Abstract
Background
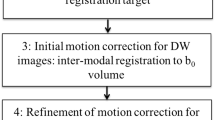
Diffusion tensor parameters can be analysed by fitting regions of interest (ROIs) to selected brain structures. The clinical usefulness of these measurements is influenced by their reproducibility and validity.
Objective
To investigate the reproducibility of fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) measurements.
Material and methods
Seventy-six infants were imaged once at term-equivalent age. We measured several brain regions. Reproducibility was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman method.
Results
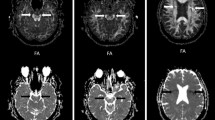
Intra-observer reproducibility was excellent for FA in the calcarine cortex (right) and frontal white matter (left), and for MD in the corpus callosum (anterior), internal capsule, corona radiata, putamen, frontal white matter, optic radiation (left), thalamus (right) and calcarine cortex (right). Inter-observer reproducibility was excellent for FA in the corpus callosum (posterior) and for MD in the internal capsule and corona radiata (right). Inter-observer reproducibility was poor for FA in frontal and posterior white matter (right) and for MD in the inferior colliculus (right). Reproducibility was fair to good in other areas. The Bland-Altman plots showed no considerable bias, and variance was independent of the mean value.
Conclusion
Reproducibility of ROI measurement was fair to good for both FA and MD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ et al (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36:893–906
Berman JI, Mukherjee P, Partridge SC et al (2005) Quantitative diffusion tensor MRI fiber tractography of sensorimotor white matter development in premature infants. Neuroimage 27:862–871
Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging assessment of brain white matter maturation during the first postnatal year. AJR 189:476–486
Rose SE, Hatziaeorgiou X, Strudwick MW et al (2008) Altered white matter diffusion anisotropy in normal and preterm infants at term-equivalent age. Magn Reson Med 60:761–767
Huppi PS, Maier SE, Peled S et al (1998) Microstructural development of human newborn cerebral white matter assessed in vivo by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Res 44:584–590
Gimenez M, Miranda MJ, Born AP et al (2008) Accelerated cerebral white matter development in preterm infants: a voxel-based morphometry study with diffusion tensor MR imaging. Neuroimage 41:728–734
Krishnan ML, Dyet LE, Boardman JP et al (2007) Relationship between white matter apparent diffusion coefficients in preterm infants at term-equivalent age and developmental outcome at 2 years. Pediatrics 120:E604–E609
Arzoumanian Y, Mirmiran M, Barnes PD et al (2003) Diffusion tensor brain imaging findings at term-equivalent age may predict neurologic abnormalities in low birth weight preterm infants. AJNR 24:1646–1653
Bester M, Heesen C, Schippling S et al (2008) Early anisotropy changes in the corpus callosum of patients with optic neuritis. Neuroradiology 50:549–557
Lin Y, Wang J, Wu C et al (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging of the auditory pathway in sensorineural hearing loss: changes in radial diffusivity and diffusion anisotropy. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:598–603
Wu CM, Ng SH, Liu TC (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging of the subcortical auditory tract in subjects with long-term unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Audiol Neurotol 14:248–253
Counsell SJ, Shen YJ, Boardman JP et al (2006) Axial and radial diffusivity in preterm infants who have diffuse white matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging at term-equivalent age. Pediatrics 117:376–386
Saksena S, Husain N, Malik GK et al (2008) Comparative evaluation of the cerebral and cerebellar white matter development in pediatric age group using quantitative diffusion tensor imaging. Cerebellum 7:392–400
Bartha AL, Yap KRL, Miller SP et al (2007) The normal neonatal brain: MR imaging, diffusion tensor imaging, and 3D MR spectroscopy in healthy term neonates. AJNR 28:1015–1021
Bonekamp D, Nagae LM, Degaonkar M et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging in children and adolescents: reproducibility, hemispheric, and age-related differences. Neuroimage 34:733–742
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Sullivan EV (2003) Replicability of diffusion tensor imaging measurements of fractional anisotropy and trace in brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:427–433
Muller MJ, Mazanek M, Weibrich C et al (2006) Distribution characteristics, reproducibility, and precision of region of interest-based hippocampal diffusion tensor imaging measures. AJNR 27:440–446
Marenco S, Rawlings R, Rohde GK et al (2006) Regional distribution of measurement error in diffusion tensor imaging. Psychiatry Res 147:69–78
Bonekamp D, Nagae LM, Sullivan EV (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging in brain. Neuroimage 18:427–433
Ozturk A, Sasson AD, Farrell JAD (2008) Regional differences in diffusion tensor imaging measurements: assessment of intrarater and interrater variability. AJNR 29:1124–1127
Partridge SC, Mukherjee P, Berman JI et al (2005) Tractography-based quantitation of diffusion tensor imaging parameters in white matter tracts of preterm newborns. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:467–474
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Costa-Santos C, Bernardes J, Ayres-de-Campos D et al (2011) The limits of agreement and the intraclass correlation coefficient may be inconsistent in the interpretation of agreement. J Clin Epidemiol (in press)
Fleiss JL (1986) The design and analysis of clinical experiments. Wiley, New York, pp xiv, 432
Nunes RG, Jezzard P, Clare S (2005) Investigations on the efficiency of cardiac-gated methods for the acquisition of diffusion-weighted images. J Magn Reson 177:102–110
Brockstedt S, Borg M, Geijer B et al (1999) Triggering in quantitative diffusion imaging with single-shot EPI. Acta Radiol 40:263–269
Skare S, Andersson JLR (2001) On the effects of gating in diffusion imaging of the brain using single shot EPI. Magn Reson Imaging 19:1125–1128
Brander A, Kataja A, Saastamoinen A et al (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain in a healthy adult population: normative values and measurement reproducibility at 3 T and 1.5 T. Acta Radiol 51:800–807
Drobyshevsky A, Bregman J, Storey P et al (2007) Serial diffusion tensor imaging detects white matter changes that correlate with motor outcome in premature infants. Dev Neurosci 29:289–301
Rose J, Butler EE, Lamont LE et al (2009) Neonatal brain structure on MRI and diffusion tensor imaging, sex, and neurodevelopment in very-low-birthweight preterm children. Dev Med Child Neurol 51:526–535
Farrell JAD, Landman BA et al (2007) Effects of signal-to-noise ratio on the accuracy and reproducibility, of diffusion tensor imaging-derived fractional anisotropy, mean diffusivity, and principal eigenvector measurements at 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:756–767
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepomäki, V.K., Paavilainen, T.P., Hurme, S.A.M. et al. Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity parameters of the brain white matter tracts in preterm infants: reproducibility of region-of-interest measurements. Pediatr Radiol 42, 175–182 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2234-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2234-9