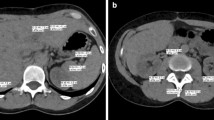
Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of advanced monoenergetic post-processing (MEI+) on the visualisation of spinal growth in contrast-enhanced dual-energy CT (DE-CT).
Methods
Twenty-six oncologic patients (age, 61 ± 17 years) with spinal tumorous growth were included. Patients underwent contrast-enhanced dual-energy CT on a third-generation dual-source CT scanner. Image acquisition was in dual-energy mode (100/Sn150kV), and scans were initiated 90 s after contrast agent administration. Virtual monoenergertic images (MEI+) were reconstructed at four different kiloelectron volts (keV) levels (40, 60, 80, 100) and compared to the standard blended portal venous computed tomography (CTpv). Image quality was assessed qualitatively (conspicuity, delineation, sharpness, noise, confidence; two independent readers; 5-point Likert scale; 5 = excellent) and quantitatively by calculating signal-to-noise (SNR) and contrast-to-noise-ratios (CNR). For a subgroup of 10 patients with MR imaging within 4 months of the DE-CT, we compared the monoenergetic images to the MRIs qualitatively.
Results
Highest contrast of spinal growth was observed in MEI+ at 40 keV, with significant differences to CTpv and all other keV reconstructions (60, 80, 100; p < 0.01). Highest conspicuity, delineation and sharpness were observed in MEI+ at 40 keV, with significant differences to CTpv (p < 0.001). Similarly, MEI+ at 40 keV yielded highest diagnostic confidence (4.6 ± 0.6), also with significant differences to CTpv (3.45 ± 0.9, p < 0.001) and to high keV reconstructions (80, 100; p ≤ 0.001). Similarly, CNR calculations revealed highest scores for MEI+ at 40 keV followed by 60 keV and CTpv, with significant differences to high keV MEI+ reconstructions. Qualitative analysis scores peaked for MR images followed by the MEI+ 40-keV reconstructions.
Conclusion
MEI+ at low keV levels can significantly improve image quality and delineation of spinal growth in patients with portal-venous phase CT scans due to increased CNR and limited image noise.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MEI+:
-
Advanced monoenergetic post-processing
- CTpv :
-
Blended portal venous computed tomography
- CNR:
-
Contrast-to-noise-ratios
- DE-CT:
-
Dual-energy CT
- HU:
-
Hounsflied Unit
- ROI:
-
Regions of interest [17]
- rm-ANOVA:
-
Repeated-measures-ANOVA
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- MEI, #5:
-
Virtual monoenergetic imaging
References
Abul-Kasim K, Thurnher MM, McKeever P, Sundgren PC (2008) Intradural spinal tumors: current classification and MRI features. Neuroradiology 50(4):301–314. doi:10.1007/s00234-007-0345-7
Albrecht MH, Scholtz JE, Husers K, Beeres M, Bucher AM, Kaup M, Martin SS, Fischer S, Bodelle B, Bauer RW, Lehnert T, Vogl TJ, Wichmann JL (2015) Advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic dual-energy CT angiography of the abdomen: optimization of kiloelectron volt settings to improve image contrast. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-015-3970-2
Albrecht MH, Scholtz JE, Kraft J, Bauer RW, Kaup M, Dewes P, Bucher AM, Burck I, Wagenblast J, Lehnert T, Kerl JM, Vogl TJ, Wichmann JL (2015) Assessment of an advanced monoenergetic reconstruction technique in dual-energy computed tomography of head and neck cancer. Eur Radiol 25(8):2493–2501. doi:10.1007/s00330-015-3627-1
Beeres M, Trommer J, Frellesen C, Nour-Eldin NE, Scholtz JE, Herrmann E, Vogl TJ, Wichmann JL (2016) Evaluation of different keV-settings in dual-energy CT angiography of the aorta using advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32(1):137–144. doi:10.1007/s10554-015-0728-5
Bloomer CW, Ackerman A, Bhatia RG (2006) Imaging for spine tumors and new applications. Top Magn Reson Imaging 17(2):69–87. doi:10.1097/RMR.0b013e31802bb38f
Bongers MN, Schabel C, Krauss B, Tsiflikas I, Ketelsen D, Mangold S, Claussen CD, Nikolaou K, Thomas C (2015) Noise-optimized virtual monoenergetic images and iodine maps for the detection of venous thrombosis in second-generation dual-energy CT (DECT): an ex vivo phantom study. Eur Radiol 25(6):1655–1664. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3544-8
Bourgouin PM, Lesage J, Fontaine S, Konan A, Roy D, Bard C, Del Carpio O’Donovan R (1998) A pattern approach to the differential diagnosis of intramedullary spinal cord lesions on MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170(6):1645–1649. doi:10.2214/ajr.170.6.9609189
