Abstract
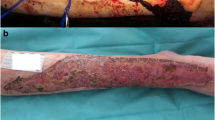
Tocilizumab is a biological immunosuppressive drug used in the treatment of psoriasis arthritis. It works by blocking the interleukin 6 receptor and therefor blocking the immune response caused by IL-6 which plays an important role in arthritis. Tocilizumab is commonly used in RA patients who either have experienced insufficient effect of other treatment options or who have had unacceptable side effects from previous treatment. With this case report, we would like to raise awareness of a potentially previously unheard of adverse effect of tocilizumab treatment on split thickness skin graft (STSG). We present a case of a 61-year-old man, treated with tocilizumab for severe poly-articular, erosive psoriasis arthritis. He was diagnosed with BCC on the scalp and underwent excision followed by STSG with no complications. The patient experienced graft loss after commencing tocilizumab treatment days to weeks post grafting on numerous occasions. We find this possible adverse effect of tocilizumab on skin grafts to be of great importance to report as it is not previously mentioned in any literature. We hope that this case report will increase the awareness of this possible adverse effect on STSG in patients treated with tocilizumab (TCZ). As the patient is dependent on arthritis symptoms to be well controlled, it is of great importance to both medical and surgical teams responsible for treatment to be able to collaborate to plan best treatment, timing, and strategy.Level of Evidence: Level V, risk / prognostic study
Level of Evidence: Level V, risk / prognostic study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, Lowenstein MB, Calvo A, Gomez-Reino JJ, Siri DA, Tomsic M, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Genovese MC (2010) Comparison of tocilizumab monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION study. Ann Rheum Dis 69(1):88–96
Mogens Pfeiffer Jensen, K.S.-P. Interleukin-6-hæmmere (biologiske antireumatika). 2017 07.03.2017; Available from: https://pro.medicin.dk/Laegemiddelgrupper/grupper/317923
Jones G, Ding C (2010) Tocilizumab: a review of its safety and efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord 3:81–89
Nishimoto N, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Azuma J, Kishimoto T (2009) Study of active controlled tocilizumab monotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate (SATORI): significant reduction in disease activity and serum vascular endothelial growth factor by IL-6 receptor inhibition therapy. Mod Rheumatol 19(1):12–19
Nishimoto N, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Azuma J (2009) Long-term safety and efficacy of tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, in monotherapy, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (the STREAM study): evidence of safety and efficacy in a 5-year extension study. Ann Rheum Dis 68(10):1580–1584
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, Woodworth T, Alten R (2008) Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 371(9617):987–997
Guo S, Dipietro LA (2010) Factors affecting wound healing. J Dent Res 89(3):219–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This case report was written in accordance with the guidelines and rules for publication and was following the COPE guidelines stated in the “Instructions for Authors” section. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethical Board of the department.
Conflict of interest
Matilda Svenning and Christian Bonde declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Patient consent
Informed consent for inclusion was obtained from the patient included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from the individual participant for whom identifying information, including photographs, is included in this article.
Funding
There was no funding received by any of the named authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svenning, M.I., Bonde, C. Adverse effect of tocilizumab treatment on split thickness skin graft—a case report. Eur J Plast Surg 42, 101–104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-018-1451-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-018-1451-y