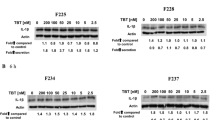
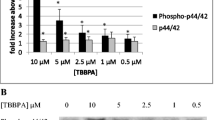
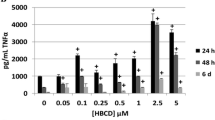
Abstract
This study investigated whether exposures to butyltins (BTs), tributylin (TBT), and dibutyltin (DBT) were able to alter cytosolic calcium levels in human natural killer (NK) cells. Additionally, the effects of cytosolic calcium ion increases on the activation state of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in NK cells were also investigated. NK cells are an intital immune defense against the development of tumors or viral infections. TBT and DBT are widespread environmental contaminants, due to their various industrial applications. Both TBT and DBT have been shown to decrease the ability of NK cells to lyse tumor cells (lytic function). TBT has also been shown to activate MAPKs in NK cells. The results of this study indicated that TBT increased cytosolic calcium levels by as much as 100% after a 60-min exposure to 500 nM TBT, whereas DBT increased cytosolic calcium levels to a much smaller extent (and required higher concentrations). The results also indicated that increases in cytosolic calcium could activate MAPKs but only for a short period of time (5 min), whereas previous studies showed that activation of MAPKs by TBT last for at least 6 h. Thus, it appears that TBT-stimulated increases in cytosolic calcium might contribute to, but are not fully responsible for, TBT-induced activation of MAPKs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluoch AO, Whalen MM (2005) Tributyltin-induced effects on MAP kinases p38 and p44/42 in human natural killer cells. Toxicology 209:263–277. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.12.034
Aluoch AO, Odman-Ghazi SO, Whalen MM (2006) Alteration of an essential NK cell signaling pathway by low doses of tributyltin in human natural killer cells. Toxicology 224:229–237. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.05.002
Aluoch AO, Odman-Ghazi SO, Whalen MM (2007) Pattern of MAP kinases p44/42 and JNK activation by non-lethal doses of tributyltin in human natural killer cells. Arch Toxicol 81:271–277. doi:10.1007/s00204-006-0155-4
Alzieu C, Sanjuan J, Michel P, Borel M, Dreno JP (1989) Monitoring and assessment of butyltins in Atlantic coastal waters. Marine Pollut Bull 20:22–26. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(89)90272-5
Bariagaber AK, Whalen MM (2003) Decreased adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase actitivities inhibit the cytotoxic function of human natural killer cells. Hum Immunol 64:866–873. doi:10.1016/S0198-8859(03)00154-X
Biron CA, Byron KS, Sullivan JL (1989) Severe herpes virus in an adolescent without natural killer cells. New Engl J Med 320:1731–1735
Chikahisa L, Oyama Y (1992) Tri-n-butyltin increases intracellular Ca2+ in mouse thymocytes: a flow-cytometric study using fluorescent dyes for membrane potential and intracellular Ca2+. Pharmacol Toxicol 71:190–195
Chow SC, Kass GE, McCabe MJ Jr, Orrenius S (1992) Tributyltin increases cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in thymocytes by mobilizing intracellular Ca2+, activating a Ca2+ entry pathway, and inhibiting Ca2+ efflux. Arch Biochem Biophys 298:143–149. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(92)90105-6
Chuang SS, Lee JK, Mathew PA (2003) Protein kinase C is involved in 2B4 (CD244)-mediated cytotoxicity and AP-1 activation in natural killer cells. Immunology 109:432–439. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01662.x
Clark EA, Sterritt RM, Lester JN (1988) The fate of tributyltin in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 22:600–604. doi:10.1021/es00171a001
Dudimah FD, Gibson C, Whalen MM (2007a) Effect of dibutyltin (DBT) on ATP levels in human natural killer cells. Environ Toxicol 22:117–123. doi:10.1002/tox.20252
Dudimah FD, Odman-Ghazi SO, Hatcher F, Whalen MM (2007b) Effect of tributyltin (TBT) on the ATP levels in human natural killer cells: relationship to TBT- induced decreases in NK function. J Appl Toxicol 27:86–94. doi:10.1002/jat.1202
Epstein RL, Phillippo ET, Harr R, Koscinski W, Vosco G (1991) Organotin residue determination in poultry and turkey sample survey in the United States. J Agric Food Chem 39:917–921. doi:10.1021/jf00005a023