Ciccu-Moore R, Grant F, Niven BA, Paterson H, Stoddart K, Wallace A (2014) Care and comfort rounds: improving standards. Nurs Manag (Harrow) 20(9):18–23. doi:10.7748/nm2014.02.20.9.18.e1140
De Cecco CN, Caruso D, Schoepf UJ, Wichmann JL, Ter Louw JR, Perry JD, Picard MM, Schaefer AR, Parker LW, Hardie AD (2016) Optimization of window settings for virtual monoenergetic imaging in dual-energy CT of the liver: a multi-reader evaluation of standard monoenergetic and advanced imaged-based monoenergetic datasets. Eur J Radiol 85(4):695–699. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.01.007
Delesalle MA, Pontana F, Duhamel A, Faivre JB, Flohr T, Tacelli N, Remy J, Remy-Jardin M (2013) Spectral optimization of chest CT angiography with reduced iodine load: experience in 80 patients evaluated with dual-source, dual-energy CT. Radiology 267(1):256–266. doi:10.1148/radiol.12120195
Frellesen C, Fessler F, Hardie AD, Wichmann JL, De Cecco CN, Schoepf UJ, Kerl JM, Schulz B, Hammerstingl R, Vogl TJ, Bauer RW (2015) Dual-energy CT of the pancreas: improved carcinoma-to-pancreas contrast with a noise-optimized monoenergetic reconstruction algorithm. Eur J Radiol 84(11):2052–2058. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.07.020
Frellesen C, Kaup M, Wichmann JL, Husers K, Scholtz JE, Albrecht MH, Metzger SC, Bauer RW, Kerl JM, Lehnert T, Vogl TJ, Bodelle B (2016) Noise-optimized advanced image-based virtual monoenergetic imaging for improved visualization of lung cancer: comparison with traditional virtual monoenergetic imaging. Eur J Radiol 85(3):665–672. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.12.022
Grant KL, Flohr TG, Krauss B, Sedlmair M, Thomas C, Schmidt B (2014) Assessment of an advanced image-based technique to calculate virtual monoenergetic computed tomographic images from a dual-energy examination to improve contrast-to-noise ratio in examinations using iodinated contrast media. Invest Radiol 49(9):586–592. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000060
Graser A, Becker CR, Staehler M, Clevert DA, Macari M, Arndt N, Nikolaou K, Sommer W, Stief C, Reiser MF, Johnson TR (2010) Single-phase dual-energy CT allows for characterization of renal masses as benign or malignant. Invest Radiol 45(7):399–405. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181e33189
Henzler T, Fink C, Schoenberg SO, Schoepf UJ (2012) Dual-energy CT: radiation dose aspects. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(5 Suppl):S16–S25. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9210
Husarik DB, Gordic S, Desbiolles L, Krauss B, Leschka S, Wildermuth S, Alkadhi H (2015) Advanced virtual monoenergetic computed tomography of hyperattenuating and hypoattenuating liver lesions: ex-vivo and patient experience in various body sizes. Invest Radiol 50(10):695–702. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000171
Itamura J, Roidis N, Mirzayan R, Vaishnav S, Learch T, Shean C (2005) Radial head fractures: MRI evaluation of associated injuries. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14(4):421–424. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.11.003
Lell MM, Meyer E, Kuefner MA, May MS, Raupach R, Uder M, Kachelriess M (2012) Normalized metal artifact reduction in head and neck computed tomography. Invest Radiol 47(7):415–421. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182532f17
Leng S, Yu L, Fletcher JG, McCollough CH (2015) Maximizing iodine contrast-to-noise ratios in abdominal CT imaging through use of energy domain noise reduction and virtual monoenergetic dual-energy CT. Radiology 276(2):562–570. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015140857
Mangold S, De Cecco CN, Schoepf UJ, Yamada RT, Varga-Szemes A, Stubenrauch AC, Caruso D, Fuller SR, Vogl TJ, Nikolaou K, Todoran TM, Wichmann JL (2016) A noise-optimized virtual monochromatic reconstruction algorithm improves stent visualization and diagnostic accuracy for detection of in-stent re-stenosis in lower extremity run-off CT angiography. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-016-4304-8
Schneider D, Apfaltrer P, Sudarski S, Nance JW Jr, Haubenreisser H, Fink C, Schoenberg SO, Henzler T (2014) Optimization of kiloelectron volt settings in cerebral and cervical dual-energy CT angiography determined with virtual monoenergetic imaging. Acad Radiol 21(4):431–436. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2013.12.006
