41:341–349
Ma IT, Rojas Y, Masand PM et al (2015) Focal nodular hyperplasia in children: an institutional experience with review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg 50:382–387
Gupta RT, Iseman CM, Leyendecker JR et al (2012) Diagnosis of focal nodular hyperplasia with MRI: multicenter retrospective study comparing gadobenate dimeglumine to gadoxetate disodium. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:35–43
Chavhan GB, Mann E, Kamath BM et al (2014) Gadobenate-dimeglumine-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for hepatic lesions in children. Pediatr Radiol 44:1266–1274
Katabathina VS, Menias CO, Shanbhogue AK et al (2011) Genetics and imaging of hepatocellular adenomas: 2011 update. Radiographics 31:1529–1543
Fowler KJ, Brown JJ, Narra VR (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging of focal liver lesions: approach to imaging diagnosis. Hepatology 54:2227–2237
Grazioli L, Olivetti L, Mazza G, Bondioni MP (2013) MR imaging of hepatocellular adenomas and differential diagnosis dilemma. Int J Hepatol 2013:374170
Van Aalten SM, Thomeer MG, Terkivatan T et al (2011) Hepatocellular adenomas: correlation of MR imaging with pathologic subtype classification. Radiology 261:172–181
Grazioli L, Bondioni MP, Haradome H et al (2012) Hepatocellular adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging in differential diagnosis. Radiology 262:520–529
Siegel MJ, Chung EM, Conran RM (2008) Pediatric liver: focal masses. Magn Reson Imaging Clin North Am 16:437–452
van Aalten SM, Thomeer MG, Terkivatan T et al (2011) Hepatocellular adenomas: correlation of MR imaging findings with pathologic subtype classification. Radiology 261:172–181
Thomeer MG, Willemssen FE, Biermann KK et al (2014) MRI features of inflammatory hepatocellular adenomas on hepatocyte phase imaging with liver-specific contrast agents. J Magn Reson Imaging 39:1259–1264
Agarwal S, Fuentes-Orrego JM, Arnason T et al (2014) Inflammatory hepatocellular adenomas can mimic focal nodular hyperplasia on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203:W408–W414
Techavichit P, Masand PM, Himes RW et al (2016) Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma of the liver (UESL): a single-center experience and review of the literature. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 38:261–268
Walther A, Geller J, Coots A et al (2014) Multimodal therapy including liver transplantation for hepatic undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma. Liver Transplant 20:191–199
Chung EM, Lattin GE Jr, Cube R et al (2011) From the archives of the AFIP: pediatric liver masses: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Part 2. Malignant tumors. Radiographics 31:483–507
Towbin AJ, Meyers RL, Woodley H et al (2018) 2017 PRETEXT: radiologic staging system for primary hepatic malignancies of childhood revised for the Paediatric Hepatic International Tumour Trial (PHITT). Pediatr Radiol 48:536–554
Felsted AE, Shi Y, Masand PM et al (2015) Intraoperative ultrasound for liver tumor resection in children. J Surg Res 198:418–423
Yikilmaz A, George M, Lee EY (2017) Pediatric hepatobiliary neoplasms: an overview and update. Radiol Clin North Am 55:741–766
Schmid I, Schweinitz VD (2017) Pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and solutions. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 4:16–21
Xue M, Masand P, Thompson P et al (2014) Angiosarcoma successfully treated with liver transplantation and sirolimus. Pediatr Transplant 18:E114–E119
Fernandez-Pineda I, Sandoval JA, Davidoff AM (2015) Hepatic metastatic disease in pediatric and adolescent solid tumors. World J Hepatol 7:1807–1817
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masand, P.M. Magnetic resonance imaging features of common focal liver lesions in children. Pediatr Radiol 48, 1234–1244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4218-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4218-5