Abstract
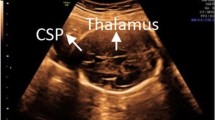
This review focuses on the optimum use of fetal MRI as an additional imaging tool to sonographic data in posterior fossa (PF) abnormalities in the second and third trimesters of gestation. We have chosen three particular situations to demonstrate the value of MRI as a complementary investigation to US: (1) the pattern of increased fluid-filled space of the PF, (2) decreased cerebellar sonographic biometry and (3) the diagnosis of focal echogenic lesions of the cerebellum. For increased fluid-filled space of the PF and decreased cerebellar sonographic biometry, a practical approach is proposed, largely based on prenatal imaging, especially MRI.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guibaud L (2002) Anomalies de la fosse cérébrale postérieure. In: Garel C, Delezoide AL, Guibaud L (eds) Imagerie du cerveau fœ tal pathologique. Sauramps Medical, Montepellier, pp 99–118
Altman NR, Naidich TP, Braffman BH (1992) Posterior fossa malformations. AJNR 13:691–724
Kollias SS, Ball WS Jr, Prenger EC (1993) Cystic malformations of the posterior fossa: differential diagnosis clarified through embryologic analysis. Radiographics 13:1211–1231
Poutamo J, Vanninen R, Partanen K, et al (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging supplements ultrasonographic imaging of the posterior fossa, pharynx and neck in malformed fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 13:327–34
Garel C, Chantrel E, Sebag G, et al (2000) Le développement du cerveau fœ tal. Atlas IRM et biométrie. Sauramps Médical, Montpellier
Adamsbaum C, Merzoug V, André C, et al (2002) Prenatal diagnosis of isolated posterior fossa anomalies: attempt at a simplified approach. J Radiol 83:321–328
Klein O, Pierre-Kahn A, Boddaert N, et al (2003) Dandy-Walker malformation: prenatal diagnosis and prognosis. Childs Nerv Syst 19:484–489
Estroff JA, Scott MR, Benacerraf BR (1992) Dandy-Walker variant: prenatal sonographic features and clinical outcome. Radiology 185:55–58
Ecker JL, Shipp TD, Bromley B, et al (2000) The sonographic diagnosis of Dandy-Walker and Dandy-Walker variant: associated findings and outcomes. Prenat Diagn 20:328–332
Barkovich AJ, Kjos BO, Norman D, et al (1989) Revised classification of posterior fossa cysts and cyst-like malformations based on the results of multiplanar MR imaging. AJR 153:1289–1300
Nyberg DA, Mahony BS, Hegge FN, et al (1991) Enlarged cisterna magna and the Dandy-Walker malformation: factors associated with chromosome abnormalities. Obstet Gynecol 77:436–442
Kolble N, Wisser J, Kurmanavicius J, et al (2000) Dandy-Walker malformation: prenatal diagnosis and outcome. Prenat Diagn 20:318–327
Ramaekers VT, Heimann G, Reul J, et al (1997) Genetic disorders and cerebellar structural abnormalities in childhood. Brain 120:1739–1751
Bromley B, Nadel AS, Pauker S, et al (1994) Closure of the cerebellar vermis: evaluation with second trimester US. Radiology 193:761–763
Laing FC, Frates MC, Brown DL, et al (1994) Sonography of the fetal posterior fossa: false appearance of mega-cisterna magna and Dandy-Walker variant. Radiology 192:247–251
Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR (1976) Neuroradiology in infants and children, vol 3. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 1014–1019
Raybaud C (1982) Cystic malformations of the posterior fossa. Abnormalities associated with the development of the roof of the fourth ventricle and adjacent meningeal structures. J Neuroradiol 9:103–133
Tortori-Donati P, Fondelli MP, Rossi A, et al (1996) Cystic malformations of the posterior cranial fossa originating from a defect of the posterior membranous area. Mega cisterna magna and persisting Blake’s pouch: two separate entities. Childs Nerv Syst 12:303–308
Goldstein I, Reece EA, Pilu G, et al (1987) Cerebellar measurements with ultrasonography in the evaluation of fetal growth and development. Am J Obstet Gynecol 156:1065–1069
Hill LM, Guzick D, Fries J, et al (1990) The transverse cerebellar diameter in estimating gestational age in the large for gestational age fetus. Obstet Gynecol 75:981–985
Barth PG (1993) Pontocerebellar hypoplasias. An overview of a group of inherited neurodegenerative disorders with fetal onset. Brain Dev 15:411–422
Barth PG (2000) Pontocerebellar hypoplasia—how many types? Eur J Paediatr Neurol 4:161–162
Mathews KD, Afifi AK, Hanson JW (1989) Autosomal recessive cerebellar hypoplasia. J Child Neurol 4:189–194
Vinkesteijn AS, Jansen CL, Los FJ, et al (2001) Fetal transcerebellar diameter and chromosomal abnormalities. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 17:502–505
Goasdoue P, Rodriguez D, Moutard ML, et al (2001) Pontoneocerebellar hypoplasia: definition of MR features. Pediatr Radiol 31:613–618
Graber D, Antignac C, Deschenes G, et al (2001) Cerebellar vermis hypoplasia with extracerebral involvement (retina, kidney, liver): difficult to classify syndromes. Arch Pediatr 8:186–190
Boltshauser E, Steinlin M, Martin E, et al (1996) Unilateral cerebellar aplasia. Neuropediatrics 27:50–53
Kendall B, Kingsley D, Lambert SR, et al (1990) Joubert syndrome: a clinico-radiological study. Neuroradiology 31:502–506
Obersteiner H (1914) Ein Kleinhirn ohne Wurm. Arb Neurol Inst (Wien) 124–136
Utsunomiya H, Takano K, Ogasawara T, et al (1998) Rhombencephalosynapsis: cerebellar embryogenesis. AJNR 19:547–549
Aydingoz U, Cila A, Aktan G (1997) Rhombencephalosynapsis associated with hand anomalies. Br J Radiol 70:764–766
Simmons G, Damiano TR, Truwit CL (1993) MRI and clinical findings in rhombencephalosynapsis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17:211–214
Truwit CL, Barkovich AJ, Shanahan R, et al (1991) MR imaging of rhombencephalosynapsis: report of three cases and review of the literature. AJNR 12:957–966
Litherland J, Ludlam A, Thomas N (1993) Antenatal ultrasound diagnosis of cerebellar vermian agenesis in a case of rhombencephalosynapsis. J Clin Ultrasound 21:636–638
Sharony R, Kidron D, Aviram R, et al (1999) Prenatal diagnosis of fetal cerebellar lesions: a case report and review of the literature. Prenat Diagn 19:1077–1080
Guibaud L, Garel C, Annie B, et al (2003) Prenatal diagnosis of capillary telangiectasia of the cerebellum-ultrasound and MRI features. Prenat Diagn 23:791–796
Acknowledgements
Special thanks for Drs. V. Desportes and C. Rousselle (Centre Hospitalier Lyon-Sud, Department of Neuropediatrics) and Dr. P. Droulle (Maternité Pinard, Nancy) for their pertinent advice in the completion of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guibaud, L. Practical approach to prenatal posterior fossa abnormalities using MRI. Pediatr Radiol 34, 700–711 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1248-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1248-y