Schueller-Weidekamm C, Schaefer-Prokop CM, Weber M, Herold CJ, Prokop M (2006) CT angiography of pulmonary arteries to detect pulmonary embolism: improvement of vascular enhancement with low kilovoltage settings. Radiology 241(3):899–907. doi:10.1148/radiol.2413040128
Shinohara Y, Sakamoto M, Iwata N, Kishimoto J, Kuya K, Fujii S, Kaminou T, Watanabe T, Ogawa T (2014) Usefulness of monochromatic imaging with metal artifact reduction software for computed tomography angiography after intracranial aneurysm coil embolization. Acta Radiol 55(8):1015–1023. doi:10.1177/0284185113510492
Soderlund KA, Smith AB, Rushing EJ, Smirniotopolous JG (2012) Radiologic-pathologic correlation of pediatric and adolescent spinal neoplasms: part 2, Intradural extramedullary spinal neoplasms. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198(1):44–51. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7121
Steinmetz MP, Mekhail A, Benzel EC (2001) Management of metastatic tumors of the spine: strategies and operative indications. Neurosurg Focus 11(6), e2
Sudarski S, Apfaltrer P, Nance JW Jr, Schneider D, Meyer M, Schoenberg SO, Fink C, Henzler T (2013) Optimization of keV-settings in abdominal and lower extremity dual-source dual-energy CT angiography determined with virtual monoenergetic imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(10):e574–e581. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.04.040
Tanaka R, Hayashi T, Ike M, Noto Y, Goto TK (2013) Reduction of dark-band-like metal artifacts caused by dental implant bodies using hypothetical monoenergetic imaging after dual-energy computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 115(6):833–838. doi:10.1016/j.oooo.2013.03.014
Tawfik AM, Kerl JM, Bauer RW, Nour-Eldin NE, Naguib NN, Vogl TJ, Mack MG (2012) Dual-energy CT of head and neck cancer: average weighting of low- and high-voltage acquisitions to improve lesion delineation and image quality-initial clinical experience. Invest Radiol 47(5):306–311. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e31821e3062
Toepker M, Czerny C, Ringl H, Fruehwald-Pallamar J, Wolf F, Weber M, Ploder O, Klug C (2014) Can dual-energy CT improve the assessment of tumor margins in oral cancer? Oral Oncol 50(3):221–227. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.12.001
Vlahos I, Chung R, Nair A, Morgan R (2012) Dual-energy CT: vascular applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(5 Suppl):S87–S97. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9114
Wichmann JL, Noske EM, Kraft J, Burck I, Wagenblast J, Eckardt A, Frellesen C, Kerl JM, Bauer RW, Bodelle B, Lehnert T, Vogl TJ, Schulz B (2014) Virtual monoenergetic dual-energy computed tomography: optimization of kiloelectron volt settings in head and neck cancer. Invest Radiol 49(11):735–741. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000077
Yu L, Christner JA, Leng S, Wang J, Fletcher JG, McCollough CH (2011) Virtual monochromatic imaging in dual-source dual-energy CT: radiation dose and image quality. Med Phys 38(12):6371–6379. doi:10.1118/1.3658568
Yu L, Leng S, McCollough CH (2012) Dual-energy CT-based monochromatic imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(5 Suppl):S9–S15. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9121
Yuan R, Shuman WP, Earls JP, Hague CJ, Mumtaz HA, Scott-Moncrieff A, Ellis JD, Mayo JR, Leipsic JA (2012) Reduced iodine load at CT pulmonary angiography with dual-energy monochromatic imaging: comparison with standard CT pulmonary angiography--a prospective randomized trial. Radiology 262(1):290–297. doi:10.1148/radiol.11110648
Zong S, Wu Y, Tao Y, Chen X, Fang Y, Du L, Zhao J, Zeng G (2015) Treatment results in different surgical approaches for intraspinal tumor in 51 patients. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(9):16627–16633
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that all human studies have been approved by the local ethics committee at the University Hospital Tübingen and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Due to the retrospective nature of this study, the ethics committee waived informed patient consent.
Conflict of interest
TF is an Employee of Siemens Healthcare GmbH.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kraus, M., Weiss, J., Selo, N. et al. Spinal dual-energy computed tomography: improved visualisation of spinal tumorous growth with a noise-optimised advanced monoenergetic post-processing algorithm. Neuroradiology 58, 1093–1102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1733-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1733-7