Fleisher G, Koven N, Kamiya H, Henle W (1982) A non-X-linked syndrome with susceptibility to severe Epstein-Bar virus infections. J Pediatr 100:727–730. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(82)80572-6
Forsyth DS, Weber D, Barlow L (1992a) The determination of organotin compounds in fruit juices using gas chromatography-atomic absorption spectrometry. Appl Organomet Chem 6:579–585. doi:10.1002/aoc.590060704
Forsyth DS, Weber D, Cldroux C (1992b) Determination of butyltin, cyclohexyltin and phenyltin compounds in beers and wines. Food Addit Contam 9:161–169
Hall LW Jr, Pinkney AE (1985) Acute and sublethal effects of organotin compounds on aquatic biota: an interpretative literature evaluation. Crit Rev Toxicol 14:159–209. doi:10.3109/10408448509089853
Kannan K, Falandyz J (1997) Butyltin residues in sediment, fish, fish eating birds, harbour porpoise and human tissues from the Polish coast of the Baltic sea. Marine Pollut Bull 34:203–207. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(96)00146-4
Kannan K, Tanabe S, Iwata H, Tatsukawa R (1995a) Butyltins in muscle and liver of fish collected from certain Asian and Oceanian countries. Environ Pollut 90:279–290. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(95)00028-P
Kannan K, Tanabe S, Tatsukawa R (1995b) Occurrence of butyltin residues in certain foodstuffs. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 55:510–516. doi:10.1007/BF00196029
Kannan K, Tanabe S, Tatsukawa R, Williams RJ (1995c) Butyltin residue in fish from Australia, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands. Int J Environ Anal Chem 61:263–273. doi:10.1080/03067319508027242
Kannan K, Senthilkumar K, Loganathan BG et al (1997) Elevated accumulation of tributyltin and its breakdown products in bottle nose dolphins (Tursiops truncates) found stranded along the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf coasts. Environ Sci Technol 31:269–301
Kannan K, Guruge KS, Thomas NJ, Tanabe S, Giesy JP (1998) Butyltin residues in southern sea utters (Enhydra lutris nereis) found dead near California coastal waters. Environ Sci Technol 32:1169–1175. doi:10.1021/es970914u
Kannan K, Senthilkumar K, Giesy JP (1999) Occurrence of butyltin compounds in human blood. Environ Sci Technol 33:1776–1779. doi:10.1021/es990011w
Kawanishi T, Kiuchi T, Asoh H et al (2001) Effect of tributyltin chloride on the release of calcium ion from intracellular calcium stores in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 62:863–872. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(01)00740-7
Laughlin RB, Linden O (1985) Fate and effects of organotin compounds. Ambio 14:88–94
Lotzova E (1993) Definition and function of natural killer cells. Natl Immun 12:177–193
Merkord J, Jonas L, Weber H, Kroning G, Nizze H (1997) Acute interstitial pancreatitis in rats induced by dibutyltin dichloride (DBDC) pathogenesis and natural cause of lesions. Pancreas 15:392–401. doi:10.1097/00006676-199711000-00010
Moretta L, Biassoni R, Bottino C, Mingari MC, Moretta A (2002) Natural killer cells: a mystery no more. Scand J Immunol 55:229–232. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3083.2002.01055.x
Nakashima H, Hori S, Nakazawa H (1990) Determination of dibutyltin and dioctyltin compounds in PVC food containers, wrappage and clothes by reversed phase HPLC with column switching. Eisei Kagaku 36:155–220
Nakata H, Sakakibara A, Kanoh M et al (2002) Evaluation of mitogen induced responses in marine mammal and human lymphocytes by in-vitro exposure of butyltins and non-ortho coplanar PCBs. Environ Pollut 120:245–253. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00155-0
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T et al (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22:153–183. doi:10.1210/er.22.2.153
Pieters RH, Bol M, Seinen W, Penninks AH (1994) Cellular and molecular aspects of organotin-induced thymus atrophy. Hum Exp Toxicol 12:876–879. doi:10.1177/096032719401301210
Podack ER (1992) Perforin: structure, function, and regulation. Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol 178:175–184
Procopio ADG, Paolini R, Gismondi A et al (1989) Effects of protein kinase C (PK-C) activators and inhibitors on human large granular lymphocytes (LGL): role of PK-C on natural killer (NK) activity. Cell Immunol 118:470–481. doi:10.1016/0008-8749(89)90394-8
Roper WL (1992) Toxicological profile for tin. US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Washington, DC
Sadiki A-I, Williams DT, Carrier R, Thomas B (1996) Pilot study on the contamination of drinking water by organotin compounds from PVC materials. Chemosphere 32:2389–2398. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(96)00134-8
Senthil Kumar K, Kannan K, Tanabe S, Prudente M (1998) Butyltin compounds in resident and migrant birds collected from the Philippines. Fresenius Environ Bull 7:561–571
Senthil Kumar K, Duda CA, Villeneuve DL et al (1999a) Butyltin compounds in sediment and fish from the Polish coast of the Baltic Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 6:200–206. doi:10.1007/BF02987327
Senthil Kumar K, Tanabe S, Kannan K, Subramanian AN (1999b) Butyltin residues in migratory and resident birds collected from South India. Toxicol Environ Chem 68:91–104. doi:10.1080/02772249909358648
Stallard M, Hodge V, Goldberg ED (1987) TBT in California coastal waters: monitoring and assessment. Environ Monit Assess 9:195–220. doi:10.1007/BF00394351
Steele TA, Brahmi Z (1988) Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by the protein kinase C inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine is an early but post binding event. J Immunoly 141:3164–3169
Steinberg SF (2008) Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev 88:1341–1378. doi:10.1152/physrev.00034.2007
Stridh H, Gigliotti D, Orrenius S, Cotgreave I (1999) The role of calcium in pre- and postmitochondrial events in tributytin-induced T-cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266:460–465. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1821
Takahashi S, Mukai H, Tanabe S et al (1999) Butyltin residues in the liver of humans and wild terrestrial mammals and in the plastic products. Environ Pollut 106:213–218. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00068-8
Talanian RV, Yang X, Turbov J et al (1997) Granule-mediated killing:pathways for granzyme B-initiated apoptosis. J Exp Med 186:1323–1331. doi:10.1084/jem.186.8.1323
Tanabe S, Prudente M, Mizuno T et al (1998) Butyltin contamination in marine mammals from north Pacific and Asian coastal waters. Environ Sci Technol 32:193–198. doi:10.1021/es970543h
Trotta R, Puorro KA, Paroli M et al (1998) Dependence of both spontaneous and antibody-dependent, granule exocytosis-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity on extracellular signal-related kinases. J Immunol 161:6648–6656
Trotta R, Fettucciari K, Azzoni L et al (2000) Differential role of p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 mitogen-activated protein kinases in NK cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol 165:1782–1789
Vivier E, Nunes JA, Vely F (2004) Natural killer cell signaling pathways. Science 306:1517–1519. doi:10.1126/science.1103478
Wester PW, Krajnc EI, van Leeuwen FX et al (1990) Chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity of bis(tri-n-butyltin)oxide (TBTO) in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol 28:179–196. doi:10.1016/0278-6915(90)90006-9
Whalen MM, Loganathan BG, Kannan K (1999) Immunotoxicity of environmentally relevant concentrations of butyltins on human natural killer cells in vitro. Environ Res 81:108–116. doi:10.1006/enrs.1999.3968
Whalen MM, Ghazi S, Longanathan BG, Hatcher F (2002) Expression of CD16, CD18 and CD56 in tributyltin-exposed human natural killer cells. Chem-Biol Interact 139:159–176. doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(01)00297-6
Yamada S, Fuji Y, Mikami E, Kawamura N, Hayakawa J (1993) Small-scale survey of organotin compounds in household commodities. J AOAC Int 76:436–441
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by grant No. S06GM008092-33 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lane, R., Ghazi, S.O. & Whalen, M.M. Increases in Cytosolic Calcium Ion Levels in Human Natural Killer Cells in Response to Butyltin Exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57, 816–825 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9313-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9313-z